Yuangang Li
S2D-ALIGN: Shallow-to-Deep Auxiliary Learning for Anatomically-Grounded Radiology Report Generation
Nov 14, 2025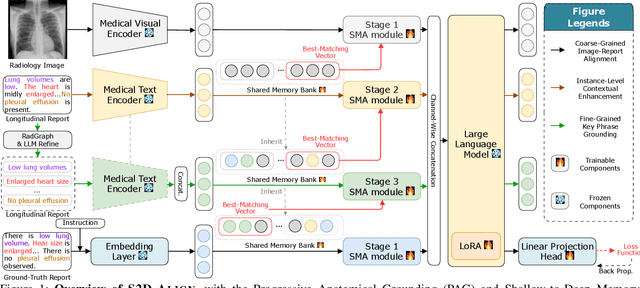
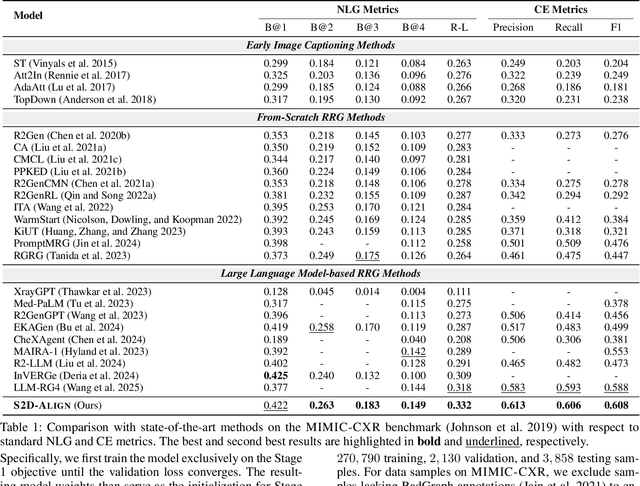
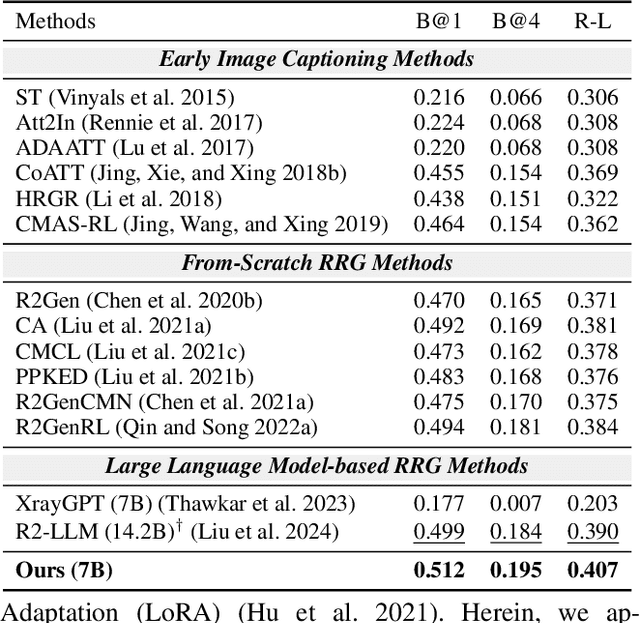
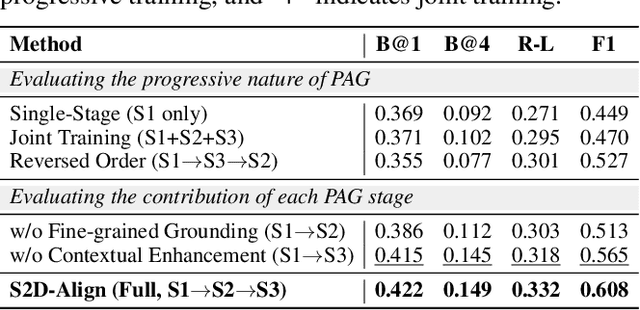
Abstract:Radiology Report Generation (RRG) aims to automatically generate diagnostic reports from radiology images. To achieve this, existing methods have leveraged the powerful cross-modal generation capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), primarily focusing on optimizing cross-modal alignment between radiographs and reports through Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). However, by only performing instance-level alignment with the image-text pairs, the standard SFT paradigm fails to establish anatomically-grounded alignment, where the templated nature of reports often leads to sub-optimal generation quality. To address this, we propose \textsc{S2D-Align}, a novel SFT paradigm that establishes anatomically-grounded alignment by leveraging auxiliary signals of varying granularities. \textsc{S2D-Align} implements a shallow-to-deep strategy, progressively enriching the alignment process: it begins with the coarse radiograph-report pairing, then introduces reference reports for instance-level guidance, and ultimately utilizes key phrases to ground the generation in specific anatomical details. To bridge the different alignment stages, we introduce a memory-based adapter that empowers feature sharing, thereby integrating coarse and fine-grained guidance. For evaluation, we conduct experiments on the public \textsc{MIMIC-CXR} and \textsc{IU X-Ray} benchmarks, where \textsc{S2D-Align} achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods. Ablation studies validate the effectiveness of our multi-stage, auxiliary-guided approach, highlighting a promising direction for enhancing grounding capabilities in complex, multi-modal generation tasks.
A Large-scale Empirical Study on Large Language Models for Election Prediction
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Can Large Language Models (LLMs) accurately predict election outcomes? While LLMs have demonstrated impressive performance in healthcare, legal analysis, and creative applications, their capabilities in election forecasting remain uncertain. Notably, election prediction poses unique challenges: limited voter-level data, evolving political contexts, and the complexity of modeling human behavior. In the first part of this paper, we explore and introduce a multi-step reasoning framework for election prediction, which systematically integrates demographic, ideological, and time-sensitive factors. Validated on 2016 and 2020 real-world data and extensive synthetic personas, our approach adapts to changing political landscapes, reducing bias and significantly improving predictive accuracy. We further apply our pipeline to the 2024 U.S. presidential election, illustrating its ability to generalize beyond observed historical data. Beyond enhancing accuracy, the second part of the paper provides insights into the broader implications of LLM-based election forecasting. We identify potential political biases embedded in pretrained corpora, examine how demographic patterns can become exaggerated, and suggest strategies for mitigating these issues. Together, this project, a large-scale LLM empirical study, advances the accuracy of election predictions and establishes directions for more balanced, transparent, and context-aware modeling in political science research and practice.
AD-LLM: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Anomaly Detection
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD) is an important machine learning task with many real-world uses, including fraud detection, medical diagnosis, and industrial monitoring. Within natural language processing (NLP), AD helps detect issues like spam, misinformation, and unusual user activity. Although large language models (LLMs) have had a strong impact on tasks such as text generation and summarization, their potential in AD has not been studied enough. This paper introduces AD-LLM, the first benchmark that evaluates how LLMs can help with NLP anomaly detection. We examine three key tasks: (i) zero-shot detection, using LLMs' pre-trained knowledge to perform AD without tasks-specific training; (ii) data augmentation, generating synthetic data and category descriptions to improve AD models; and (iii) model selection, using LLMs to suggest unsupervised AD models. Through experiments with different datasets, we find that LLMs can work well in zero-shot AD, that carefully designed augmentation methods are useful, and that explaining model selection for specific datasets remains challenging. Based on these results, we outline six future research directions on LLMs for AD.
H-FedSN: Personalized Sparse Networks for Efficient and Accurate Hierarchical Federated Learning for IoT Applications
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) has increased interest in federated learning (FL) for privacy-preserving distributed data utilization. However, traditional two-tier FL architectures inadequately adapt to multi-tier IoT environments. While Hierarchical Federated Learning (HFL) improves practicality in multi-tier IoT environments by multi-layer aggregation, it still faces challenges in communication efficiency and accuracy due to high data transfer volumes, data heterogeneity, and imbalanced device distribution, struggling to meet the low-latency and high-accuracy model training requirements of practical IoT scenarios. To overcome these limitations, we propose H-FedSN, an innovative approach for practical IoT environments. H-FedSN introduces a binary mask mechanism with shared and personalized layers to reduce communication overhead by creating a sparse network while keeping original weights frozen. To address data heterogeneity and imbalanced device distribution, we integrate personalized layers for local data adaptation and apply Bayesian aggregation with cumulative Beta distribution updates at edge and cloud levels, effectively balancing contributions from diverse client groups. Evaluations on three real-world IoT datasets and MNIST under non-IID settings demonstrate that H-FedSN significantly reduces communication costs by 58 to 238 times compared to HierFAVG while achieving high accuracy, making it highly effective for practical IoT applications in hierarchical federated learning scenarios.
NLP-ADBench: NLP Anomaly Detection Benchmark
Dec 06, 2024


Abstract:Anomaly detection (AD) is a critical machine learning task with diverse applications in web systems, including fraud detection, content moderation, and user behavior analysis. Despite its significance, AD in natural language processing (NLP) remains underexplored, limiting advancements in detecting anomalies in text data such as harmful content, phishing attempts, or spam reviews. In this paper, we introduce NLP-ADBench, the most comprehensive benchmark for NLP anomaly detection (NLP-AD), comprising eight curated datasets and evaluations of nineteen state-of-the-art algorithms. These include three end-to-end methods and sixteen two-step algorithms that apply traditional anomaly detection techniques to language embeddings generated by bert-base-uncased and OpenAI's text-embedding-3-large models. Our results reveal critical insights and future directions for NLP-AD. Notably, no single model excels across all datasets, highlighting the need for automated model selection. Moreover, two-step methods leveraging transformer-based embeddings consistently outperform specialized end-to-end approaches, with OpenAI embeddings demonstrating superior performance over BERT embeddings. By releasing NLP-ADBench at https://github.com/USC-FORTIS/NLP-ADBench, we provide a standardized framework for evaluating NLP-AD methods, fostering the development of innovative approaches. This work fills a crucial gap in the field and establishes a foundation for advancing NLP anomaly detection, particularly in the context of improving the safety and reliability of web-based systems.
FedMetaMed: Federated Meta-Learning for Personalized Medication in Distributed Healthcare Systems
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Personalized medication aims to tailor healthcare to individual patient characteristics. However, the heterogeneity of patient data across healthcare systems presents significant challenges to achieving accurate and effective personalized treatments. Ethical concerns further complicate the aggregation of large volumes of data from diverse institutions. Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising decentralized solution by enabling collaborative model training through the exchange of client models rather than raw data, thus preserving privacy. However, existing FL methods often suffer from retrogression during server aggregation, leading to a decline in model performance in real-world medical FL settings. To address data variability in distributed healthcare systems, we introduce Federated Meta-Learning for Personalized Medication (FedMetaMed), which combines federated learning and meta-learning to create models that adapt to diverse patient data across healthcare systems. The FedMetaMed framework aims to produce superior personalized models for individual clients by addressing these limitations. Specifically, we introduce Cumulative Fourier Aggregation (CFA) at the server to improve stability and effectiveness in global knowledge aggregation. CFA achieves this by gradually integrating client models from low to high frequencies. At the client level, we implement a Collaborative Transfer Optimization (CTO) strategy with a three-step process - Retrieve, Reciprocate, and Refine - to enhance the personalized local model through seamless global knowledge transfer. Experiments on real-world medical imaging datasets demonstrate that FedMetaMed outperforms state-of-the-art FL methods, showing superior generalization even on out-of-distribution cohorts.
Fed-LDR: Federated Local Data-infused Graph Creation with Node-centric Model Refinement
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:The rapid acceleration of global urbanization has introduced novel challenges in enhancing urban infrastructure and services. Spatio-temporal data, integrating spatial and temporal dimensions, has emerged as a critical tool for understanding urban phenomena and promoting sustainability. In this context, Federated Learning (FL) has gained prominence as a distributed learning paradigm aligned with the privacy requirements of urban IoT environments. However, integrating traditional and deep learning models into the FL framework poses significant challenges, particularly in capturing complex spatio-temporal dependencies and adapting to diverse urban conditions. To address these challenges, we propose the Federated Local Data-Infused Graph Creation with Node-centric Model Refinement (Fed-LDR) algorithm. Fed-LDR leverages FL and Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN) to enhance spatio-temporal data analysis in urban environments. The algorithm comprises two key modules: (1) the Local Data-Infused Graph Creation (LDIGC) module, which dynamically reconfigures adjacency matrices to reflect evolving spatial relationships within urban environments, and (2) the Node-centric Model Refinement (NoMoR) module, which customizes model parameters for individual urban nodes to accommodate heterogeneity. Evaluations on the PeMSD4 and PeMSD8 datasets demonstrate Fed-LDR's superior performance over six baseline methods. Fed-LDR achieved the lowest Mean Absolute Error (MAE) values of 20.15 and 17.30, and the lowest Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) values of 32.30 and 27.15, respectively, while maintaining a high correlation coefficient of 0.96 across both datasets. Notably, on the PeMSD4 dataset, Fed-LDR reduced MAE and RMSE by up to 81\% and 78\%, respectively, compared to the best-performing baseline FedMedian.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge