Yuefang Gao
Adaptive Global-Local Representation Learning and Selection for Cross-Domain Facial Expression Recognition
Jan 20, 2024Abstract:Domain shift poses a significant challenge in Cross-Domain Facial Expression Recognition (CD-FER) due to the distribution variation across different domains. Current works mainly focus on learning domain-invariant features through global feature adaptation, while neglecting the transferability of local features. Additionally, these methods lack discriminative supervision during training on target datasets, resulting in deteriorated feature representation in target domain. To address these limitations, we propose an Adaptive Global-Local Representation Learning and Selection (AGLRLS) framework. The framework incorporates global-local adversarial adaptation and semantic-aware pseudo label generation to enhance the learning of domain-invariant and discriminative feature during training. Meanwhile, a global-local prediction consistency learning is introduced to improve classification results during inference. Specifically, the framework consists of separate global-local adversarial learning modules that learn domain-invariant global and local features independently. We also design a semantic-aware pseudo label generation module, which computes semantic labels based on global and local features. Moreover, a novel dynamic threshold strategy is employed to learn the optimal thresholds by leveraging independent prediction of global and local features, ensuring filtering out the unreliable pseudo labels while retaining reliable ones. These labels are utilized for model optimization through the adversarial learning process in an end-to-end manner. During inference, a global-local prediction consistency module is developed to automatically learn an optimal result from multiple predictions. We conduct comprehensive experiments and analysis based on a fair evaluation benchmark. The results demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms the current competing methods by a substantial margin.
Broad Recommender System: An Efficient Nonlinear Collaborative Filtering Approach
Apr 20, 2022
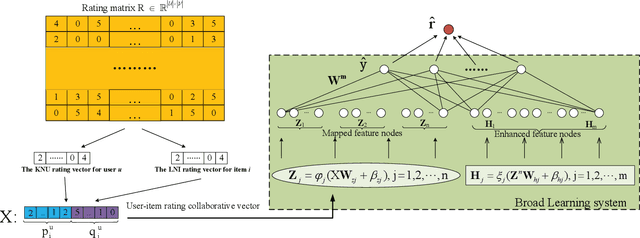
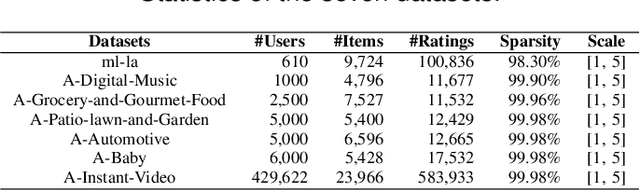
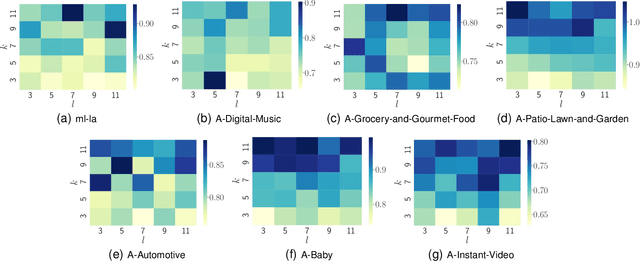
Abstract:Recently, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have been widely introduced into Collaborative Filtering (CF) to produce more accurate recommendation results due to their capability of capturing the complex nonlinear relationships between items and users.However, the DNNs-based models usually suffer from high computational complexity, i.e., consuming very long training time and storing huge amount of trainable parameters. To address these problems, we propose a new broad recommender system called Broad Collaborative Filtering (BroadCF), which is an efficient nonlinear collaborative filtering approach. Instead of DNNs, Broad Learning System (BLS) is used as a mapping function to learn the complex nonlinear relationships between users and items, which can avoid the above issues while achieving very satisfactory recommendation performance. However, it is not feasible to directly feed the original rating data into BLS. To this end, we propose a user-item rating collaborative vector preprocessing procedure to generate low-dimensional user-item input data, which is able to harness quality judgments of the most similar users/items. Extensive experiments conducted on seven benchmark datasets have confirmed the effectiveness of the proposed BroadCF algorithm
Fine-Grained Representation Learning and Recognition by Exploiting Hierarchical Semantic Embedding
Aug 14, 2018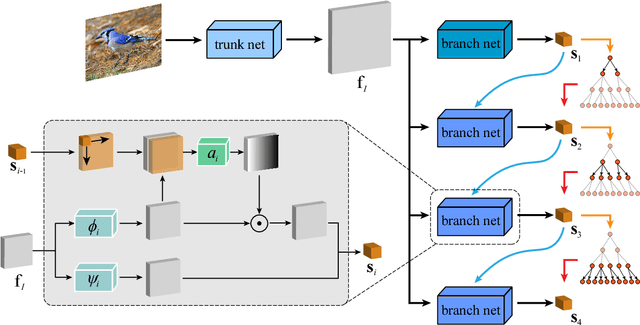
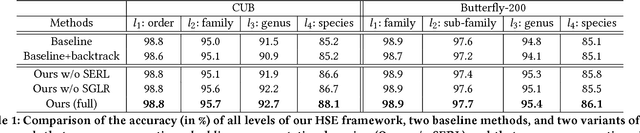
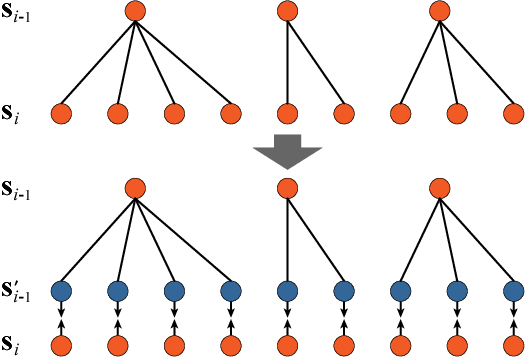
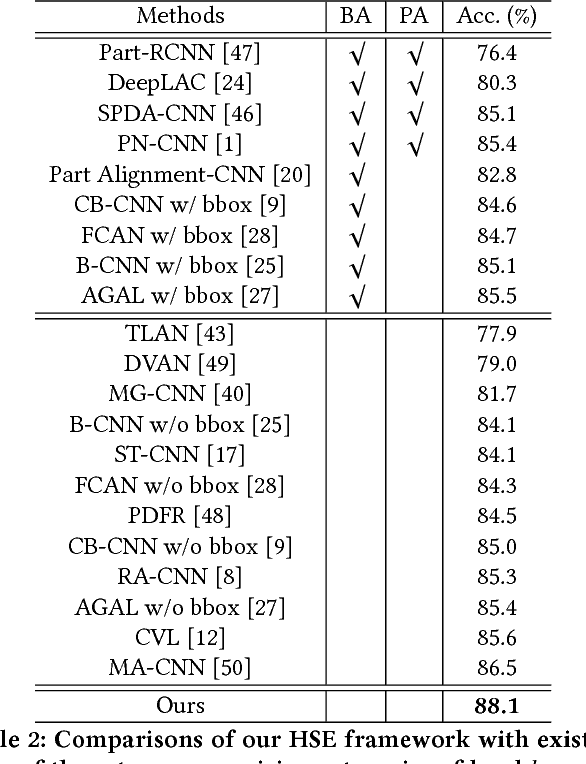
Abstract:Object categories inherently form a hierarchy with different levels of concept abstraction, especially for fine-grained categories. For example, birds (Aves) can be categorized according to a four-level hierarchy of order, family, genus, and species. This hierarchy encodes rich correlations among various categories across different levels, which can effectively regularize the semantic space and thus make prediction less ambiguous. However, previous studies of fine-grained image recognition primarily focus on categories of one certain level and usually overlook this correlation information. In this work, we investigate simultaneously predicting categories of different levels in the hierarchy and integrating this structured correlation information into the deep neural network by developing a novel Hierarchical Semantic Embedding (HSE) framework. Specifically, the HSE framework sequentially predicts the category score vector of each level in the hierarchy, from highest to lowest. At each level, it incorporates the predicted score vector of the higher level as prior knowledge to learn finer-grained feature representation. During training, the predicted score vector of the higher level is also employed to regularize label prediction by using it as soft targets of corresponding sub-categories. To evaluate the proposed framework, we organize the 200 bird species of the Caltech-UCSD birds dataset with the four-level category hierarchy and construct a large-scale butterfly dataset that also covers four level categories. Extensive experiments on these two and the newly-released VegFru datasets demonstrate the superiority of our HSE framework over the baseline methods and existing competitors.
A Universal Update-pacing Framework For Visual Tracking
Mar 01, 2016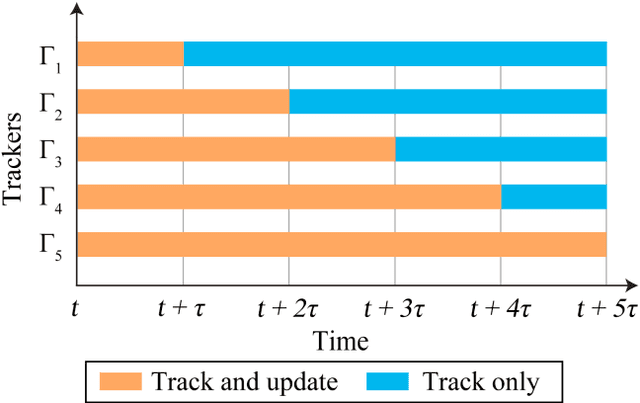
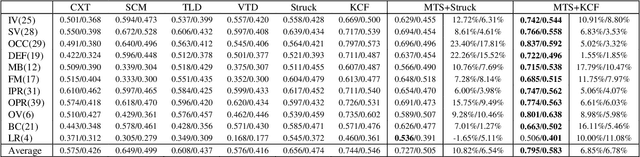
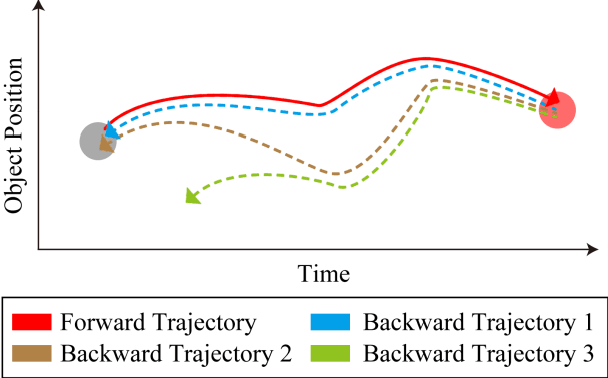
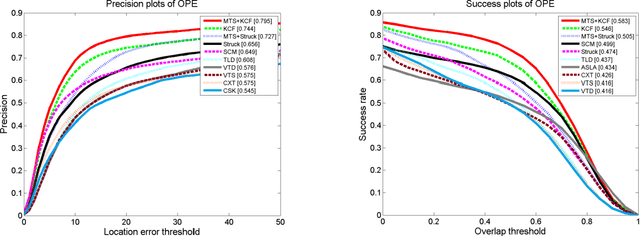
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel framework to alleviate the model drift problem in visual tracking, which is based on paced updates and trajectory selection. Given a base tracker, an ensemble of trackers is generated, in which each tracker's update behavior will be paced and then traces the target object forward and backward to generate a pair of trajectories in an interval. Then, we implicitly perform self-examination based on trajectory pair of each tracker and select the most robust tracker. The proposed framework can effectively leverage temporal context of sequential frames and avoid to learn corrupted information. Extensive experiments on the standard benchmark suggest that the proposed framework achieves superior performance against state-of-the-art trackers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge