Zhankai Ye
GeoMotionGPT: Geometry-Aligned Motion Understanding with Large Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Discrete motion tokenization has recently enabled Large Language Models (LLMs) to serve as versatile backbones for motion understanding and motion-language reasoning. However, existing pipelines typically decouple motion quantization from semantic embedding learning, linking them solely via token IDs. This approach fails to effectively align the intrinsic geometry of the motion space with the embedding space, thereby hindering the LLM's capacity for nuanced motion reasoning. We argue that alignment is most effective when both modalities share a unified geometric basis. Therefore, instead of forcing the LLM to reconstruct the complex geometry among motion tokens from scratch, we present a novel framework that explicitly enforces orthogonality on both the motion codebook and the LLM embedding space, ensuring that their relational structures naturally mirror each other. Specifically, we employ a decoder-only quantizer with Gumbel-Softmax for differentiable training and balanced codebook usage. To bridge the modalities, we use a sparse projection that maps motion codes into the LLM embedding space while preserving orthogonality. Finally, a two-stage orthonormal regularization schedule enforces soft constraints during tokenizer training and LLM fine-tuning to maintain geometric alignment without hindering semantic adaptation. Extensive experiments on HumanML3D demonstrate that our framework achieves a 20% performance improvement over current state-of-the-art methods, validating that a unified geometric basis effectively empowers the LLM for nuanced motion reasoning.
HyperEdit: Unlocking Instruction-based Text Editing in LLMs via Hypernetworks
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Instruction-based text editing is increasingly critical for real-world applications such as code editors (e.g., Cursor), but Large Language Models (LLMs) continue to struggle with this task. Unlike free-form generation, editing requires faithfully implementing user instructions while preserving unchanged content, as even minor unintended modifications can break functionality. Existing approaches treat editing as generic text generation, leading to two key failures: they struggle to faithfully align edits with diverse user intents, and they often over-edit unchanged regions. We propose HyperEdit to address both issues. First, we introduce hypernetwork-based dynamic adaptation that generates request-specific parameters, enabling the model to tailor its editing strategy to each instruction. Second, we develop difference-aware regularization that focuses supervision on modified spans, preventing over-editing while ensuring precise, minimal changes. HyperEdit achieves a 9%--30% relative improvement in BLEU on modified regions over state-of-the-art baselines, despite utilizing only 3B parameters.
Image-based Vehicle Re-identification Model with Adaptive Attention Modules and Metadata Re-ranking
Jul 03, 2020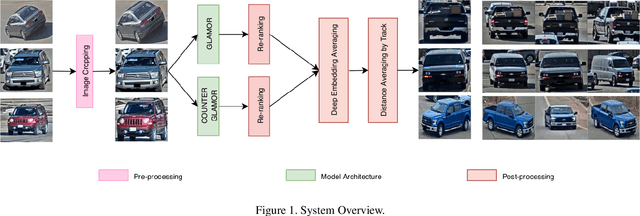
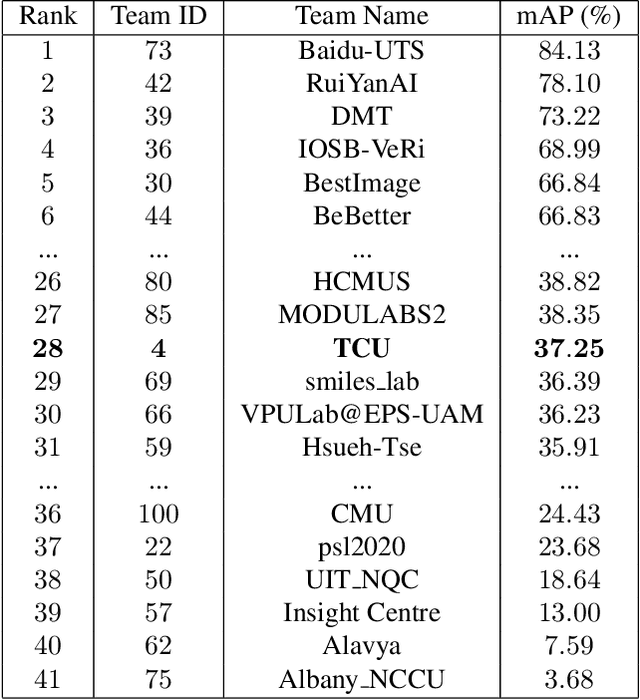

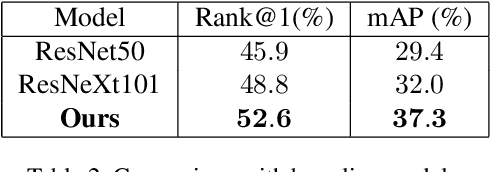
Abstract:Vehicle Re-identification is a challenging task due to intra-class variability and inter-class similarity across non-overlapping cameras. To tackle these problems, recently proposed methods require additional annotation to extract more features for false positive image exclusion. In this paper, we propose a model powered by adaptive attention modules that requires fewer label annotations but still out-performs the previous models. We also include a re-ranking method that takes account of the importance of metadata feature embeddings in our paper. The proposed method is evaluated on CVPR AI City Challenge 2020 dataset and achieves mAP of 37.25% in Track 2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge