Yiming Ai
Debt Collection Negotiations with Large Language Models: An Evaluation System and Optimizing Decision Making with Multi-Agent
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Debt collection negotiations (DCN) are vital for managing non-performing loans (NPLs) and reducing creditor losses. Traditional methods are labor-intensive, while large language models (LLMs) offer promising automation potential. However, prior systems lacked dynamic negotiation and real-time decision-making capabilities. This paper explores LLMs in automating DCN and proposes a novel evaluation framework with 13 metrics across 4 aspects. Our experiments reveal that LLMs tend to over-concede compared to human negotiators. To address this, we propose the Multi-Agent Debt Negotiation (MADeN) framework, incorporating planning and judging modules to improve decision rationality. We also apply post-training techniques, including DPO with rejection sampling, to optimize performance. Our studies provide valuable insights for practitioners and researchers seeking to enhance efficiency and outcomes in this domain.
Improving Open-Ended Text Generation via Adaptive Decoding
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Current language models decode text token by token according to probabilistic distribution, and determining the appropriate candidates for the next token is crucial to ensure generation quality. This study introduces adaptive decoding, a mechanism that empowers the language models to ascertain a sensible candidate set during the generation process dynamically. Specifically, we introduce an entropy-based metric called confidence and conceptualize determining the optimal candidate set as a confidence-increasing process. The rationality of including a token in the candidate set is assessed by leveraging the increment of confidence, enabling the model to determine the most suitable candidate set adaptively. The experimental results reveal that our method achieves higher MAUVE and diversity in story generation tasks and maintains certain coherence, underscoring its superiority over existing algorithms. The code is available at https://github.com/zwhong714/adaptive_decoding.
Is Cognition and Action Consistent or Not: Investigating Large Language Model's Personality
Feb 22, 2024Abstract:In this study, we investigate the reliability of Large Language Models (LLMs) in professing human-like personality traits through responses to personality questionnaires. Our goal is to evaluate the consistency between LLMs' professed personality inclinations and their actual "behavior", examining the extent to which these models can emulate human-like personality patterns. Through a comprehensive analysis of LLM outputs against established human benchmarks, we seek to understand the cognition-action divergence in LLMs and propose hypotheses for the observed results based on psychological theories and metrics.
TeCS: A Dataset and Benchmark for Tense Consistency of Machine Translation
May 23, 2023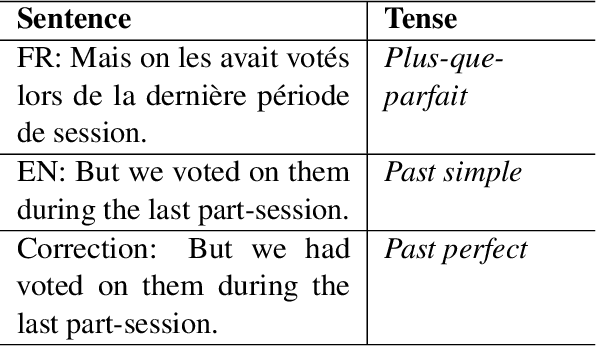
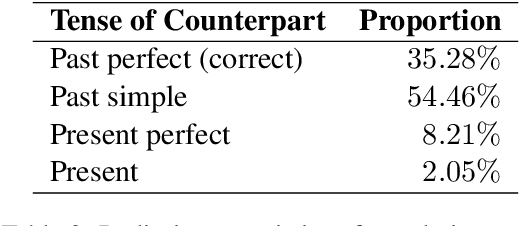
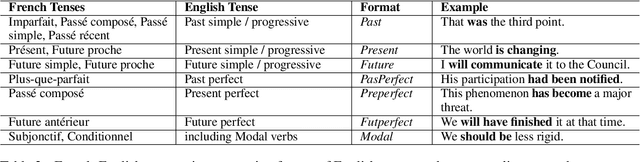
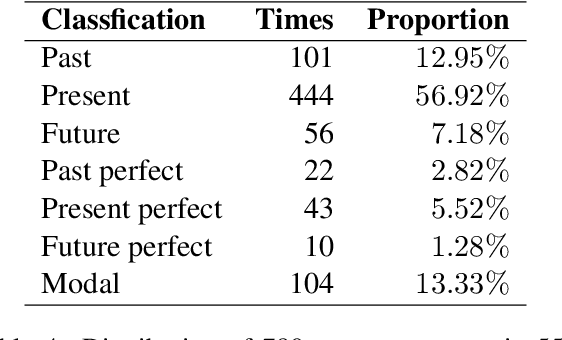
Abstract:Tense inconsistency frequently occurs in machine translation. However, there are few criteria to assess the model's mastery of tense prediction from a linguistic perspective. In this paper, we present a parallel tense test set, containing French-English 552 utterances. We also introduce a corresponding benchmark, tense prediction accuracy. With the tense test set and the benchmark, researchers are able to measure the tense consistency performance of machine translation systems for the first time.
A Convolutional Spiking Network for Gesture Recognition in Brain-Computer Interfaces
Apr 27, 2023Abstract:Brain-computer interfaces are being explored for a wide variety of therapeutic applications. Typically, this involves measuring and analyzing continuous-time electrical brain activity via techniques such as electrocorticogram (ECoG) or electroencephalography (EEG) to drive external devices. However, due to the inherent noise and variability in the measurements, the analysis of these signals is challenging and requires offline processing with significant computational resources. In this paper, we propose a simple yet efficient machine learning-based approach for the exemplary problem of hand gesture classification based on brain signals. We use a hybrid machine learning approach that uses a convolutional spiking neural network employing a bio-inspired event-driven synaptic plasticity rule for unsupervised feature learning of the measured analog signals encoded in the spike domain. We demonstrate that this approach generalizes to different subjects with both EEG and ECoG data and achieves superior accuracy in the range of 92.74-97.07% in identifying different hand gesture classes and motor imagery tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge