Yichun Tai
DefFiller: Mask-Conditioned Diffusion for Salient Steel Surface Defect Generation
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Current saliency-based defect detection methods show promise in industrial settings, but the unpredictability of defects in steel production environments complicates dataset creation, hampering model performance. Existing data augmentation approaches using generative models often require pixel-level annotations, which are time-consuming and resource-intensive. To address this, we introduce DefFiller, a mask-conditioned defect generation method that leverages a layout-to-image diffusion model. DefFiller generates defect samples paired with mask conditions, eliminating the need for pixel-level annotations and enabling direct use in model training. We also develop an evaluation framework to assess the quality of generated samples and their impact on detection performance. Experimental results on the SD-Saliency-900 dataset demonstrate that DefFiller produces high-quality defect images that accurately match the provided mask conditions, significantly enhancing the performance of saliency-based defect detection models trained on the augmented dataset.
Defect Image Sample Generation With Diffusion Prior for Steel Surface Defect Recognition
May 03, 2024
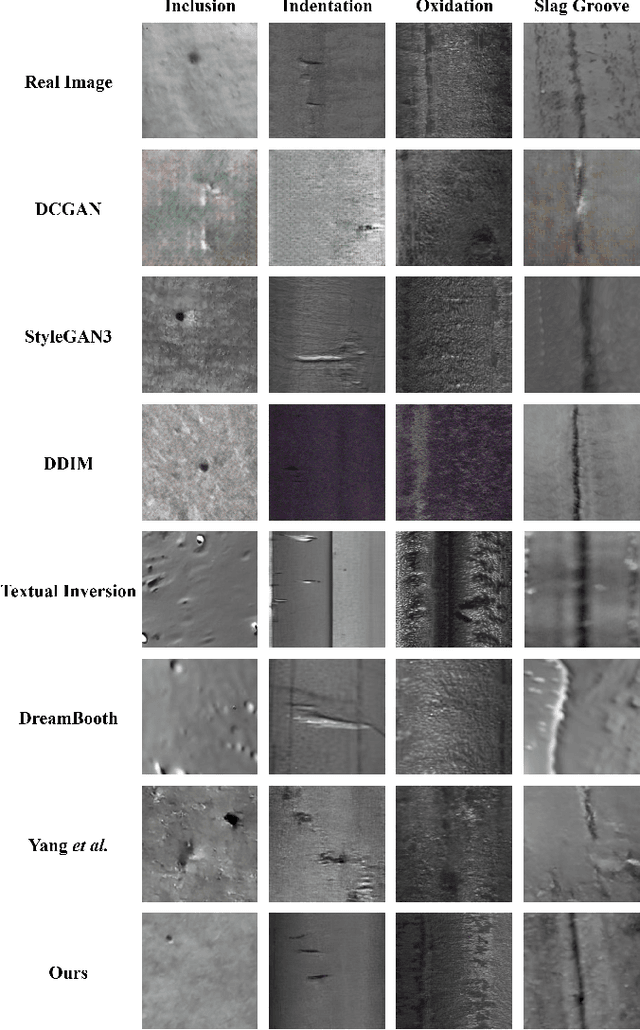


Abstract:The task of steel surface defect recognition is an industrial problem with great industry values. The data insufficiency is the major challenge in training a robust defect recognition network. Existing methods have investigated to enlarge the dataset by generating samples with generative models. However, their generation quality is still limited by the insufficiency of defect image samples. To this end, we propose Stable Surface Defect Generation (StableSDG), which transfers the vast generation distribution embedded in Stable Diffusion model for steel surface defect image generation. To tackle with the distinctive distribution gap between steel surface images and generated images of the diffusion model, we propose two processes. First, we align the distribution by adapting parameters of the diffusion model, adopted both in the token embedding space and network parameter space. Besides, in the generation process, we propose image-oriented generation rather than from pure Gaussian noises. We conduct extensive experiments on steel surface defect dataset, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on generating high-quality samples and training recognition models, and both designed processes are significant for the performance.
BARS: A Benchmark for Airport Runway Segmentation
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Airport runway segmentation can effectively reduce the accident rate during the landing phase, which has the largest risk of flight accidents. With the rapid development of deep learning, related methods have good performance on segmentation tasks and can be well adapted to complex scenes. However, the lack of large-scale, publicly available datasets in this field makes the development of methods based on deep learning difficult. Therefore, we propose a Benchmark for Airport Runway Segmentation, named BARS. Meanwhile, a semi-automatic annotation pipeline is designed to reduce the workload of annotation. BARS has the largest dataset with the richest categories and the only instance annotation in the field. The dataset, which is collected using the X-Plane simulation platform, contains 10,002 images and 29,347 instances with three categories. We evaluate eight representative instance segmentation methods on BARS and analyze their performance. Based on the characteristic of the airport runway with a regular shape, we propose a plug-and-play smoothing post-processing module (SPPM) and a contour point constraint loss (CPCL) function to smooth segmentation results for mask-based and contour-based methods, respectively. Furthermore, a novel evaluation metric named average smoothness (AS) is developed to measure smoothness. The experiments show that existing instance segmentation methods can achieve prediction results with good performance on BARS. SPPM and CPCL can improve the average accuracy by 0.9% and 1.13%, respectively. And the average smoothness enhancements for SPPM and CPCL are more than 50% and 28%, respectively. Our work will be released at https://github.com/c-wenhui/BARS.
Multi-Agent Semi-Siamese Training for Long-tail and Shallow Face Learning
May 10, 2021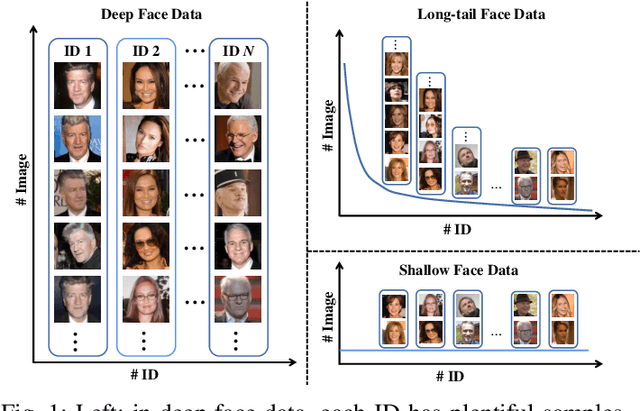
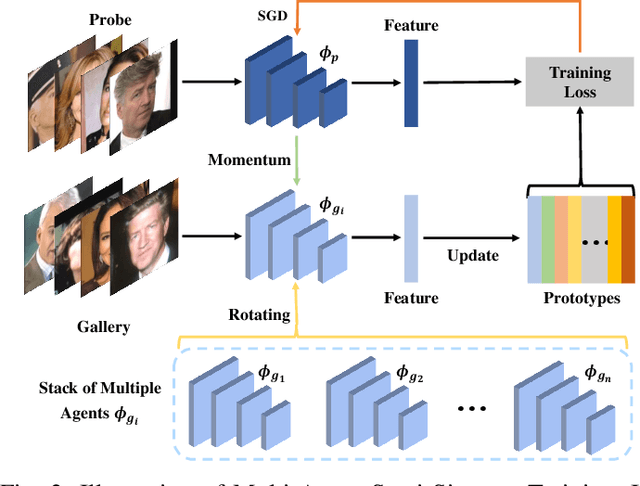
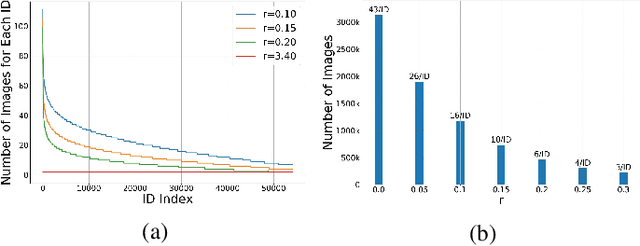
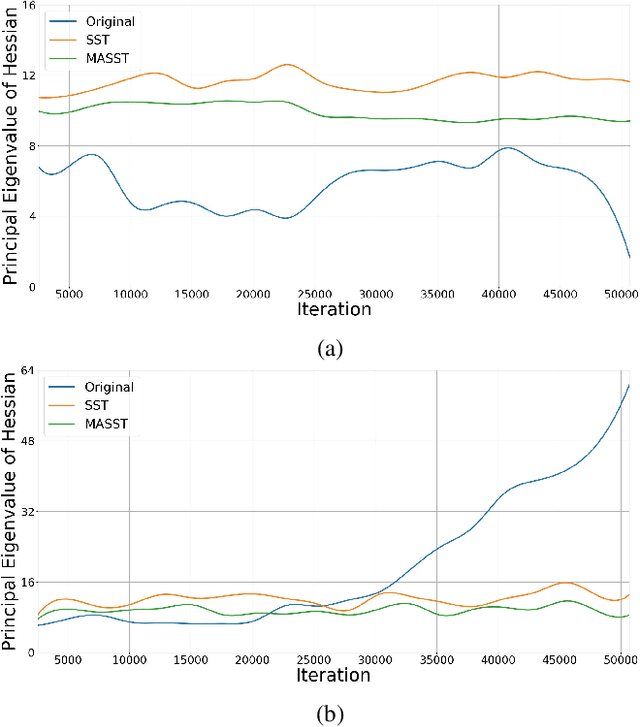
Abstract:With the recent development of deep convolutional neural networks and large-scale datasets, deep face recognition has made remarkable progress and been widely used in various applications. However, unlike the existing public face datasets, in many real-world scenarios of face recognition, the depth of training dataset is shallow, which means only two face images are available for each ID. With the non-uniform increase of samples, such issue is converted to a more general case, a.k.a long-tail face learning, which suffers from data imbalance and intra-class diversity dearth simultaneously. These adverse conditions damage the training and result in the decline of model performance. Based on the Semi-Siamese Training (SST), we introduce an advanced solution, named Multi-Agent Semi-Siamese Training (MASST), to address these problems. MASST includes a probe network and multiple gallery agents, the former aims to encode the probe features, and the latter constitutes a stack of networks that encode the prototypes (gallery features). For each training iteration, the gallery network, which is sequentially rotated from the stack, and the probe network form a pair of semi-siamese networks. We give theoretical and empirical analysis that, given the long-tail (or shallow) data and training loss, MASST smooths the loss landscape and satisfies the Lipschitz continuity with the help of multiple agents and the updating gallery queue. The proposed method is out of extra-dependency, thus can be easily integrated with the existing loss functions and network architectures. It is worth noting that, although multiple gallery agents are employed for training, only the probe network is needed for inference, without increasing the inference cost. Extensive experiments and comparisons demonstrate the advantages of MASST for long-tail and shallow face learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge