Zhen-Hua Feng
A Flatter Loss for Bias Mitigation in Cross-dataset Facial Age Estimation
Oct 26, 2020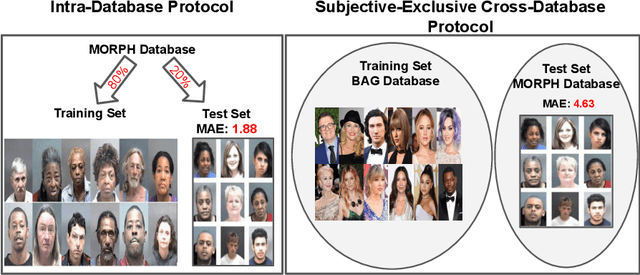
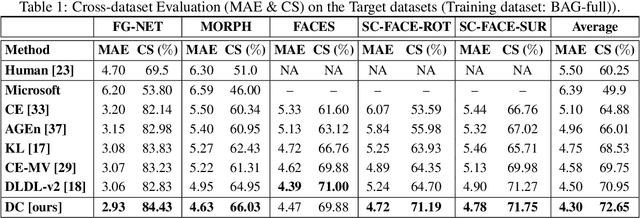
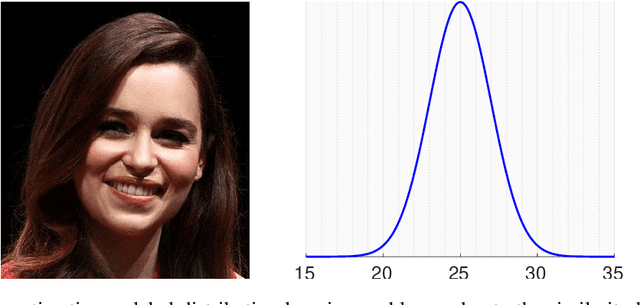
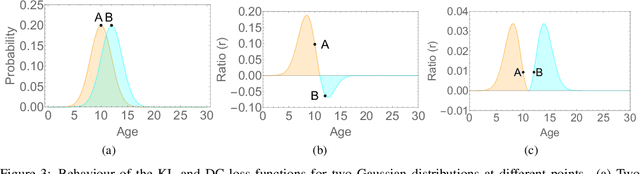
Abstract:The most existing studies in the facial age estimation assume training and test images are captured under similar shooting conditions. However, this is rarely valid in real-world applications, where training and test sets usually have different characteristics. In this paper, we advocate a cross-dataset protocol for age estimation benchmarking. In order to improve the cross-dataset age estimation performance, we mitigate the inherent bias caused by the learning algorithm itself. To this end, we propose a novel loss function that is more effective for neural network training. The relative smoothness of the proposed loss function is its advantage with regards to the optimisation process performed by stochastic gradient descent (SGD). Compared with existing loss functions, the lower gradient of the proposed loss function leads to the convergence of SGD to a better optimum point, and consequently a better generalisation. The cross-dataset experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of accuracy and generalisation capability.
DD-CNN: Depthwise Disout Convolutional Neural Network for Low-complexity Acoustic Scene Classification
Jul 25, 2020



Abstract:This paper presents a Depthwise Disout Convolutional Neural Network (DD-CNN) for the detection and classification of urban acoustic scenes. Specifically, we use log-mel as feature representations of acoustic signals for the inputs of our network. In the proposed DD-CNN, depthwise separable convolution is used to reduce the network complexity. Besides, SpecAugment and Disout are used for further performance boosting. Experimental results demonstrate that our DD-CNN can learn discriminative acoustic characteristics from audio fragments and effectively reduce the network complexity. Our DD-CNN was used for the low-complexity acoustic scene classification task of the DCASE2020 Challenge, which achieves 92.04% accuracy on the validation set.
Affine Non-negative Collaborative Representation Based Pattern Classification
Jul 10, 2020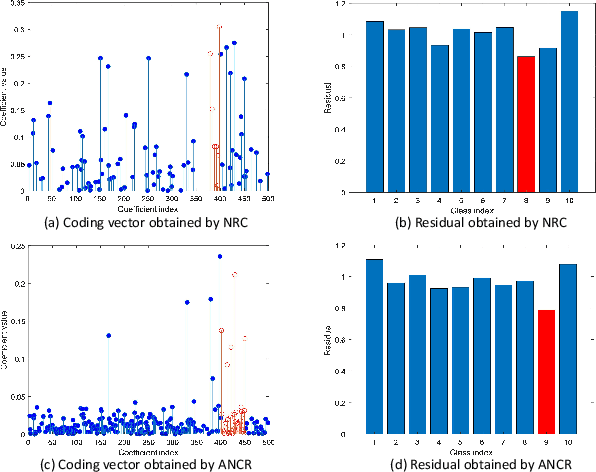



Abstract:During the past decade, representation-based classification methods have received considerable attention in pattern recognition. In particular, the recently proposed non-negative representation based classification (NRC) method has been reported to achieve promising results in a wide range of classification tasks. However, NRC has two major drawbacks. First, there is no regularization term in the formulation of NRC, which may result in unstable solution and misclassification. Second, NRC ignores the fact that data usually lies in a union of multiple affine subspaces, rather than linear subspaces in practical applications. To address the above issues, this paper presents an affine non-negative collaborative representation (ANCR) model for pattern classification. To be more specific, ANCR imposes a regularization term on the coding vector. Moreover, ANCR introduces an affine constraint to better represent the data from affine subspaces. The experimental results on several benchmarking datasets demonstrate the merits of the proposed ANCR method. The source code of our ANCR is publicly available at https://github.com/yinhefeng/ANCR.
AFAT: Adaptive Failure-Aware Tracker for Robust Visual Object Tracking
May 27, 2020



Abstract:Siamese approaches have achieved promising performance in visual object tracking recently. The key to the success of Siamese trackers is to learn appearance-invariant feature embedding functions via pair-wise offline training on large-scale video datasets. However, the Siamese paradigm uses one-shot learning to model the online tracking task, which impedes online adaptation in the tracking process. Additionally, the uncertainty of an online tracking response is not measured, leading to the problem of ignoring potential failures. In this paper, we advocate online adaptation in the tracking stage. To this end, we propose a failure-aware system, realised by a Quality Prediction Network (QPN), based on convolutional and LSTM modules in the decision stage, enabling online reporting of potential tracking failures. Specifically, sequential response maps from previous successive frames as well as current frame are collected to predict the tracking confidence, realising spatio-temporal fusion in the decision level. In addition, we further provide an Adaptive Failure-Aware Tracker (AFAT) by combing the state-of-the-art Siamese trackers with our system. The experimental results obtained on standard benchmarking datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed failure-aware system and the merits of our AFAT tracker, with outstanding and balanced performance in both accuracy and speed.
An Accelerated Correlation Filter Tracker
Dec 05, 2019



Abstract:Recent visual object tracking methods have witnessed a continuous improvement in the state-of-the-art with the development of efficient discriminative correlation filters (DCF) and robust deep neural network features. Despite the outstanding performance achieved by the above combination, existing advanced trackers suffer from the burden of high computational complexity of the deep feature extraction and online model learning. We propose an accelerated ADMM optimisation method obtained by adding a momentum to the optimisation sequence iterates, and by relaxing the impact of the error between DCF parameters and their norm. The proposed optimisation method is applied to an innovative formulation of the DCF design, which seeks the most discriminative spatially regularised feature channels. A further speed up is achieved by an adaptive initialisation of the filter optimisation process. The significantly increased convergence of the DCF filter is demonstrated by establishing the optimisation process equivalence with a continuous dynamical system for which the convergence properties can readily be derived. The experimental results obtained on several well-known benchmarking datasets demonstrate the efficiency and robustness of the proposed ACFT method, with a tracking accuracy comparable to the start-of-the-art trackers.
Learning a Representation with the Block-Diagonal Structure for Pattern Classification
Nov 23, 2019



Abstract:Sparse-representation-based classification (SRC) has been widely studied and developed for various practical signal classification applications. However, the performance of a SRC-based method is degraded when both the training and test data are corrupted. To counteract this problem, we propose an approach that learns Representation with Block-Diagonal Structure (RBDS) for robust image recognition. To be more specific, we first introduce a regularization term that captures the block-diagonal structure of the target representation matrix of the training data. The resulting problem is then solved by an optimizer. Last, based on the learned representation, a simple yet effective linear classifier is used for the classification task. The experimental results obtained on several benchmarking datasets demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed RBDS method.
Dual Encoder-Decoder based Generative Adversarial Networks for Disentangled Facial Representation Learning
Sep 19, 2019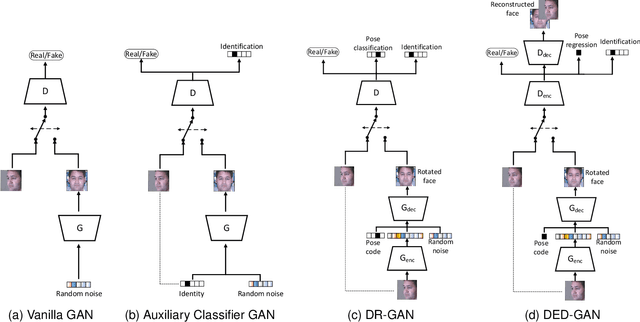

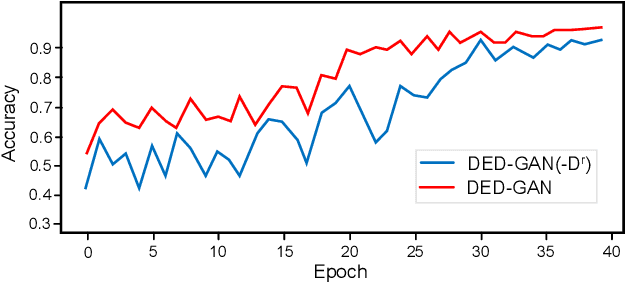
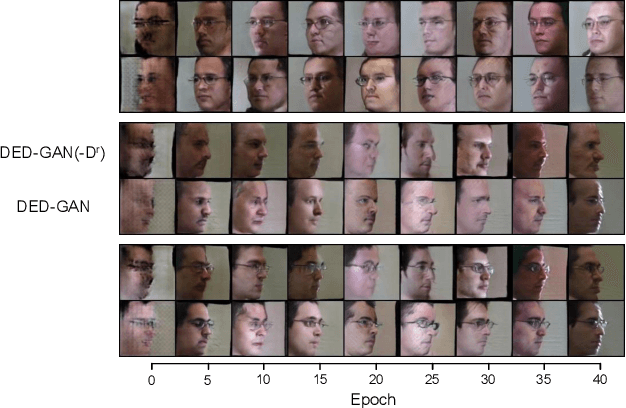
Abstract:To learn disentangled representations of facial images, we present a Dual Encoder-Decoder based Generative Adversarial Network (DED-GAN). In the proposed method, both the generator and discriminator are designed with deep encoder-decoder architectures as their backbones. To be more specific, the encoder-decoder structured generator is used to learn a pose disentangled face representation, and the encoder-decoder structured discriminator is tasked to perform real/fake classification, face reconstruction, determining identity and estimating face pose. We further improve the proposed network architecture by minimising the additional pixel-wise loss defined by the Wasserstein distance at the output of the discriminator so that the adversarial framework can be better trained. Additionally, we consider face pose variation to be continuous, rather than discrete in existing literature, to inject richer pose information into our model. The pose estimation task is formulated as a regression problem, which helps to disentangle identity information from pose variations. The proposed network is evaluated on the tasks of pose-invariant face recognition (PIFR) and face synthesis across poses. An extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluation carried out on several controlled and in-the-wild benchmarking datasets demonstrates the superiority of the proposed DED-GAN method over the state-of-the-art approaches.
Joint Group Feature Selection and Discriminative Filter Learning for Robust Visual Object Tracking
Aug 02, 2019



Abstract:We propose a new Group Feature Selection method for Discriminative Correlation Filters (GFS-DCF) based visual object tracking. The key innovation of the proposed method is to perform group feature selection across both channel and spatial dimensions, thus to pinpoint the structural relevance of multi-channel features to the filtering system. In contrast to the widely used spatial regularisation or feature selection methods, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that channel selection has been advocated for DCF-based tracking. We demonstrate that our GFS-DCF method is able to significantly improve the performance of a DCF tracker equipped with deep neural network features. In addition, our GFS-DCF enables joint feature selection and filter learning, achieving enhanced discrimination and interpretability of the learned filters. To further improve the performance, we adaptively integrate historical information by constraining filters to be smooth across temporal frames, using an efficient low-rank approximation. By design, specific temporal-spatial-channel configurations are dynamically learned in the tracking process, highlighting the relevant features, and alleviating the performance degrading impact of less discriminative representations and reducing information redundancy. The experimental results obtained on OTB2013, OTB2015, VOT2017, VOT2018 and TrackingNet demonstrate the merits of our GFS-DCF and its superiority over the state-of-the-art trackers. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/XU-TIANYANG/GFS-DCF.
Wing Loss for Robust Facial Landmark Localisation with Convolutional Neural Networks
Oct 23, 2018



Abstract:We present a new loss function, namely Wing loss, for robust facial landmark localisation with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). We first compare and analyse different loss functions including L2, L1 and smooth L1. The analysis of these loss functions suggests that, for the training of a CNN-based localisation model, more attention should be paid to small and medium range errors. To this end, we design a piece-wise loss function. The new loss amplifies the impact of errors from the interval (-w, w) by switching from L1 loss to a modified logarithm function. To address the problem of under-representation of samples with large out-of-plane head rotations in the training set, we propose a simple but effective boosting strategy, referred to as pose-based data balancing. In particular, we deal with the data imbalance problem by duplicating the minority training samples and perturbing them by injecting random image rotation, bounding box translation and other data augmentation approaches. Last, the proposed approach is extended to create a two-stage framework for robust facial landmark localisation. The experimental results obtained on AFLW and 300W demonstrate the merits of the Wing loss function, and prove the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art approaches.
Learning Adaptive Discriminative Correlation Filters via Temporal Consistency Preserving Spatial Feature Selection for Robust Visual Tracking
Jul 30, 2018



Abstract:With efficient appearance learning models, Discriminative Correlation Filter (DCF) has been proven to be very successful in recent video object tracking benchmarks and competitions. However, the existing DCF paradigm suffers from two major problems, \ie spatial boundary effect and temporal filter degeneration. To mitigate these challenges, we propose a new DCF-based tracking method. The key innovations of the proposed method include adaptive spatial feature selection and temporal consistent constraints, with which the new tracker enables joint spatio-temporal filter learning in a lower dimensional discriminative manifold. More specifically, we apply structured sparsity constraints to multi-channel filers. Consequently, the process of learning spatial filters can be approximated by the lasso regularisation. To encourage temporal consistency, the filter model is restricted to lie around its historical value and updated locally to preserve the global structure in the manifold. Last, a unified optimisation framework is proposed to jointly select temporal consistency preserving spatial features and learn discriminative filters with the augmented Lagrangian method. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations have been conducted on a number of well-known benchmarking datasets such as OTB2013, OTB50, OTB100, Temple-Colour and UAV123. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge