Yavuz Yetim
KernelEvolve: Scaling Agentic Kernel Coding for Heterogeneous AI Accelerators at Meta
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Making deep learning recommendation model (DLRM) training and inference fast and efficient is important. However, this presents three key system challenges - model architecture diversity, kernel primitive diversity, and hardware generation and architecture heterogeneity. This paper presents KernelEvolve-an agentic kernel coding framework-to tackle heterogeneity at-scale for DLRM. KernelEvolve is designed to take kernel specifications as input and automate the process of kernel generation and optimization for recommendation model across heterogeneous hardware architectures. KernelEvolve does so by operating at multiple programming abstractions, from Triton and CuTe DSL to low-level hardware agnostic languages, spanning the full hardware-software optimization stack. The kernel optimization process is described as graph-based search with selection policy, universal operator, fitness function, and termination rule, dynamically adapts to runtime execution context through retrieval-augmented prompt synthesis. We designed, implemented, and deployed KernelEvolve to optimize a wide variety of production recommendation models across generations of NVIDIA and AMD GPUs, as well as Meta's AI accelerators. We validate KernelEvolve on the publicly-available KernelBench suite, achieving 100% pass rate on all 250 problems across three difficulty levels, and 160 PyTorch ATen operators across three heterogeneous hardware platforms, demonstrating 100% correctness. KernelEvolve reduces development time from weeks to hours and achieves substantial performance improvements over PyTorch baselines across diverse production use cases and for heterogeneous AI systems at-scale. Beyond performance efficiency improvements, KernelEvolve significantly mitigates the programmability barrier for new AI hardware by enabling automated kernel generation for in-house developed AI hardware.
External Large Foundation Model: How to Efficiently Serve Trillions of Parameters for Online Ads Recommendation
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Ads recommendation is a prominent service of online advertising systems and has been actively studied. Recent studies indicate that scaling-up and advanced design of the recommendation model can bring significant performance improvement. However, with a larger model scale, such prior studies have a significantly increasing gap from industry as they often neglect two fundamental challenges in industrial-scale applications. First, training and inference budgets are restricted for the model to be served, exceeding which may incur latency and impair user experience. Second, large-volume data arrive in a streaming mode with data distributions dynamically shifting, as new users/ads join and existing users/ads leave the system. We propose the External Large Foundation Model (ExFM) framework to address the overlooked challenges. Specifically, we develop external distillation and a data augmentation system (DAS) to control the computational cost of training/inference while maintaining high performance. We design the teacher in a way like a foundation model (FM) that can serve multiple students as vertical models (VMs) to amortize its building cost. We propose Auxiliary Head and Student Adapter to mitigate the data distribution gap between FM and VMs caused by the streaming data issue. Comprehensive experiments on internal industrial-scale applications and public datasets demonstrate significant performance gain by ExFM.
Understanding Capacity-Driven Scale-Out Neural Recommendation Inference
Nov 11, 2020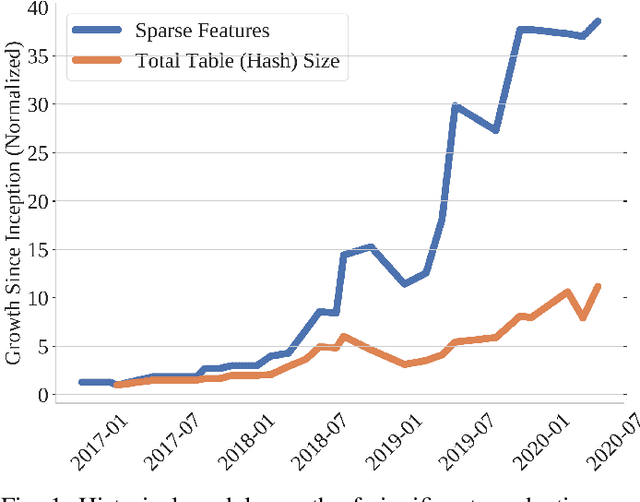
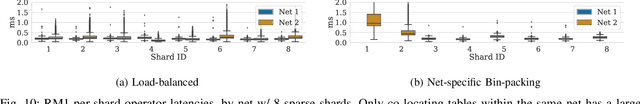
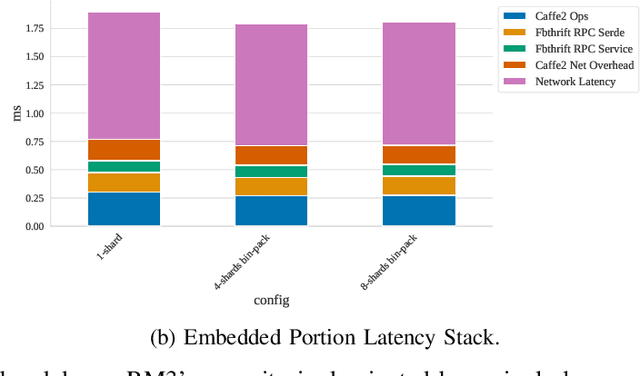
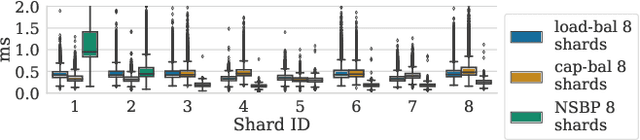
Abstract:Deep learning recommendation models have grown to the terabyte scale. Traditional serving schemes--that load entire models to a single server--are unable to support this scale. One approach to support this scale is with distributed serving, or distributed inference, which divides the memory requirements of a single large model across multiple servers. This work is a first-step for the systems research community to develop novel model-serving solutions, given the huge system design space. Large-scale deep recommender systems are a novel workload and vital to study, as they consume up to 79% of all inference cycles in the data center. To that end, this work describes and characterizes scale-out deep learning recommendation inference using data-center serving infrastructure. This work specifically explores latency-bounded inference systems, compared to the throughput-oriented training systems of other recent works. We find that the latency and compute overheads of distributed inference are largely a result of a model's static embedding table distribution and sparsity of input inference requests. We further evaluate three embedding table mapping strategies of three DLRM-like models and specify challenging design trade-offs in terms of end-to-end latency, compute overhead, and resource efficiency. Overall, we observe only a marginal latency overhead when the data-center scale recommendation models are served with the distributed inference manner--P99 latency is increased by only 1% in the best case configuration. The latency overheads are largely a result of the commodity infrastructure used and the sparsity of embedding tables. Even more encouragingly, we also show how distributed inference can account for efficiency improvements in data-center scale recommendation serving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge