Zehang Lin
Conflict-Aware Client Selection for Multi-Server Federated Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a promising distributed machine learning (ML) that enables collaborative model training across clients without exposing raw data, thereby preserving user privacy and reducing communication costs. Despite these benefits, traditional single-server FL suffers from high communication latency due to the aggregation of models from a large number of clients. While multi-server FL distributes workloads across edge servers, overlapping client coverage and uncoordinated selection often lead to resource contention, causing bandwidth conflicts and training failures. To address these limitations, we propose a decentralized reinforcement learning with conflict risk prediction, named RL CRP, to optimize client selection in multi-server FL systems. Specifically, each server estimates the likelihood of client selection conflicts using a categorical hidden Markov model based on its sparse historical client selection sequence. Then, a fairness-aware reward mechanism is incorporated to promote long-term client participation for minimizing training latency and resource contention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed RL-CRP framework effectively reduces inter-server conflicts and significantly improves training efficiency in terms of convergence speed and communication cost.
NSC-SL: A Bandwidth-Aware Neural Subspace Compression for Communication-Efficient Split Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:The expanding scale of neural networks poses a major challenge for distributed machine learning, particularly under limited communication resources. While split learning (SL) alleviates client computational burden by distributing model layers between clients and server, it incurs substantial communication overhead from frequent transmission of intermediate activations and gradients. To tackle this issue, we propose NSC-SL, a bandwidth-aware adaptive compression algorithm for communication-efficient SL. NSC-SL first dynamically determines the optimal rank of low-rank approximation based on the singular value distribution for adapting real-time bandwidth constraints. Then, NSC-SL performs error-compensated tensor factorization using alternating orthogonal iteration with residual feedback, effectively minimizing truncation loss. The collaborative mechanisms enable NSC-SL to achieve high compression ratios while preserving semantic-rich information essential for convergence. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superb performance of NSC-SL.
Benchmarking the CoW with the TopCoW Challenge: Topology-Aware Anatomical Segmentation of the Circle of Willis for CTA and MRA
Dec 29, 2023



Abstract:The Circle of Willis (CoW) is an important network of arteries connecting major circulations of the brain. Its vascular architecture is believed to affect the risk, severity, and clinical outcome of serious neuro-vascular diseases. However, characterizing the highly variable CoW anatomy is still a manual and time-consuming expert task. The CoW is usually imaged by two angiographic imaging modalities, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA), but there exist limited public datasets with annotations on CoW anatomy, especially for CTA. Therefore we organized the TopCoW Challenge in 2023 with the release of an annotated CoW dataset and invited submissions worldwide for the CoW segmentation task, which attracted over 140 registered participants from four continents. TopCoW dataset was the first public dataset with voxel-level annotations for CoW's 13 vessel components, made possible by virtual-reality (VR) technology. It was also the first dataset with paired MRA and CTA from the same patients. TopCoW challenge aimed to tackle the CoW characterization problem as a multiclass anatomical segmentation task with an emphasis on topological metrics. The top performing teams managed to segment many CoW components to Dice scores around 90%, but with lower scores for communicating arteries and rare variants. There were also topological mistakes for predictions with high Dice scores. Additional topological analysis revealed further areas for improvement in detecting certain CoW components and matching CoW variant's topology accurately. TopCoW represented a first attempt at benchmarking the CoW anatomical segmentation task for MRA and CTA, both morphologically and topologically.
MMED: A Multi-domain and Multi-modality Event Dataset
Apr 09, 2019
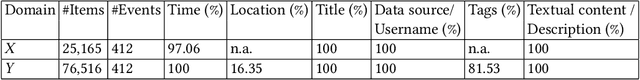
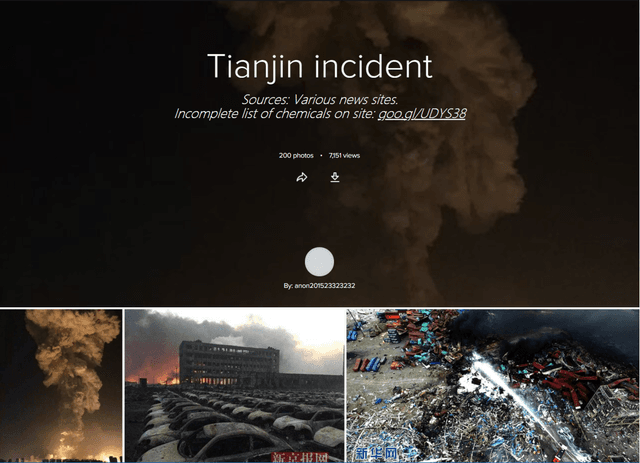
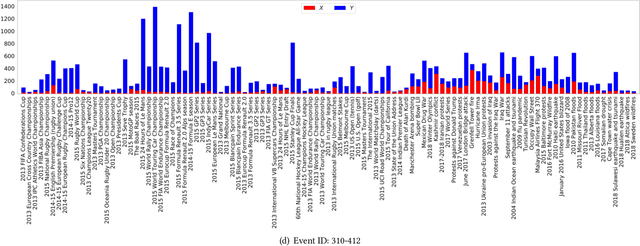
Abstract:In this work, we construct and release a multi-domain and multi-modality event dataset (MMED), containing 25,165 textual news articles collected from hundreds of news media sites (e.g., Yahoo News, Google News, CNN News.) and 76,516 image posts shared on Flickr social media, which are annotated according to 412 real-world events. The dataset is collected to explore the problem of organizing heterogeneous data contributed by professionals and amateurs in different data domains, and the problem of transferring event knowledge obtained from one data domain to heterogeneous data domain, thus summarizing the data with different contributors. We hope that the release of the MMED dataset can stimulate innovate research on related challenging problems, such as event discovery, cross-modal (event) retrieval, and visual question answering, etc.
Learning Shared Semantic Space with Correlation Alignment for Cross-modal Event Retrieval
Jan 15, 2019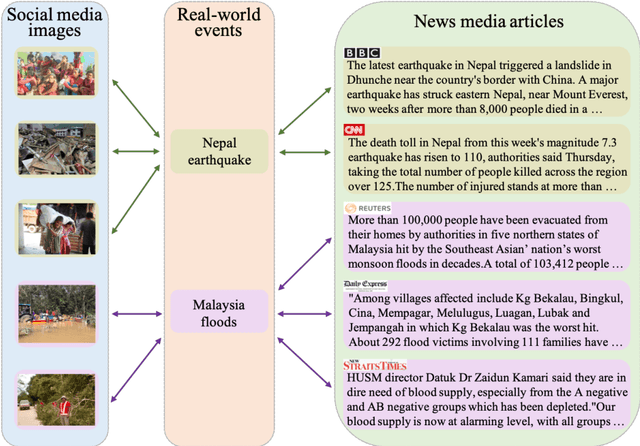
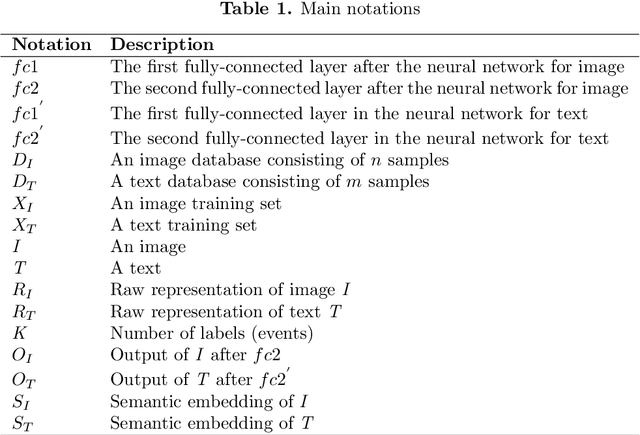
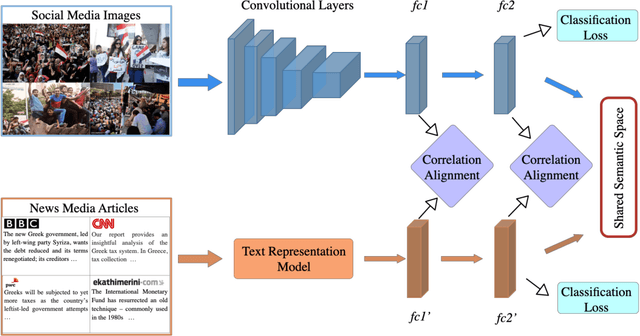
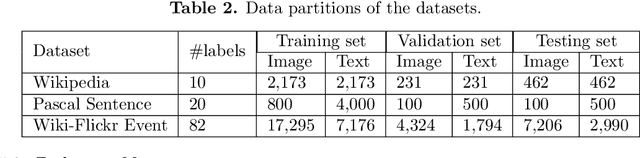
Abstract:In this paper, we propose to learn shared semantic space with correlation alignment (${S}^{3}CA$) for multimodal data representations, which aligns nonlinear correlations of multimodal data distributions in deep neural networks designed for heterogeneous data. In the context of cross-modal (event) retrieval, we design a neural network with convolutional layers and fully-connected layers to extract features for images, including images on Flickr-like social media. Simultaneously, we exploit a fully-connected neural network to extract semantic features for texts, including news articles from news media. In particular, nonlinear correlations of layer activations in the two neural networks are aligned with correlation alignment during the joint training of the networks. Furthermore, we project the multimodal data into a shared semantic space for cross-modal (event) retrieval, where the distances between heterogeneous data samples can be measured directly. In addition, we contribute a Wiki-Flickr Event dataset, where the multimodal data samples are not describing each other in pairs like the existing paired datasets, but all of them are describing semantic events. Extensive experiments conducted on both paired and unpaired datasets manifest the effectiveness of ${S}^{3}CA$, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge