Yubo Hou
On the Nonasymptotic Scaling Guarantee of Hyperparameter Estimation in Inhomogeneous, Weakly-Dependent Complex Network Dynamical Systems
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Hierarchical Bayesian models are increasingly used in large, inhomogeneous complex network dynamical systems by modeling parameters as draws from a hyperparameter-governed distribution. However, theoretical guarantees for these estimates as the system size grows have been lacking. A critical concern is that hyperparameter estimation may diverge for larger networks, undermining the model's reliability. Formulating the system's evolution in a measure transport perspective, we propose a theoretical framework for estimating hyperparameters with mean-type observations, which are prevalent in many scientific applications. Our primary contribution is a nonasymptotic bound for the deviation of estimate of hyperparameters in inhomogeneous complex network dynamical systems with respect to network population size, which is established for a general family of optimization algorithms within a fixed observation duration. While we firstly establish a consistency result for systems with independent nodes, our main result extends this guarantee to the more challenging and realistic setting of weakly-dependent nodes. We validate our theoretical findings with numerical experiments on two representative models: a Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible model and a Spiking Neuronal Network model. In both cases, the results confirm that the estimation error decreases as the network population size increases, aligning with our theoretical guarantees. This research proposes the foundational theory to ensure that hierarchical Bayesian methods are statistically consistent for large-scale inhomogeneous systems, filling a gap in this area of theoretical research and justifying their application in practice.
Digital Twin Brain: a simulation and assimilation platform for whole human brain
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:In this work, we present a computing platform named digital twin brain (DTB) that can simulate spiking neuronal networks of the whole human brain scale and more importantly, a personalized biological brain structure. In comparison to most brain simulations with a homogeneous global structure, we highlight that the sparseness, couplingness and heterogeneity in the sMRI, DTI and PET data of the brain has an essential impact on the efficiency of brain simulation, which is proved from the scaling experiments that the DTB of human brain simulation is communication-intensive and memory-access intensive computing systems rather than computation-intensive. We utilize a number of optimization techniques to balance and integrate the computation loads and communication traffics from the heterogeneous biological structure to the general GPU-based HPC and achieve leading simulation performance for the whole human brain-scaled spiking neuronal networks. On the other hand, the biological structure, equipped with a mesoscopic data assimilation, enables the DTB to investigate brain cognitive function by a reverse-engineering method, which is demonstrated by a digital experiment of visual evaluation on the DTB. Furthermore, we believe that the developing DTB will be a promising powerful platform for a large of research orients including brain-inspiredintelligence, rain disease medicine and brain-machine interface.
Automatic Assessment of Divergent Thinking in Chinese Language with TransDis: A Transformer-Based Language Model Approach
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Language models have been increasingly popular for automatic creativity assessment, generating semantic distances to objectively measure the quality of creative ideas. However, there is currently a lack of an automatic assessment system for evaluating creative ideas in the Chinese language. To address this gap, we developed TransDis, a scoring system using transformer-based language models, capable of providing valid originality (quality) and flexibility (variety) scores for Alternative Uses Task (AUT) responses in Chinese. Study 1 demonstrated that the latent model-rated originality factor, comprised of three transformer-based models, strongly predicted human originality ratings, and the model-rated flexibility strongly correlated with human flexibility ratings as well. Criterion validity analyses indicated that model-rated originality and flexibility positively correlated to other creativity measures, demonstrating similar validity to human ratings. Study 2 & 3 showed that TransDis effectively distinguished participants instructed to provide creative vs. common uses (Study 2) and participants instructed to generate ideas in a flexible vs. persistent way (Study 3). Our findings suggest that TransDis can be a reliable and low-cost tool for measuring idea originality and flexibility in Chinese language, potentially paving the way for automatic creativity assessment in other languages. We offer an open platform to compute originality and flexibility for AUT responses in Chinese and over 50 other languages (https://osf.io/59jv2/).
Adaptive Mean-Residue Loss for Robust Facial Age Estimation
Mar 31, 2022

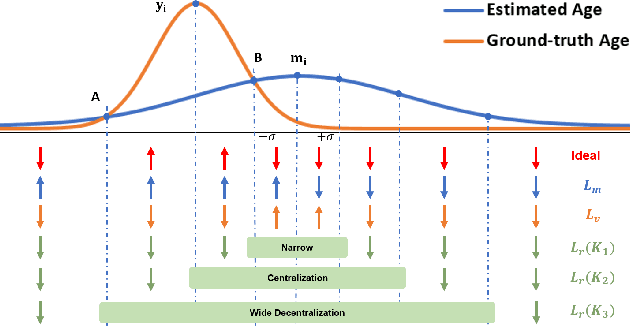

Abstract:Automated facial age estimation has diverse real-world applications in multimedia analysis, e.g., video surveillance, and human-computer interaction. However, due to the randomness and ambiguity of the aging process, age assessment is challenging. Most research work over the topic regards the task as one of age regression, classification, and ranking problems, and cannot well leverage age distribution in representing labels with age ambiguity. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective loss function for robust facial age estimation via distribution learning, i.e., adaptive mean-residue loss, in which, the mean loss penalizes the difference between the estimated age distribution's mean and the ground-truth age, whereas the residue loss penalizes the entropy of age probability out of dynamic top-K in the distribution. Experimental results in the datasets FG-NET and CLAP2016 have validated the effectiveness of the proposed loss. Our code is available at https://github.com/jacobzhaoziyuan/AMR-Loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge