Zhenshan Tan
Breaking the Resolution Barrier: Arbitrary-resolution Deep Image Steganography Framework
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Deep image steganography (DIS) has achieved significant results in capacity and invisibility. However, current paradigms enforce the secret image to maintain the same resolution as the cover image during hiding and revealing. This leads to two challenges: secret images with inconsistent resolutions must undergo resampling beforehand which results in detail loss during recovery, and the secret image cannot be recovered to its original resolution when the resolution value is unknown. To address these, we propose ARDIS, the first Arbitrary Resolution DIS framework, which shifts the paradigm from discrete mapping to reference-guided continuous signal reconstruction. Specifically, to minimize the detail loss caused by resolution mismatch, we first design a Frequency Decoupling Architecture in hiding stage. It disentangles the secret into a resolution-aligned global basis and a resolution-agnostic high-frequency latent to hide in a fixed-resolution cover. Second, for recovery, we propose a Latent-Guided Implicit Reconstructor to perform deterministic restoration. The recovered detail latent code modulates a continuous implicit function to accurately query and render high-frequency residuals onto the recovered global basis, ensuring faithful restoration of original details. Furthermore, to achieve blind recovery, we introduce an Implicit Resolution Coding strategy. By transforming discrete resolution values into dense feature maps and hiding them in the redundant space of the feature domain, the reconstructor can correctly decode the secret's resolution directly from the steganographic representation. Experimental results demonstrate that ARDIS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both invisibility and cross-resolution recovery fidelity.
A Unified Two-Stage Group Semantics Propagation and Contrastive Learning Network for Co-Saliency Detection
Aug 13, 2022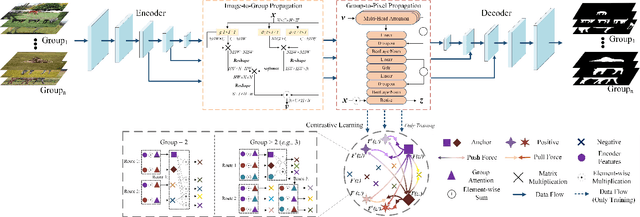
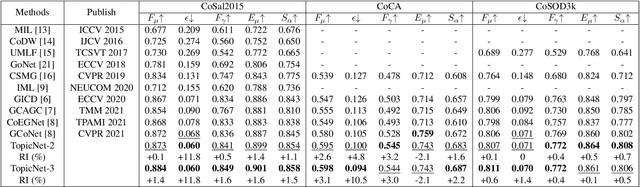


Abstract:Co-saliency detection (CoSOD) aims at discovering the repetitive salient objects from multiple images. Two primary challenges are group semantics extraction and noise object suppression. In this paper, we present a unified Two-stage grOup semantics PropagatIon and Contrastive learning NETwork (TopicNet) for CoSOD. TopicNet can be decomposed into two substructures, including a two-stage group semantics propagation module (TGSP) to address the first challenge and a contrastive learning module (CLM) to address the second challenge. Concretely, for TGSP, we design an image-to-group propagation module (IGP) to capture the consensus representation of intra-group similar features and a group-to-pixel propagation module (GPP) to build the relevancy of consensus representation. For CLM, with the design of positive samples, the semantic consistency is enhanced. With the design of negative samples, the noise objects are suppressed. Experimental results on three prevailing benchmarks reveal that TopicNet outperforms other competitors in terms of various evaluation metrics.
Contrastive Cross-Modal Knowledge Sharing Pre-training for Vision-Language Representation Learning and Retrieval
Jul 08, 2022



Abstract:Recently, the cross-modal pre-training task has been a hotspot because of its wide application in various down-streaming researches including retrieval, captioning, question answering and so on. However, exiting methods adopt a one-stream pre-training model to explore the united vision-language representation for conducting cross-modal retrieval, which easily suffer from the calculation explosion. Moreover, although the conventional double-stream structures are quite efficient, they still lack the vital cross-modal interactions, resulting in low performances. Motivated by these challenges, we put forward a Contrastive Cross-Modal Knowledge Sharing Pre-training (COOKIE) to grasp the joint text-image representations. Structurally, COOKIE adopts the traditional double-stream structure because of the acceptable time consumption. To overcome the inherent defects of double-stream structure as mentioned above, we elaborately design two effective modules. Concretely, the first module is a weight-sharing transformer that builds on the head of the visual and textual encoders, aiming to semantically align text and image. This design enables visual and textual paths focus on the same semantics. The other one is three specially designed contrastive learning, aiming to share knowledge between different models. The shared cross-modal knowledge develops the study of unimodal representation greatly, promoting the single-modal retrieval tasks. Extensive experimental results on multi-modal matching researches that includes cross-modal retrieval, text matching, and image retrieval reveal the superiors in calculation efficiency and statistical indicators of our pre-training model.
UTC: A Unified Transformer with Inter-Task Contrastive Learning for Visual Dialog
May 03, 2022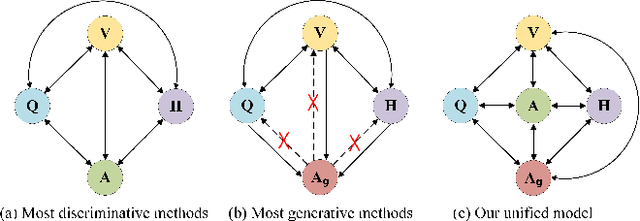
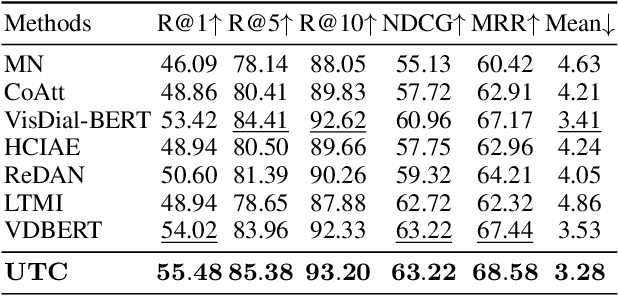
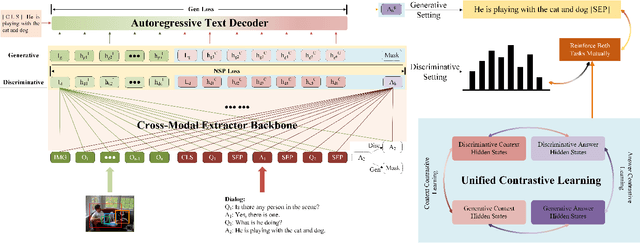
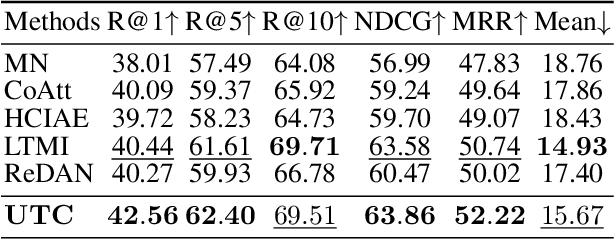
Abstract:Visual Dialog aims to answer multi-round, interactive questions based on the dialog history and image content. Existing methods either consider answer ranking and generating individually or only weakly capture the relation across the two tasks implicitly by two separate models. The research on a universal framework that jointly learns to rank and generate answers in a single model is seldom explored. In this paper, we propose a contrastive learning-based framework UTC to unify and facilitate both discriminative and generative tasks in visual dialog with a single model. Specifically, considering the inherent limitation of the previous learning paradigm, we devise two inter-task contrastive losses i.e., context contrastive loss and answer contrastive loss to make the discriminative and generative tasks mutually reinforce each other. These two complementary contrastive losses exploit dialog context and target answer as anchor points to provide representation learning signals from different perspectives. We evaluate our proposed UTC on the VisDial v1.0 dataset, where our method outperforms the state-of-the-art on both discriminative and generative tasks and surpasses previous state-of-the-art generative methods by more than 2 absolute points on Recall@1.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge