Yizhen Chen
Tagging before Alignment: Integrating Multi-Modal Tags for Video-Text Retrieval
Jan 30, 2023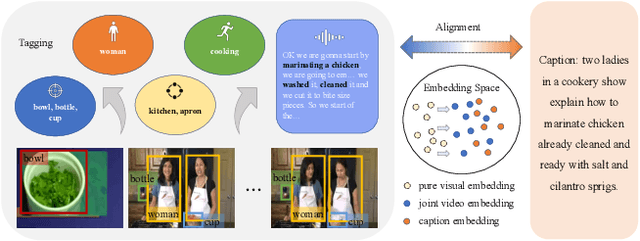
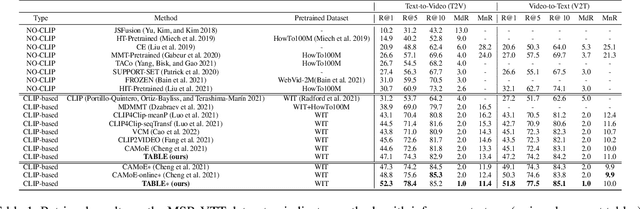
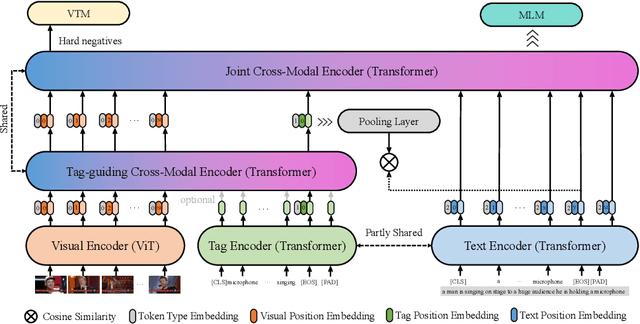
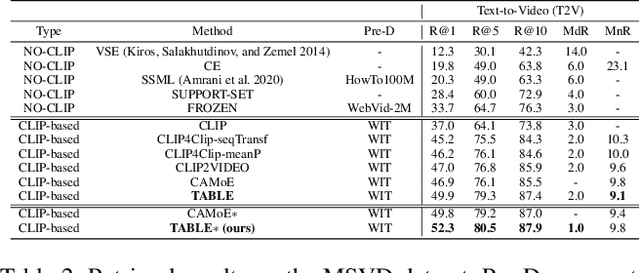
Abstract:Vision-language alignment learning for video-text retrieval arouses a lot of attention in recent years. Most of the existing methods either transfer the knowledge of image-text pretraining model to video-text retrieval task without fully exploring the multi-modal information of videos, or simply fuse multi-modal features in a brute force manner without explicit guidance. In this paper, we integrate multi-modal information in an explicit manner by tagging, and use the tags as the anchors for better video-text alignment. Various pretrained experts are utilized for extracting the information of multiple modalities, including object, person, motion, audio, etc. To take full advantage of these information, we propose the TABLE (TAgging Before aLignmEnt) network, which consists of a visual encoder, a tag encoder, a text encoder, and a tag-guiding cross-modal encoder for jointly encoding multi-frame visual features and multi-modal tags information. Furthermore, to strengthen the interaction between video and text, we build a joint cross-modal encoder with the triplet input of [vision, tag, text] and perform two additional supervised tasks, Video Text Matching (VTM) and Masked Language Modeling (MLM). Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the TABLE model is capable of achieving State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) performance on various video-text retrieval benchmarks, including MSR-VTT, MSVD, LSMDC and DiDeMo.
Multi-modal Self-supervised Pre-training for Regulatory Genome Across Cell Types
Nov 03, 2021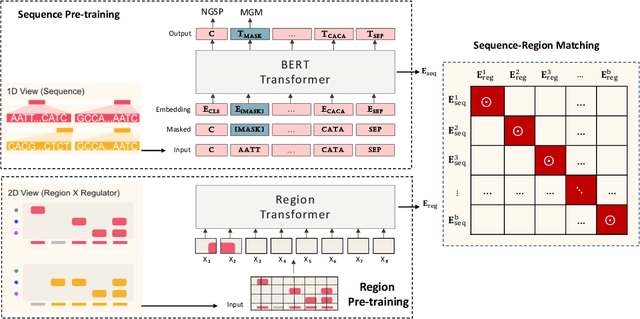
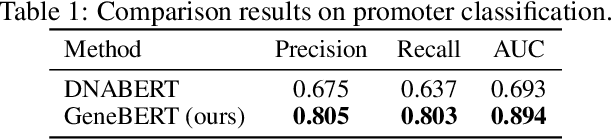
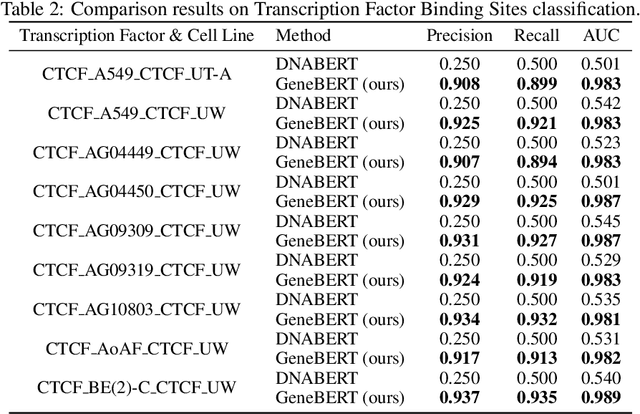
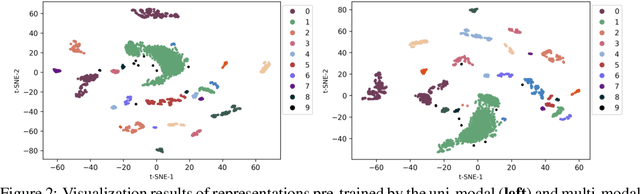
Abstract:In the genome biology research, regulatory genome modeling is an important topic for many regulatory downstream tasks, such as promoter classification, transaction factor binding sites prediction. The core problem is to model how regulatory elements interact with each other and its variability across different cell types. However, current deep learning methods often focus on modeling genome sequences of a fixed set of cell types and do not account for the interaction between multiple regulatory elements, making them only perform well on the cell types in the training set and lack the generalizability required in biological applications. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective approach for pre-training genome data in a multi-modal and self-supervised manner, which we call GeneBERT. Specifically, we simultaneously take the 1d sequence of genome data and a 2d matrix of (transcription factors x regions) as the input, where three pre-training tasks are proposed to improve the robustness and generalizability of our model. We pre-train our model on the ATAC-seq dataset with 17 million genome sequences. We evaluate our GeneBERT on regulatory downstream tasks across different cell types, including promoter classification, transaction factor binding sites prediction, disease risk estimation, and splicing sites prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of multi-modal and self-supervised pre-training for large-scale regulatory genomics data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge