Haojun Jia
Building-Block Aware Generative Modeling for 3D Crystals of Metal Organic Frameworks
May 13, 2025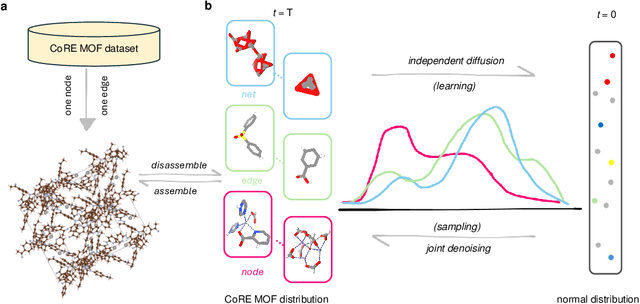
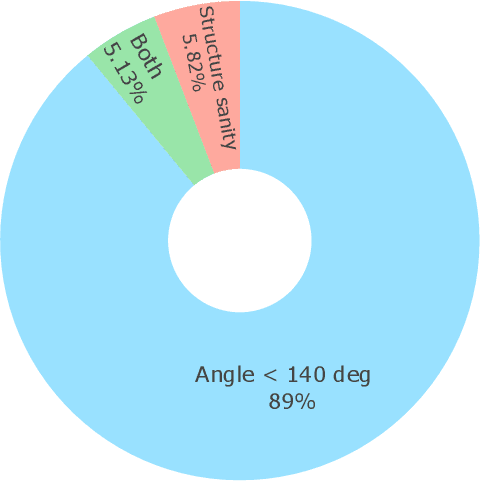
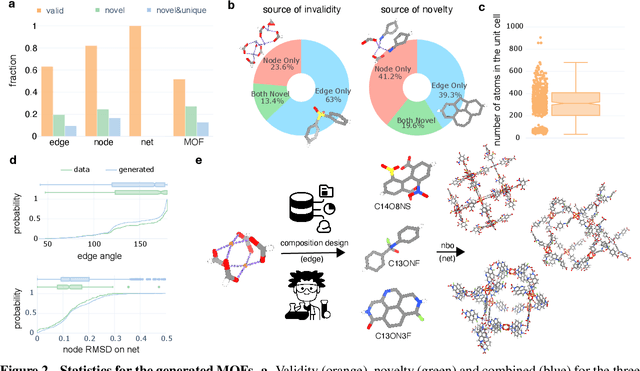
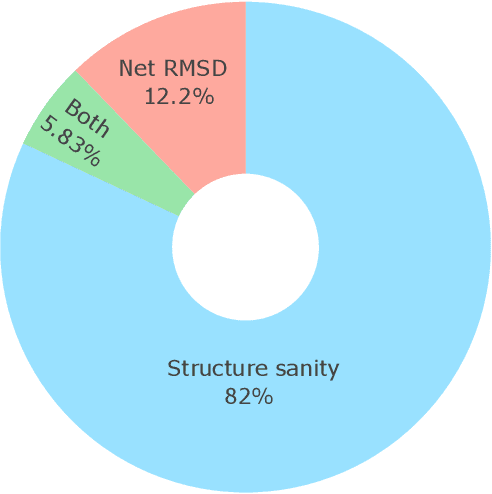
Abstract:Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) marry inorganic nodes, organic edges, and topological nets into programmable porous crystals, yet their astronomical design space defies brute-force synthesis. Generative modeling holds ultimate promise, but existing models either recycle known building blocks or are restricted to small unit cells. We introduce Building-Block-Aware MOF Diffusion (BBA MOF Diffusion), an SE(3)-equivariant diffusion model that learns 3D all-atom representations of individual building blocks, encoding crystallographic topological nets explicitly. Trained on the CoRE-MOF database, BBA MOF Diffusion readily samples MOFs with unit cells containing 1000 atoms with great geometric validity, novelty, and diversity mirroring experimental databases. Its native building-block representation produces unprecedented metal nodes and organic edges, expanding accessible chemical space by orders of magnitude. One high-scoring [Zn(1,4-TDC)(EtOH)2] MOF predicted by the model was synthesized, where powder X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, and N2 sorption confirm its structural fidelity. BBA-Diff thus furnishes a practical pathway to synthesizable and high-performing MOFs.
AlphaNet: Scaling Up Local Frame-based Atomistic Foundation Model
Jan 13, 2025
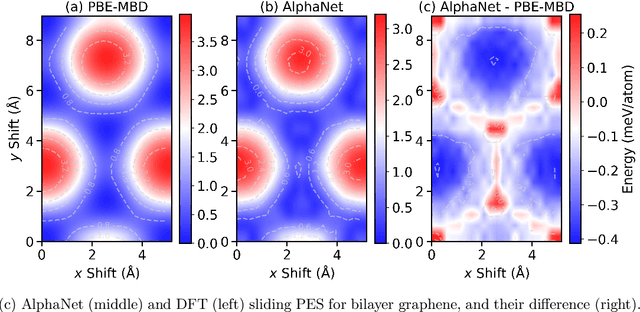
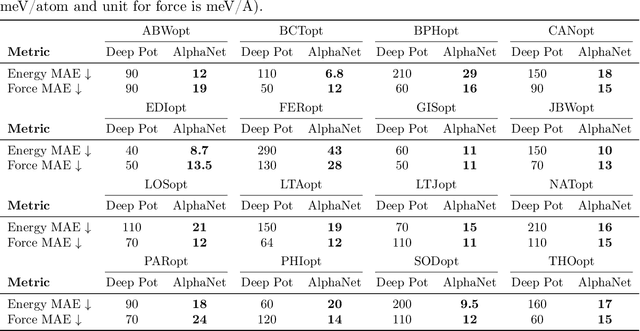
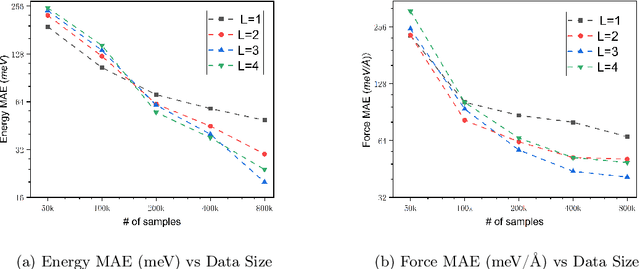
Abstract:We present AlphaNet, a local frame-based equivariant model designed to achieve both accurate and efficient simulations for atomistic systems. Recently, machine learning force fields (MLFFs) have gained prominence in molecular dynamics simulations due to their advantageous efficiency-accuracy balance compared to classical force fields and quantum mechanical calculations, alongside their transferability across various systems. Despite the advancements in improving model accuracy, the efficiency and scalability of MLFFs remain significant obstacles in practical applications. AlphaNet enhances computational efficiency and accuracy by leveraging the local geometric structures of atomic environments through the construction of equivariant local frames and learnable frame transitions. We substantiate the efficacy of AlphaNet across diverse datasets, including defected graphene, formate decomposition, zeolites, and surface reactions. AlphaNet consistently surpasses well-established models, such as NequIP and DeepPot, in terms of both energy and force prediction accuracy. Notably, AlphaNet offers one of the best trade-offs between computational efficiency and accuracy among existing models. Moreover, AlphaNet exhibits scalability across a broad spectrum of system and dataset sizes, affirming its versatility.
Generative Design of Functional Metal Complexes Utilizing the Internal Knowledge of Large Language Models
Oct 21, 2024


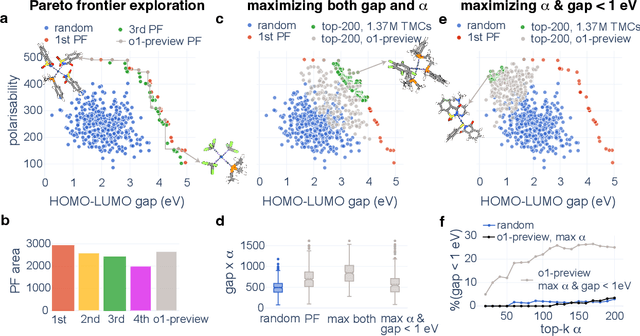
Abstract:Designing functional transition metal complexes (TMCs) faces challenges due to the vast search space of metals and ligands, requiring efficient optimization strategies. Traditional genetic algorithms (GAs) are commonly used, employing random mutations and crossovers driven by explicit mathematical objectives to explore this space. Transferring knowledge between different GA tasks, however, is difficult. We integrate large language models (LLMs) into the evolutionary optimization framework (LLM-EO) and apply it in both single- and multi-objective optimization for TMCs. We find that LLM-EO surpasses traditional GAs by leveraging the chemical knowledge of LLMs gained during their extensive pretraining. Remarkably, without supervised fine-tuning, LLMs utilize the full historical data from optimization processes, outperforming those focusing only on top-performing TMCs. LLM-EO successfully identifies eight of the top-20 TMCs with the largest HOMO-LUMO gaps by proposing only 200 candidates out of a 1.37 million TMCs space. Through prompt engineering using natural language, LLM-EO introduces unparalleled flexibility into multi-objective optimizations, thereby circumventing the necessity for intricate mathematical formulations. As generative models, LLMs can suggest new ligands and TMCs with unique properties by merging both internal knowledge and external chemistry data, thus combining the benefits of efficient optimization and molecular generation. With increasing potential of LLMs as pretrained foundational models and new post-training inference strategies, we foresee broad applications of LLM-based evolutionary optimization in chemistry and materials design.
React-OT: Optimal Transport for Generating Transition State in Chemical Reactions
Apr 20, 2024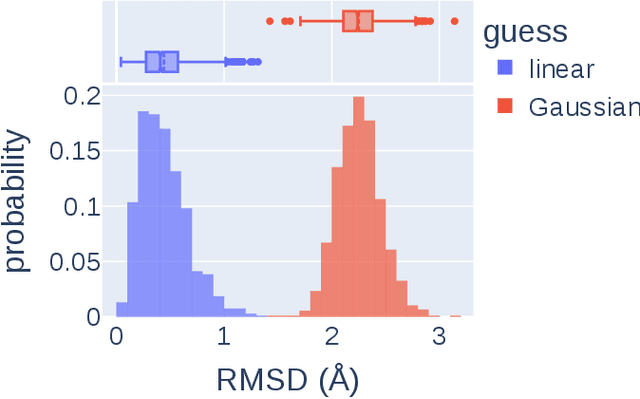
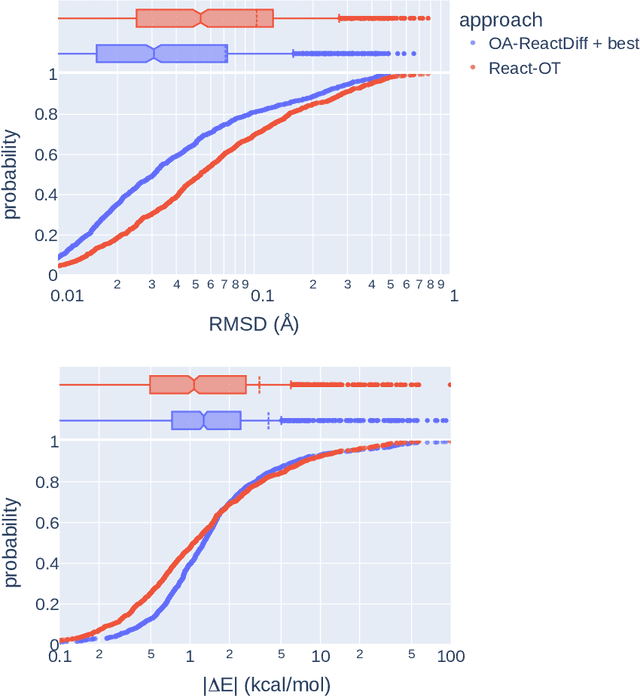
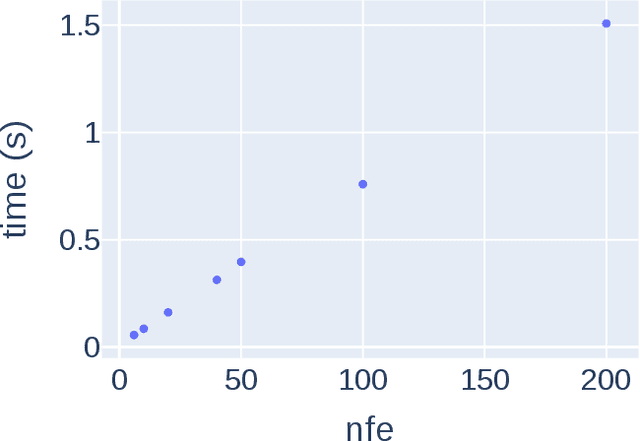
Abstract:Transition states (TSs) are transient structures that are key in understanding reaction mechanisms and designing catalysts but challenging to be captured in experiments. Alternatively, many optimization algorithms have been developed to search for TSs computationally. Yet the cost of these algorithms driven by quantum chemistry methods (usually density functional theory) is still high, posing challenges for their applications in building large reaction networks for reaction exploration. Here we developed React-OT, an optimal transport approach for generating unique TS structures from reactants and products. React-OT generates highly accurate TS structures with a median structural root mean square deviation (RMSD) of 0.053{\AA} and median barrier height error of 1.06 kcal/mol requiring only 0.4 second per reaction. The RMSD and barrier height error is further improved by roughly 25% through pretraining React-OT on a large reaction dataset obtained with a lower level of theory, GFN2-xTB. We envision the great accuracy and fast inference of React-OT useful in targeting TSs when exploring chemical reactions with unknown mechanisms.
Accurate transition state generation with an object-aware equivariant elementary reaction diffusion model
Apr 17, 2023
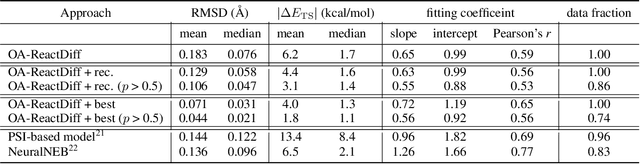
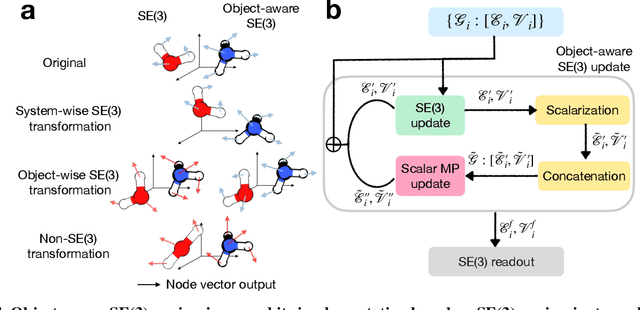
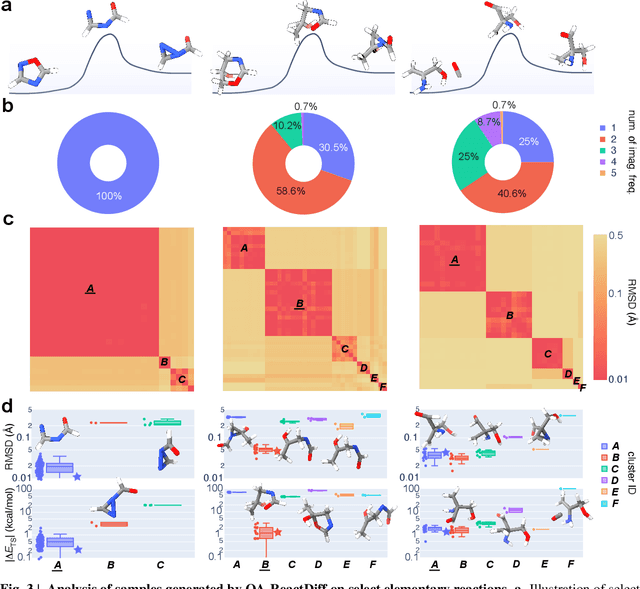
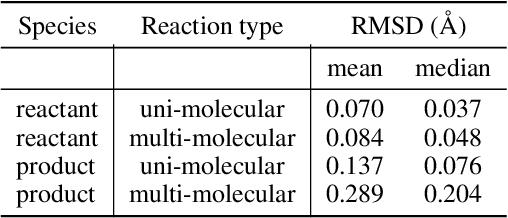
Abstract:Transition state (TS) search is key in chemistry for elucidating reaction mechanisms and exploring reaction networks. The search for accurate 3D TS structures, however, requires numerous computationally intensive quantum chemistry calculations due to the complexity of potential energy surfaces. Here, we developed an object-aware SE(3) equivariant diffusion model that satisfies all physical symmetries and constraints for generating sets of structures - reactant, TS, and product - in an elementary reaction. Provided reactant and product, this model generates a TS structure in seconds instead of hours required when performing quantum chemistry-based optimizations. The generated TS structures achieve a median of 0.08 {\AA} root mean square deviation compared to the true TS. With a confidence scoring model for uncertainty quantification, we approach an accuracy required for reaction rate estimation (2.6 kcal/mol) by only performing quantum chemistry-based optimizations on 14\% of the most challenging reactions. We envision the proposed approach useful in constructing large reaction networks with unknown mechanisms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge