Yuanhao Lai
CLEANet: Robust and Efficient Anomaly Detection in Contaminated Multivariate Time Series
Oct 26, 2025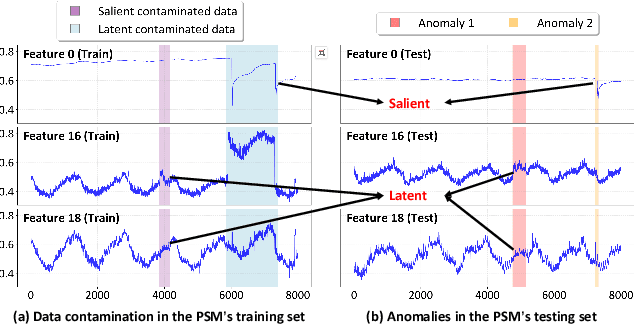
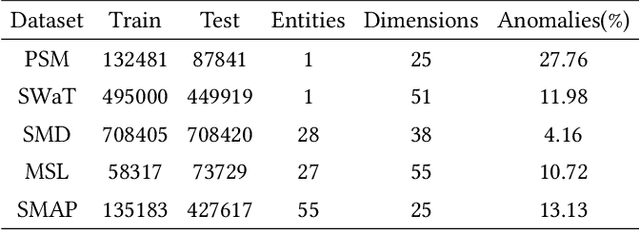
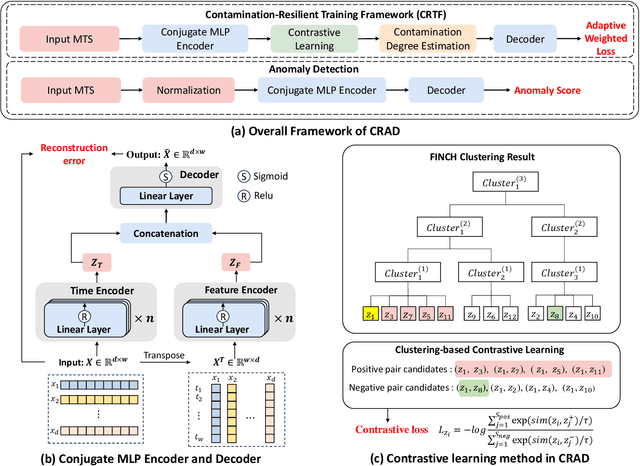
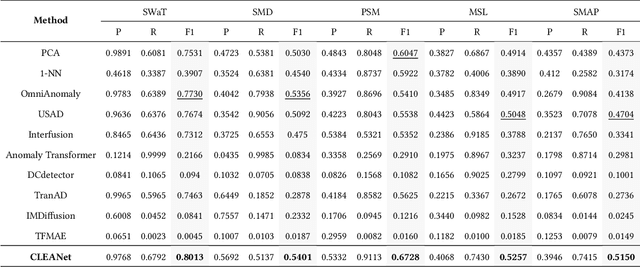
Abstract:Multivariate time series (MTS) anomaly detection is essential for maintaining the reliability of industrial systems, yet real-world deployment is hindered by two critical challenges: training data contamination (noises and hidden anomalies) and inefficient model inference. Existing unsupervised methods assume clean training data, but contamination distorts learned patterns and degrades detection accuracy. Meanwhile, complex deep models often overfit to contamination and suffer from high latency, limiting practical use. To address these challenges, we propose CLEANet, a robust and efficient anomaly detection framework in contaminated multivariate time series. CLEANet introduces a Contamination-Resilient Training Framework (CRTF) that mitigates the impact of corrupted samples through an adaptive reconstruction weighting strategy combined with clustering-guided contrastive learning, thereby enhancing robustness. To further avoid overfitting on contaminated data and improve computational efficiency, we design a lightweight conjugate MLP that disentangles temporal and cross-feature dependencies. Across five public datasets, CLEANet achieves up to 73.04% higher F1 and 81.28% lower runtime compared with ten state-of-the-art baselines. Furthermore, integrating CRTF into three advanced models yields an average 5.35% F1 gain, confirming its strong generalizability.
Centrum: Model-based Database Auto-tuning with Minimal Distributional Assumptions
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Gaussian-Process-based Bayesian optimization (GP-BO), is a prevailing model-based framework for DBMS auto-tuning. However, recent work shows GP-BO-based DBMS auto-tuners significantly outperformed auto-tuners based on SMAC, which features random forest surrogate models; such results motivate us to rethink and investigate the limitations of GP-BO in auto-tuner design. We find the fundamental assumptions of GP-BO are widely violated when modeling and optimizing DBMS performance, while tree-ensemble-BOs (e.g., SMAC) can avoid the assumption pitfalls and deliver improved tuning efficiency and effectiveness. Moreover, we argue that existing tree-ensemble-BOs restrict further advancement in DBMS auto-tuning. First, existing tree-ensemble-BOs can only achieve distribution-free point estimates, but still impose unrealistic distributional assumptions on uncertainty estimates, compromising surrogate modeling and distort the acquisition function. Second, recent advances in gradient boosting, which can further enhance surrogate modeling against vanilla GP and random forest counterparts, have rarely been applied in optimizing DBMS auto-tuners. To address these issues, we propose a novel model-based DBMS auto-tuner, Centrum. Centrum improves distribution-free point and interval estimation in surrogate modeling with a two-phase learning procedure of stochastic gradient boosting ensembles. Moreover, Centrum adopts a generalized SGBE-estimated locally-adaptive conformal prediction to facilitate a distribution-free uncertainty estimation and acquisition function. To our knowledge, Centrum is the first auto-tuner to realize distribution-freeness, enhancing BO's practicality in DBMS auto-tuning, and the first to seamlessly fuse gradient boosting ensembles and conformal inference in BO. Extensive physical and simulation experiments on two DBMSs and three workloads show Centrum outperforms 21 SOTA methods.
Speculative MoE: Communication Efficient Parallel MoE Inference with Speculative Token and Expert Pre-scheduling
Mar 07, 2025



Abstract:MoE (Mixture of Experts) prevails as a neural architecture that can scale modern transformer-based LLMs (Large Language Models) to unprecedented scales. Nevertheless, large MoEs' great demands of computing power, memory capacity and memory bandwidth make scalable serving a fundamental challenge and efficient parallel inference has become a requisite to attain adequate throughput under latency constraints. DeepSpeed-MoE, one state-of-the-art MoE inference framework, adopts a 3D-parallel paradigm including EP (Expert Parallelism), TP (Tensor Parallel) and DP (Data Parallelism). However, our analysis shows DeepSpeed-MoE's inference efficiency is largely bottlenecked by EP, which is implemented with costly all-to-all collectives to route token activation. Our work aims to boost DeepSpeed-MoE by strategically reducing EP's communication overhead with a technique named Speculative MoE. Speculative MoE has two speculative parallelization schemes, speculative token shuffling and speculative expert grouping, which predict outstanding tokens' expert routing paths and pre-schedule tokens and experts across devices to losslessly trim EP's communication volume. Besides DeepSpeed-MoE, we also build Speculative MoE into a prevailing MoE inference engine SGLang. Experiments show Speculative MoE can significantly boost state-of-the-art MoE inference frameworks on fast homogeneous and slow heterogeneous interconnects.
Hessian Aware Low-Rank Weight Perturbation for Continual Learning
Nov 26, 2023Abstract:Continual learning aims to learn a series of tasks sequentially without forgetting the knowledge acquired from the previous ones. In this work, we propose the Hessian Aware Low-Rank Perturbation algorithm for continual learning. By modeling the parameter transitions along the sequential tasks with the weight matrix transformation, we propose to apply the low-rank approximation on the task-adaptive parameters in each layer of the neural networks. Specifically, we theoretically demonstrate the quantitative relationship between the Hessian and the proposed low-rank approximation. The approximation ranks are then globally determined according to the marginal increment of the empirical loss estimated by the layer-specific gradient and low-rank approximation error. Furthermore, we control the model capacity by pruning less important parameters to diminish the parameter growth. We conduct extensive experiments on various benchmarks, including a dataset with large-scale tasks, and compare our method against some recent state-of-the-art methods to demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of our proposed method. Empirical results show that our method performs better on different benchmarks, especially in achieving task order robustness and handling the forgetting issue. A demo code can be found at https://github.com/lijiaqi/HALRP.
Ensemble Quantile Classifier
Oct 28, 2019

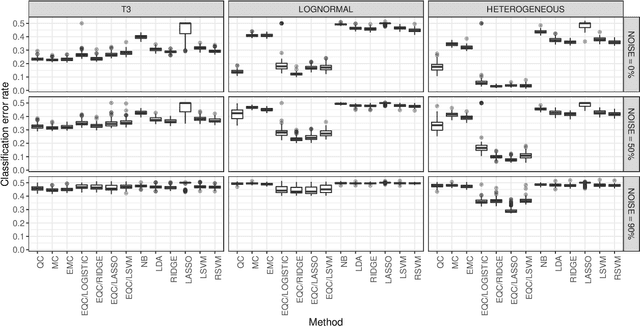
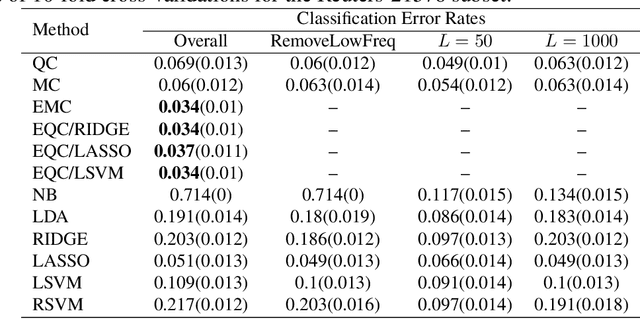
Abstract:Both the median-based classifier and the quantile-based classifier are useful for discriminating high-dimensional data with heavy-tailed or skewed inputs. But these methods are restricted as they assign equal weight to each variable in an unregularized way. The ensemble quantile classifier is a more flexible regularized classifier that provides better performance with high-dimensional data, asymmetric data or when there are many irrelevant extraneous inputs. The improved performance is demonstrated by a simulation study as well as an application to text categorization. It is proven that the estimated parameters of the ensemble quantile classifier consistently estimate the minimal population loss under suitable general model assumptions. It is also shown that the ensemble quantile classifier is Bayes optimal under suitable assumptions with asymmetric Laplace distribution inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge