Peipei Kang
Solving the Travelling Thief Problem based on Item Selection Weight and Reverse Order Allocation
Dec 16, 2020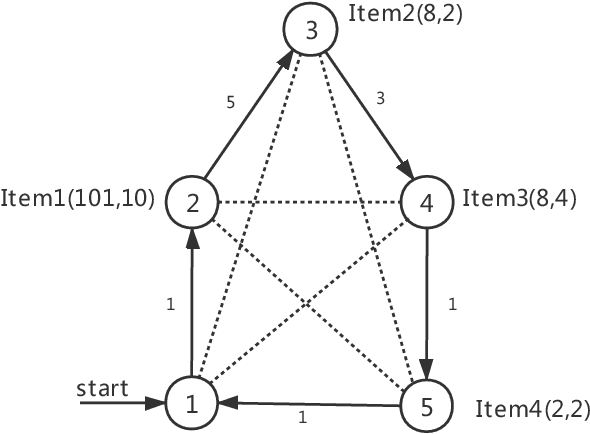
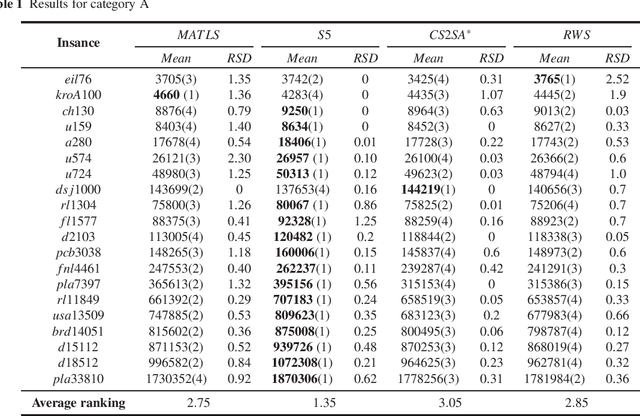
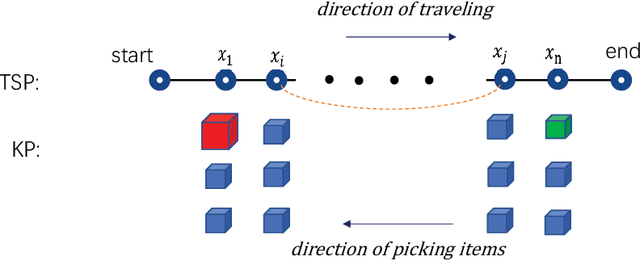
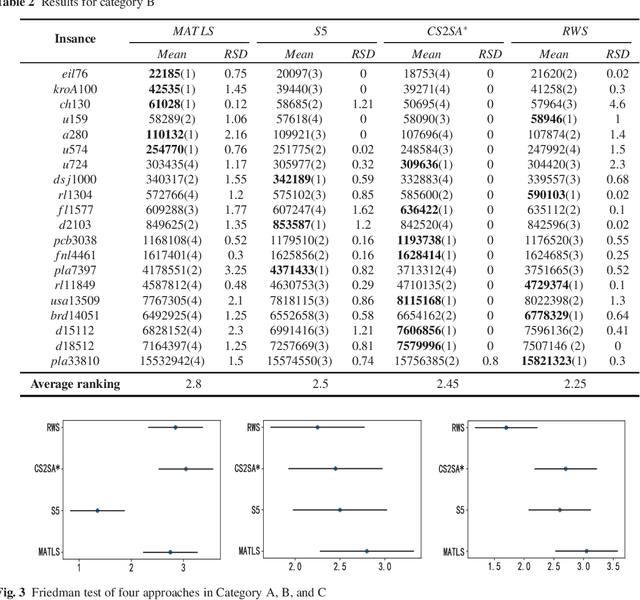
Abstract:The Travelling Thief Problem (TTP) is a challenging combinatorial optimization problem that attracts many scholars. The TTP interconnects two well-known NP-hard problems: the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP) and the 0-1 Knapsack Problem (KP). Increasingly algorithms have been proposed for solving this novel problem that combines two interdependent sub-problems. In this paper, TTP is investigated theoretically and empirically. An algorithm based on the score value calculated by our proposed formulation in picking items and sorting items in the reverse order in the light of the scoring value is proposed to solve the problem. Different approaches for solving the TTP are compared and analyzed; the experimental investigations suggest that our proposed approach is very efficient in meeting or beating current state-of-the-art heuristic solutions on a comprehensive set of benchmark TTP instances.
Learning Shared Semantic Space with Correlation Alignment for Cross-modal Event Retrieval
Jan 15, 2019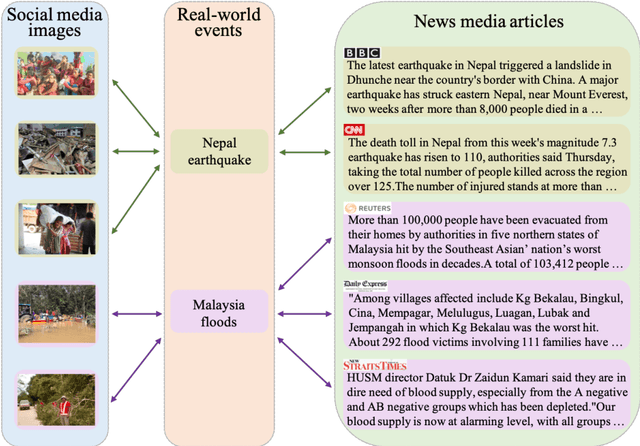
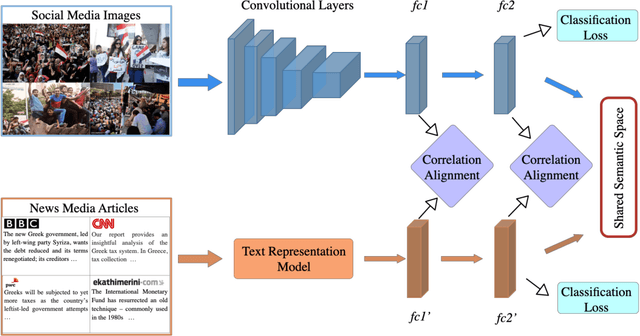
Abstract:In this paper, we propose to learn shared semantic space with correlation alignment (${S}^{3}CA$) for multimodal data representations, which aligns nonlinear correlations of multimodal data distributions in deep neural networks designed for heterogeneous data. In the context of cross-modal (event) retrieval, we design a neural network with convolutional layers and fully-connected layers to extract features for images, including images on Flickr-like social media. Simultaneously, we exploit a fully-connected neural network to extract semantic features for texts, including news articles from news media. In particular, nonlinear correlations of layer activations in the two neural networks are aligned with correlation alignment during the joint training of the networks. Furthermore, we project the multimodal data into a shared semantic space for cross-modal (event) retrieval, where the distances between heterogeneous data samples can be measured directly. In addition, we contribute a Wiki-Flickr Event dataset, where the multimodal data samples are not describing each other in pairs like the existing paired datasets, but all of them are describing semantic events. Extensive experiments conducted on both paired and unpaired datasets manifest the effectiveness of ${S}^{3}CA$, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge