Zhaowei Shang
Image Quality Assessment: Exploring Regional Heterogeneity via Response of Adaptive Multiple Quality Factors in Dictionary Space
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Given that the factors influencing image quality vary significantly with scene, content, and distortion type, particularly in the context of regional heterogeneity, we propose an adaptive multi-quality factor (AMqF) framework to represent image quality in a dictionary space, enabling the precise capture of quality features in non-uniformly distorted regions. By designing an adapter, the framework can flexibly decompose quality factors (such as brightness, structure, contrast, etc.) that best align with human visual perception and quantify them into discrete visual words. These visual words respond to the constructed dictionary basis vector, and by obtaining the corresponding coordinate vectors, we can measure visual similarity. Our method offers two key contributions. First, an adaptive mechanism that extracts and decomposes quality factors according to human visual perception principles enhances their representation ability through reconstruction constraints. Second, the construction of a comprehensive and discriminative dictionary space and basis vector allows quality factors to respond effectively to the dictionary basis vector and capture non-uniform distortion patterns in images, significantly improving the accuracy of visual similarity measurement. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in handling various types of distorted images. The source code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AMqF-44B2.
Underwater Image Quality Assessment: A Perceptual Framework Guided by Physical Imaging
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we propose a physically imaging-guided framework for underwater image quality assessment (UIQA), called PIGUIQA. First, we formulate UIQA as a comprehensive problem that considers the combined effects of direct transmission attenuation and backwards scattering on image perception. On this basis, we incorporate advanced physics-based underwater imaging estimation into our method and define distortion metrics that measure the impact of direct transmission attenuation and backwards scattering on image quality. Second, acknowledging the significant content differences across various regions of an image and the varying perceptual sensitivity to distortions in these regions, we design a local perceptual module on the basis of the neighborhood attention mechanism. This module effectively captures subtle features in images, thereby enhancing the adaptive perception of distortions on the basis of local information. Finally, by employing a global perceptual module to further integrate the original image content with underwater image distortion information, the proposed model can accurately predict the image quality score. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that PIGUIQA achieves state-of-the-art performance in underwater image quality prediction and exhibits strong generalizability. The code for PIGUIQA is available on https://anonymous.4open.science/r/PIGUIQA-A465/
Learning a Deep Part-based Representation by Preserving Data Distribution
Sep 17, 2020



Abstract:Unsupervised dimensionality reduction is one of the commonly used techniques in the field of high dimensional data recognition problems. The deep autoencoder network which constrains the weights to be non-negative, can learn a low dimensional part-based representation of data. On the other hand, the inherent structure of the each data cluster can be described by the distribution of the intraclass samples. Then one hopes to learn a new low dimensional representation which can preserve the intrinsic structure embedded in the original high dimensional data space perfectly. In this paper, by preserving the data distribution, a deep part-based representation can be learned, and the novel algorithm is called Distribution Preserving Network Embedding (DPNE). In DPNE, we first need to estimate the distribution of the original high dimensional data using the $k$-nearest neighbor kernel density estimation, and then we seek a part-based representation which respects the above distribution. The experimental results on the real-world data sets show that the proposed algorithm has good performance in terms of cluster accuracy and AMI. It turns out that the manifold structure in the raw data can be well preserved in the low dimensional feature space.
A Multiscale Image Denoising Algorithm Based On Dilated Residual Convolution Network
Dec 21, 2018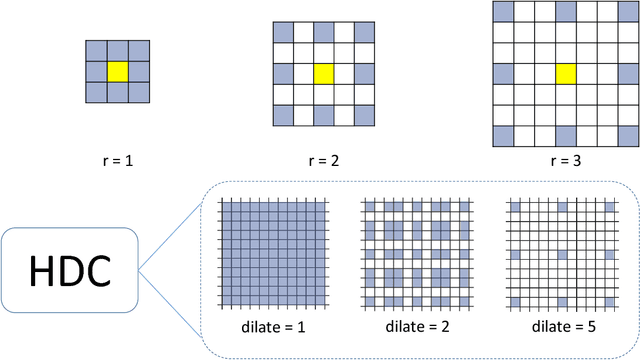
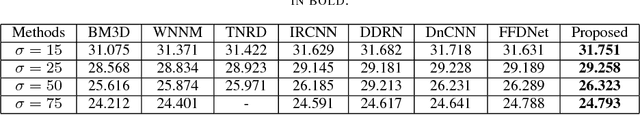
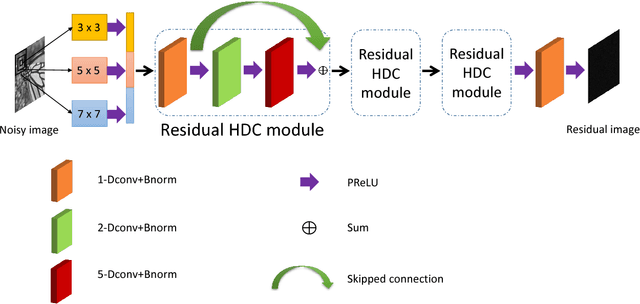
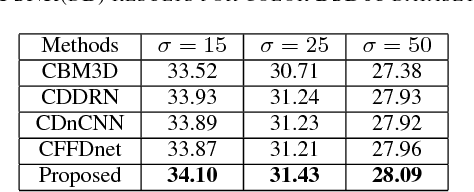
Abstract:Image denoising is a classical problem in low level computer vision. Model-based optimization methods and deep learning approaches have been the two main strategies for solving the problem. Model-based optimization methods are flexible for handling different inverse problems but are usually time-consuming. In contrast, deep learning methods have fast testing speed but the performance of these CNNs is still inferior. To address this issue, here we propose a novel deep residual learning model that combines the dilated residual convolution and multi-scale convolution groups. Due to the complex patterns and structures of inside an image, the multiscale convolution group is utilized to learn those patterns and enlarge the receptive field. Specifically, the residual connection and batch normalization are utilized to speed up the training process and maintain the denoising performance. In order to decrease the gridding artifacts, we integrate the hybrid dilated convolution design into our model. To this end, this paper aims to train a lightweight and effective denoiser based on multiscale convolution group. Experimental results have demonstrated that the enhanced denoiser can not only achieve promising denoising results, but also become a strong competitor in practical application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge