Yi Qu
Building-Block Aware Generative Modeling for 3D Crystals of Metal Organic Frameworks
May 13, 2025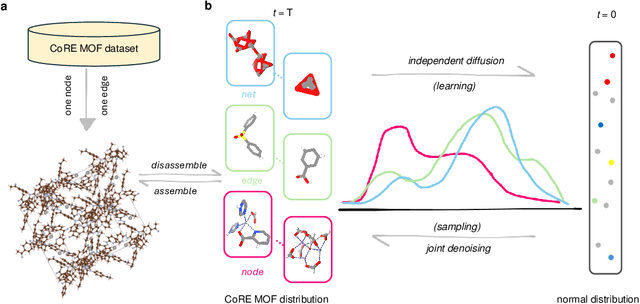
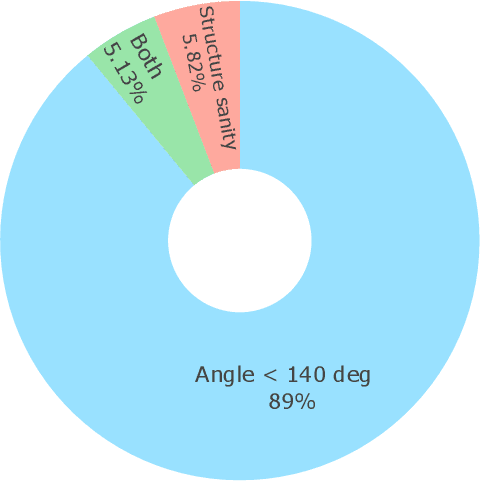
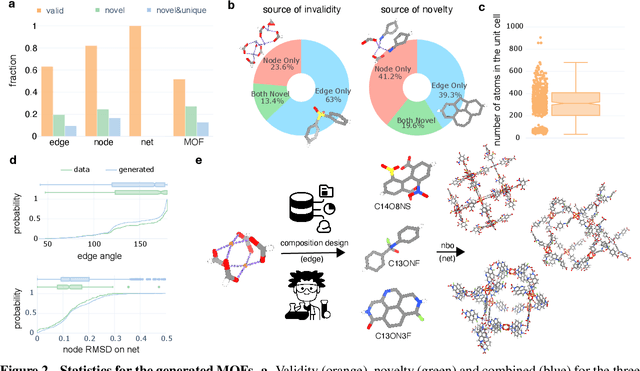
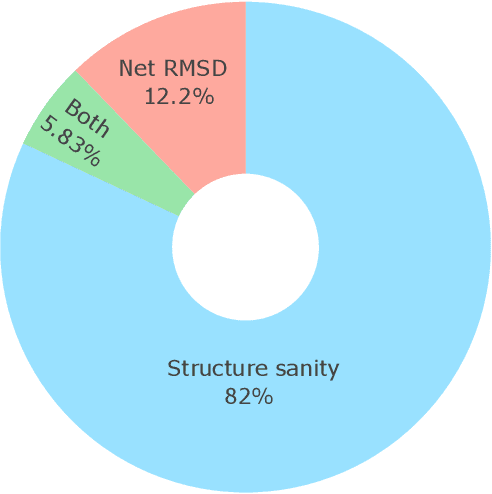
Abstract:Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) marry inorganic nodes, organic edges, and topological nets into programmable porous crystals, yet their astronomical design space defies brute-force synthesis. Generative modeling holds ultimate promise, but existing models either recycle known building blocks or are restricted to small unit cells. We introduce Building-Block-Aware MOF Diffusion (BBA MOF Diffusion), an SE(3)-equivariant diffusion model that learns 3D all-atom representations of individual building blocks, encoding crystallographic topological nets explicitly. Trained on the CoRE-MOF database, BBA MOF Diffusion readily samples MOFs with unit cells containing 1000 atoms with great geometric validity, novelty, and diversity mirroring experimental databases. Its native building-block representation produces unprecedented metal nodes and organic edges, expanding accessible chemical space by orders of magnitude. One high-scoring [Zn(1,4-TDC)(EtOH)2] MOF predicted by the model was synthesized, where powder X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, and N2 sorption confirm its structural fidelity. BBA-Diff thus furnishes a practical pathway to synthesizable and high-performing MOFs.
BatchNorm-based Weakly Supervised Video Anomaly Detection
Nov 26, 2023Abstract:In weakly supervised video anomaly detection (WVAD), where only video-level labels indicating the presence or absence of abnormal events are available, the primary challenge arises from the inherent ambiguity in temporal annotations of abnormal occurrences. Inspired by the statistical insight that temporal features of abnormal events often exhibit outlier characteristics, we propose a novel method, BN-WVAD, which incorporates BatchNorm into WVAD. In the proposed BN-WVAD, we leverage the Divergence of Feature from Mean vector (DFM) of BatchNorm as a reliable abnormality criterion to discern potential abnormal snippets in abnormal videos. The proposed DFM criterion is also discriminative for anomaly recognition and more resilient to label noise, serving as the additional anomaly score to amend the prediction of the anomaly classifier that is susceptible to noisy labels. Moreover, a batch-level selection strategy is devised to filter more abnormal snippets in videos where more abnormal events occur. The proposed BN-WVAD model demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on UCF-Crime with an AUC of 87.24%, and XD-Violence, where AP reaches up to 84.93%. Our code implementation is accessible at https://github.com/cool-xuan/BN-WVAD.
ImbSAM: A Closer Look at Sharpness-Aware Minimization in Class-Imbalanced Recognition
Aug 15, 2023



Abstract:Class imbalance is a common challenge in real-world recognition tasks, where the majority of classes have few samples, also known as tail classes. We address this challenge with the perspective of generalization and empirically find that the promising Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) fails to address generalization issues under the class-imbalanced setting. Through investigating this specific type of task, we identify that its generalization bottleneck primarily lies in the severe overfitting for tail classes with limited training data. To overcome this bottleneck, we leverage class priors to restrict the generalization scope of the class-agnostic SAM and propose a class-aware smoothness optimization algorithm named Imbalanced-SAM (ImbSAM). With the guidance of class priors, our ImbSAM specifically improves generalization targeting tail classes. We also verify the efficacy of ImbSAM on two prototypical applications of class-imbalanced recognition: long-tailed classification and semi-supervised anomaly detection, where our ImbSAM demonstrates remarkable performance improvements for tail classes and anomaly. Our code implementation is available at https://github.com/cool-xuan/Imbalanced_SAM.
AnoOnly: Semi-Supervised Anomaly Detection without Loss on Normal Data
May 30, 2023Abstract:Semi-supervised anomaly detection (SSAD) methods have demonstrated their effectiveness in enhancing unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) by leveraging few-shot but instructive abnormal instances. However, the dominance of homogeneous normal data over anomalies biases the SSAD models against effectively perceiving anomalies. To address this issue and achieve balanced supervision between heavily imbalanced normal and abnormal data, we develop a novel framework called AnoOnly (Anomaly Only). Unlike existing SSAD methods that resort to strict loss supervision, AnoOnly suspends it and introduces a form of weak supervision for normal data. This weak supervision is instantiated through the utilization of batch normalization, which implicitly performs cluster learning on normal data. When integrated into existing SSAD methods, the proposed AnoOnly demonstrates remarkable performance enhancements across various models and datasets, achieving new state-of-the-art performance. Additionally, our AnoOnly is natively robust to label noise when suffering from data contamination. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/cool-xuan/AnoOnly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge