Yuchen Niu
The Demon is in Ambiguity: Revisiting Situation Recognition with Single Positive Multi-Label Learning
Aug 29, 2025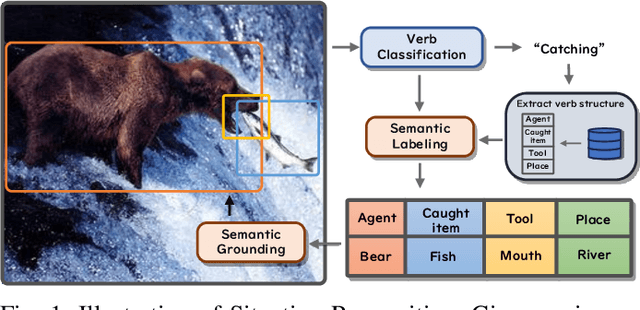
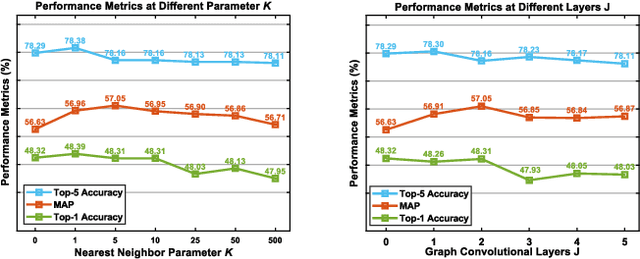
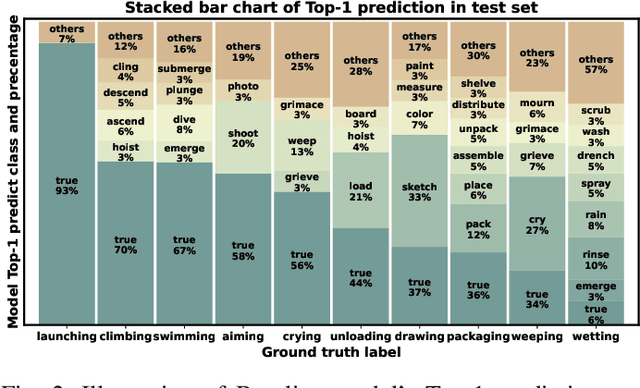
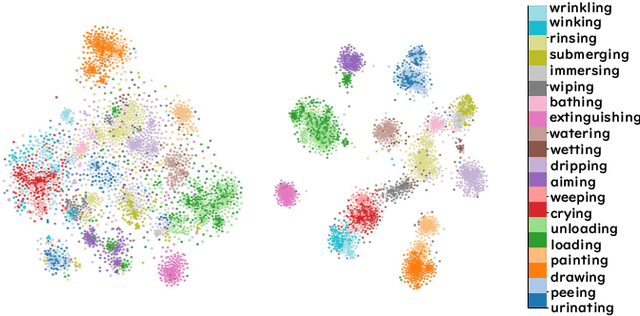
Abstract:Context recognition (SR) is a fundamental task in computer vision that aims to extract structured semantic summaries from images by identifying key events and their associated entities. Specifically, given an input image, the model must first classify the main visual events (verb classification), then identify the participating entities and their semantic roles (semantic role labeling), and finally localize these entities in the image (semantic role localization). Existing methods treat verb classification as a single-label problem, but we show through a comprehensive analysis that this formulation fails to address the inherent ambiguity in visual event recognition, as multiple verb categories may reasonably describe the same image. This paper makes three key contributions: First, we reveal through empirical analysis that verb classification is inherently a multi-label problem due to the ubiquitous semantic overlap between verb categories. Second, given the impracticality of fully annotating large-scale datasets with multiple labels, we propose to reformulate verb classification as a single positive multi-label learning (SPMLL) problem - a novel perspective in SR research. Third, we design a comprehensive multi-label evaluation benchmark for SR that is carefully designed to fairly evaluate model performance in a multi-label setting. To address the challenges of SPMLL, we futher develop the Graph Enhanced Verb Multilayer Perceptron (GE-VerbMLP), which combines graph neural networks to capture label correlations and adversarial training to optimize decision boundaries. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that our approach achieves more than 3\% MAP improvement while remaining competitive on traditional top-1 and top-5 accuracy metrics.
StableToolBench-MirrorAPI: Modeling Tool Environments as Mirrors of 7,000+ Real-World APIs
Mar 26, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has spurred significant interest in tool learning, where LLMs are augmented with external tools to tackle complex tasks. However, existing tool environments face challenges in balancing stability, scalability, and realness, particularly for benchmarking purposes. To address this problem, we propose MirrorAPI, a novel framework that trains specialized LLMs to accurately simulate real API responses, effectively acting as "mirrors" to tool environments. Using a comprehensive dataset of request-response pairs from 7,000+ APIs, we employ supervised fine-tuning and chain-of-thought reasoning to enhance simulation fidelity. MirrorAPI achieves superior accuracy and stability compared to state-of-the-art methods, as demonstrated by its performance on the newly constructed MirrorAPI-Bench and its integration into StableToolBench.
An Empathetic User-Centric Chatbot for Emotional Support
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:This paper explores the intersection of Otome Culture and artificial intelligence, particularly focusing on how Otome-oriented games fulfill the emotional needs of young women. These games, which are deeply rooted in a subcultural understanding of love, provide players with feelings of satisfaction, companionship, and protection through carefully crafted narrative structures and character development. With the proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs), there is an opportunity to transcend traditional static game narratives and create dynamic, emotionally responsive interactions. We present a case study of Tears of Themis, where we have integrated LLM technology to enhance the interactive experience. Our approach involves augmenting existing game narratives with a Question and Answer (QA) system, enriched through data augmentation and emotional enhancement techniques, resulting in a chatbot that offers realistic and supportive companionship.
Exploring Generalization Ability of Pretrained Language Models on Arithmetic and Logical Reasoning
Aug 15, 2021



Abstract:To quantitatively and intuitively explore the generalization ability of pre-trained language models (PLMs), we have designed several tasks of arithmetic and logical reasoning. We both analyse how well PLMs generalize when the test data is in the same distribution as the train data and when it is different, for the latter analysis, we have also designed a cross-distribution test set other than the in-distribution test set. We conduct experiments on one of the most advanced and publicly released generative PLM - BART. Our research finds that the PLMs can easily generalize when the distribution is the same, however, it is still difficult for them to generalize out of the distribution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge