Yueqi Zhang
Learning More from Less: Unlocking Internal Representations for Benchmark Compression
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The prohibitive cost of evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) necessitates efficient alternatives to full-scale benchmarking. Prevalent approaches address this by identifying a small coreset of items to approximate full-benchmark performance. However, existing methods must estimate a reliable item profile from response patterns across many source models, which becomes statistically unstable when the source pool is small. This dependency is particularly limiting for newly released benchmarks with minimal historical evaluation data. We argue that discrete correctness labels are a lossy view of the model's decision process and fail to capture information encoded in hidden states. To address this, we introduce REPCORE, which aligns heterogeneous hidden states into a unified latent space to construct representative coresets. Using these subsets for performance extrapolation, REPCORE achieves precise estimation accuracy with as few as ten source models. Experiments on five benchmarks and over 200 models show consistent gains over output-based baselines in ranking correlation and estimation accuracy. Spectral analysis further indicates that the aligned representations contain separable components reflecting broad response tendencies and task-specific reasoning patterns.
Do Not Waste Your Rollouts: Recycling Search Experience for Efficient Test-Time Scaling
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Test-Time Scaling enhances the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models by allocating additional inference compute to broaden the exploration of the solution space. However, existing search strategies typically treat rollouts as disposable samples, where valuable intermediate insights are effectively discarded after each trial. This systemic memorylessness leads to massive computational redundancy, as models repeatedly re-derive discovered conclusions and revisit known dead ends across extensive attempts. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{Recycling Search Experience (RSE)}, a self-guided, training-free strategy that turns test-time search from a series of isolated trials into a cumulative process. By actively distilling raw trajectories into a shared experience bank, RSE enables positive recycling of intermediate conclusions to shortcut redundant derivations and negative recycling of failure patterns to prune encountered dead ends. Theoretically, we provide an analysis that formalizes the efficiency gains of RSE, validating its advantage over independent sampling in solving complex reasoning tasks. Empirically, extensive experiments on HMMT24, HMMT25, IMO-Bench, and HLE show that RSE consistently outperforms strong baselines with comparable computational cost, achieving state-of-the-art scaling efficiency.
A Scheduling Framework for Efficient MoE Inference on Edge GPU-NDP Systems
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models facilitate edge deployment by decoupling model capacity from active computation, yet their large memory footprint drives the need for GPU systems with near-data processing (NDP) capabilities that offload experts to dedicated processing units. However, deploying MoE models on such edge-based GPU-NDP systems faces three critical challenges: 1) severe load imbalance across NDP units due to non-uniform expert selection and expert parallelism, 2) insufficient GPU utilization during expert computation within NDP units, and 3) extensive data pre-profiling necessitated by unpredictable expert activation patterns for pre-fetching. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an efficient inference framework featuring three key optimizations. First, the underexplored tensor parallelism in MoE inference is exploited to partition and compute large expert parameters across multiple NDP units simultaneously towards edge low-batch scenarios. Second, a load-balancing-aware scheduling algorithm distributes expert computations across NDP units and GPU to maximize resource utilization. Third, a dataset-free pre-fetching strategy proactively loads frequently accessed experts to minimize activation delays. Experimental results show that our framework enables GPU-NDP systems to achieve 2.41x on average and up to 2.56x speedup in end-to-end latency compared to state-of-the-art approaches, significantly enhancing MoE inference efficiency in resource-constrained environments.
RENet: Fault-Tolerant Motion Control for Quadruped Robots via Redundant Estimator Networks under Visual Collapse
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-based locomotion in outdoor environments presents significant challenges for quadruped robots. Accurate environmental prediction and effective handling of depth sensor noise during real-world deployment remain difficult, severely restricting the outdoor applications of such algorithms. To address these deployment challenges in vision-based motion control, this letter proposes the Redundant Estimator Network (RENet) framework. The framework employs a dual-estimator architecture that ensures robust motion performance while maintaining deployment stability during onboard vision failures. Through an online estimator adaptation, our method enables seamless transitions between estimation modules when handling visual perception uncertainties. Experimental validation on a real-world robot demonstrates the framework's effectiveness in complex outdoor environments, showing particular advantages in scenarios with degraded visual perception. This framework demonstrates its potential as a practical solution for reliable robotic deployment in challenging field conditions. Project website: https://RENet-Loco.github.io/
* Accepted for IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L)
Mind the Quote: Enabling Quotation-Aware Dialogue in LLMs via Plug-and-Play Modules
May 30, 2025Abstract:Human-AI conversation frequently relies on quoting earlier text-"check it with the formula I just highlighted"-yet today's large language models (LLMs) lack an explicit mechanism for locating and exploiting such spans. We formalise the challenge as span-conditioned generation, decomposing each turn into the dialogue history, a set of token-offset quotation spans, and an intent utterance. Building on this abstraction, we introduce a quotation-centric data pipeline that automatically synthesises task-specific dialogues, verifies answer correctness through multi-stage consistency checks, and yields both a heterogeneous training corpus and the first benchmark covering five representative scenarios. To meet the benchmark's zero-overhead and parameter-efficiency requirements, we propose QuAda, a lightweight training-based method that attaches two bottleneck projections to every attention head, dynamically amplifying or suppressing attention to quoted spans at inference time while leaving the prompt unchanged and updating < 2.8% of backbone weights. Experiments across models show that QuAda is suitable for all scenarios and generalises to unseen topics, offering an effective, plug-and-play solution for quotation-aware dialogue.
Does Machine Unlearning Truly Remove Model Knowledge? A Framework for Auditing Unlearning in LLMs
May 29, 2025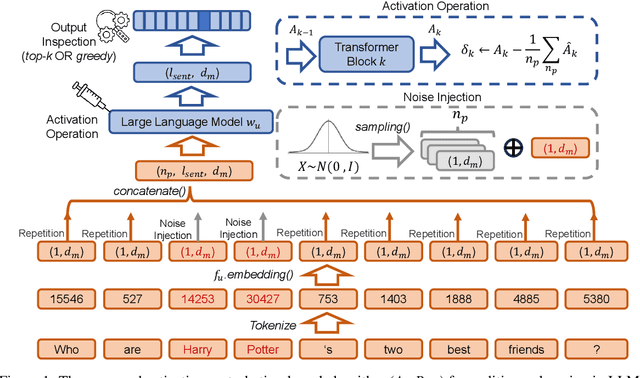
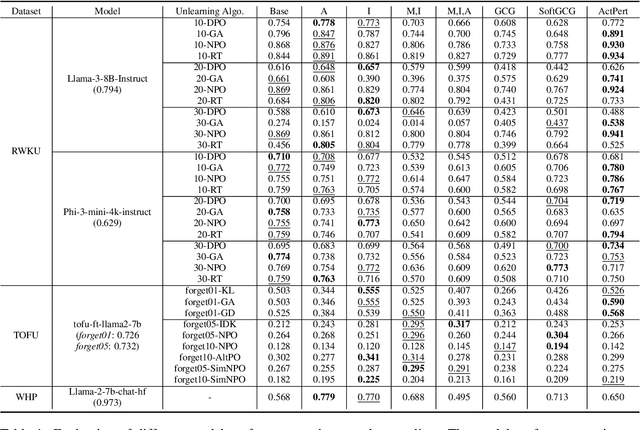
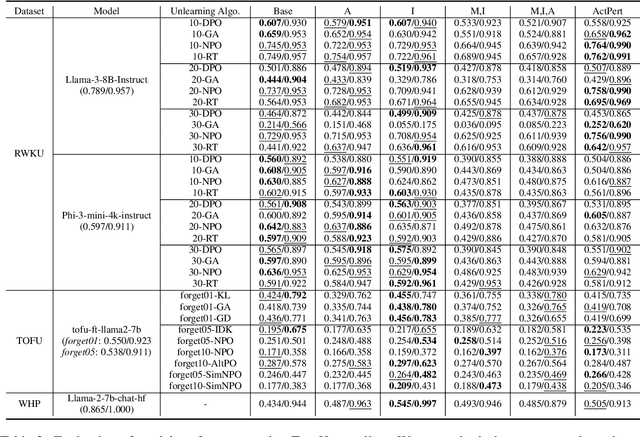
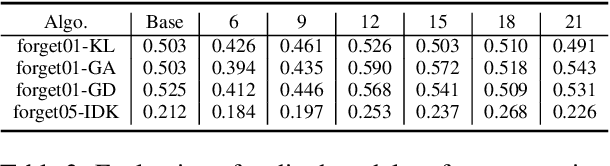
Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable advancements, drawing significant attention from the research community. Their capabilities are largely attributed to large-scale architectures, which require extensive training on massive datasets. However, such datasets often contain sensitive or copyrighted content sourced from the public internet, raising concerns about data privacy and ownership. Regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), grant individuals the right to request the removal of such sensitive information. This has motivated the development of machine unlearning algorithms that aim to remove specific knowledge from models without the need for costly retraining. Despite these advancements, evaluating the efficacy of unlearning algorithms remains a challenge due to the inherent complexity and generative nature of LLMs. In this work, we introduce a comprehensive auditing framework for unlearning evaluation, comprising three benchmark datasets, six unlearning algorithms, and five prompt-based auditing methods. By using various auditing algorithms, we evaluate the effectiveness and robustness of different unlearning strategies. To explore alternatives beyond prompt-based auditing, we propose a novel technique that leverages intermediate activation perturbations, addressing the limitations of auditing methods that rely solely on model inputs and outputs.
Silencer: From Discovery to Mitigation of Self-Bias in LLM-as-Benchmark-Generator
May 27, 2025



Abstract:LLM-as-Benchmark-Generator methods have been widely studied as a supplement to human annotators for scalable evaluation, while the potential biases within this paradigm remain underexplored. In this work, we systematically define and validate the phenomenon of inflated performance in models evaluated on their self-generated benchmarks, referred to as self-bias, and attribute it to sub-biases arising from question domain, language style, and wrong labels. On this basis, we propose Silencer, a general framework that leverages the heterogeneity between multiple generators at both the sample and benchmark levels to neutralize bias and generate high-quality, self-bias-silenced benchmark. Experimental results across various settings demonstrate that Silencer can suppress self-bias to near zero, significantly improve evaluation effectiveness of the generated benchmark (with an average improvement from 0.655 to 0.833 in Pearson correlation with high-quality human-annotated benchmark), while also exhibiting strong generalizability.
Speculative Decoding for Multi-Sample Inference
Mar 07, 2025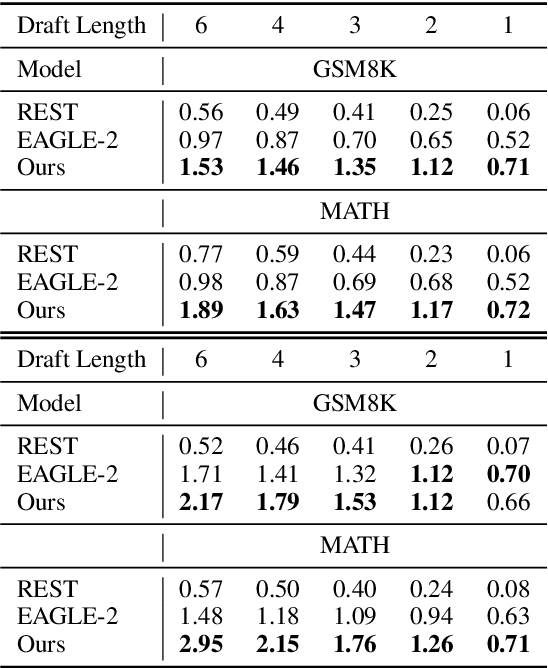
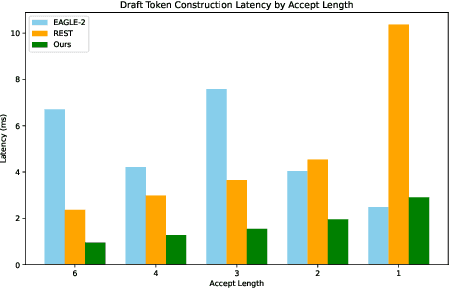
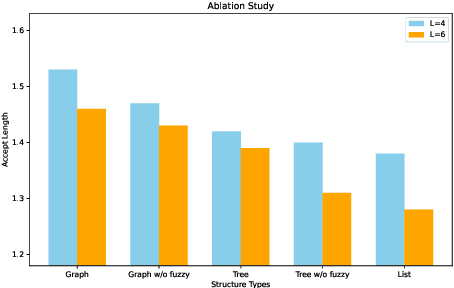
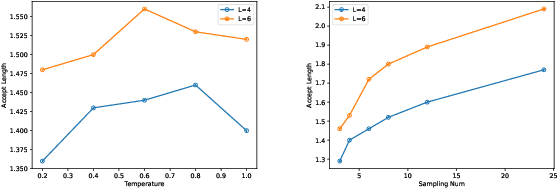
Abstract:We propose a novel speculative decoding method tailored for multi-sample reasoning scenarios, such as self-consistency and Best-of-N sampling. Our method exploits the intrinsic consensus of parallel generation paths to synthesize high-quality draft tokens without requiring auxiliary models or external databases. By dynamically analyzing structural patterns across parallel reasoning paths through a probabilistic aggregation mechanism, it identifies consensus token sequences that align with the decoding distribution. Evaluations on mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate a substantial improvement in draft acceptance rates over baselines, while reducing the latency in draft token construction. This work establishes a paradigm shift for efficient multi-sample inference, enabling seamless integration of speculative decoding with sampling-based reasoning techniques.
Music-Driven Legged Robots: Synchronized Walking to Rhythmic Beats
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:We address the challenge of effectively controlling the locomotion of legged robots by incorporating precise frequency and phase characteristics, which is often ignored in locomotion policies that do not account for the periodic nature of walking. We propose a hierarchical architecture that integrates a low-level phase tracker, oscillators, and a high-level phase modulator. This controller allows quadruped robots to walk in a natural manner that is synchronized with external musical rhythms. Our method generates diverse gaits across different frequencies and achieves real-time synchronization with music in the physical world. This research establishes a foundational framework for enabling real-time execution of accurate rhythmic motions in legged robots. Video is available at website: https://music-walker.github.io/.
Continuous Control of Diverse Skills in Quadruped Robots Without Complete Expert Datasets
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Learning diverse skills for quadruped robots presents significant challenges, such as mastering complex transitions between different skills and handling tasks of varying difficulty. Existing imitation learning methods, while successful, rely on expensive datasets to reproduce expert behaviors. Inspired by introspective learning, we propose Progressive Adversarial Self-Imitation Skill Transition (PASIST), a novel method that eliminates the need for complete expert datasets. PASIST autonomously explores and selects high-quality trajectories based on predefined target poses instead of demonstrations, leveraging the Generative Adversarial Self-Imitation Learning (GASIL) framework. To further enhance learning, We develop a skill selection module to mitigate mode collapse by balancing the weights of skills with varying levels of difficulty. Through these methods, PASIST is able to reproduce skills corresponding to the target pose while achieving smooth and natural transitions between them. Evaluations on both simulation platforms and the Solo 8 robot confirm the effectiveness of PASIST, offering an efficient alternative to expert-driven learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge