Yanli Zhou
Compositional learning of functions in humans and machines
Mar 18, 2024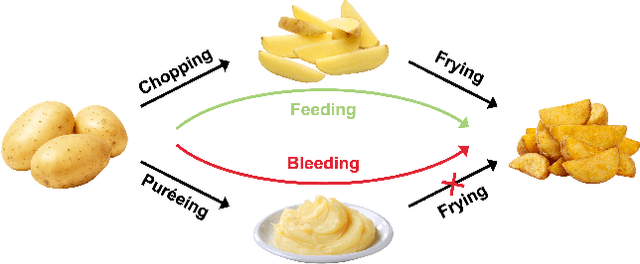
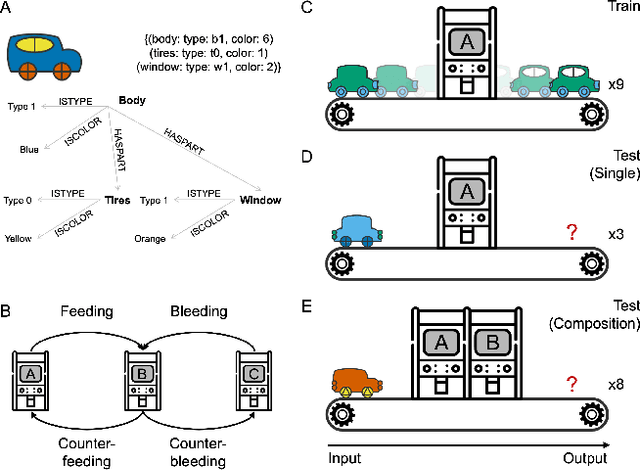
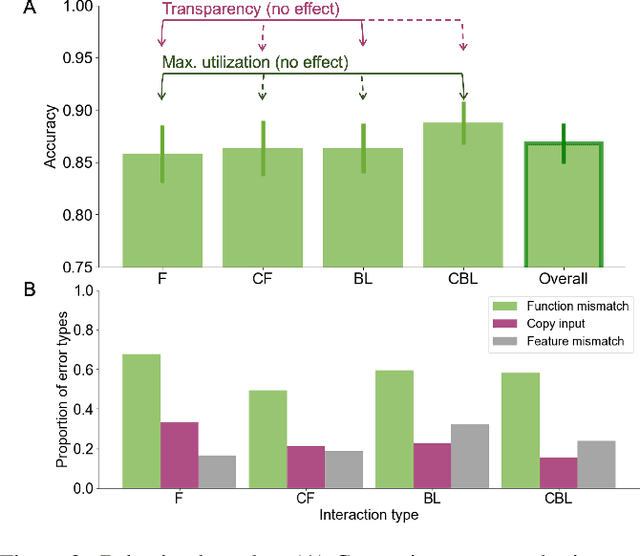
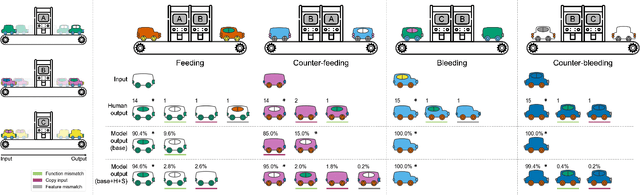
Abstract:The ability to learn and compose functions is foundational to efficient learning and reasoning in humans, enabling flexible generalizations such as creating new dishes from known cooking processes. Beyond sequential chaining of functions, existing linguistics literature indicates that humans can grasp more complex compositions with interacting functions, where output production depends on context changes induced by different function orderings. Extending the investigation into the visual domain, we developed a function learning paradigm to explore the capacity of humans and neural network models in learning and reasoning with compositional functions under varied interaction conditions. Following brief training on individual functions, human participants were assessed on composing two learned functions, in ways covering four main interaction types, including instances in which the application of the first function creates or removes the context for applying the second function. Our findings indicate that humans can make zero-shot generalizations on novel visual function compositions across interaction conditions, demonstrating sensitivity to contextual changes. A comparison with a neural network model on the same task reveals that, through the meta-learning for compositionality (MLC) approach, a standard sequence-to-sequence Transformer can mimic human generalization patterns in composing functions.
Compositional diversity in visual concept learning
May 30, 2023

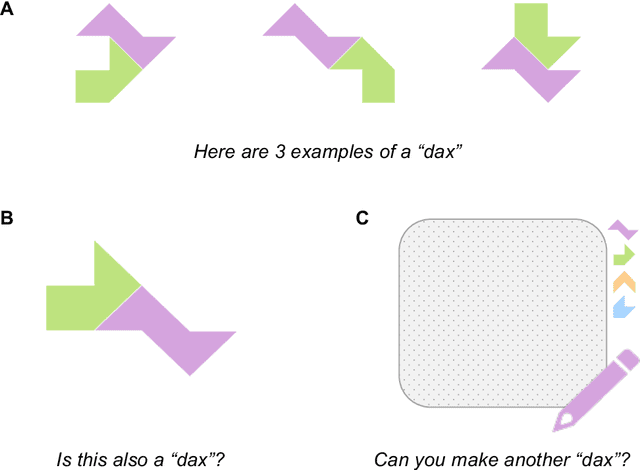

Abstract:Humans leverage compositionality to efficiently learn new concepts, understanding how familiar parts can combine together to form novel objects. In contrast, popular computer vision models struggle to make the same types of inferences, requiring more data and generalizing less flexibly than people do. Here, we study these distinctively human abilities across a range of different types of visual composition, examining how people classify and generate ``alien figures'' with rich relational structure. We also develop a Bayesian program induction model which searches for the best programs for generating the candidate visual figures, utilizing a large program space containing different compositional mechanisms and abstractions. In few shot classification tasks, we find that people and the program induction model can make a range of meaningful compositional generalizations, with the model providing a strong account of the experimental data as well as interpretable parameters that reveal human assumptions about the factors invariant to category membership (here, to rotation and changing part attachment). In few shot generation tasks, both people and the models are able to construct compelling novel examples, with people behaving in additional structured ways beyond the model capabilities, e.g. making choices that complete a set or reconfiguring existing parts in highly novel ways. To capture these additional behavioral patterns, we develop an alternative model based on neuro-symbolic program induction: this model also composes new concepts from existing parts yet, distinctively, it utilizes neural network modules to successfully capture residual statistical structure. Together, our behavioral and computational findings show how people and models can produce a rich variety of compositional behavior when classifying and generating visual objects.
Spatial-temporal V-Net for automatic segmentation and quantification of right ventricles in gated myocardial perfusion SPECT images
Oct 11, 2021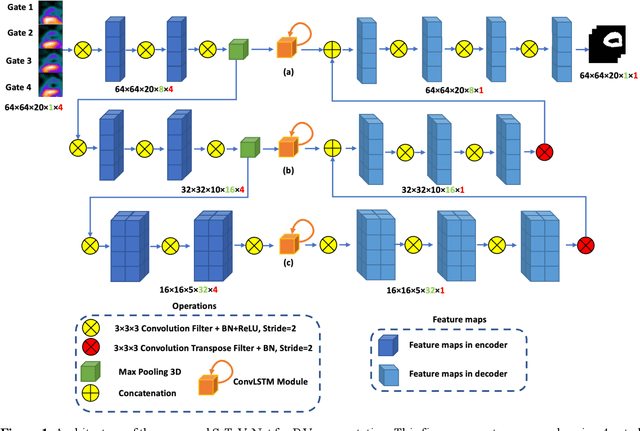
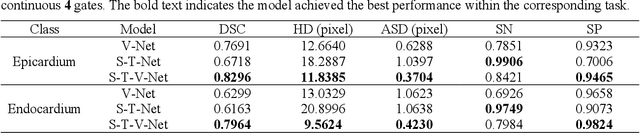
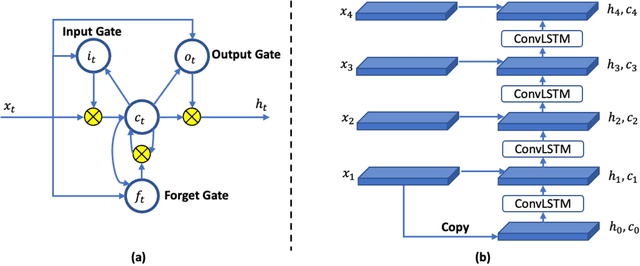
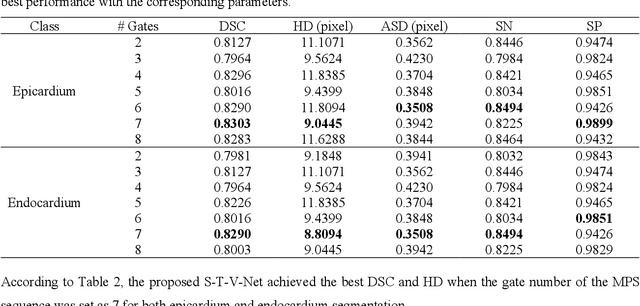
Abstract:Background. Functional assessment of right ventricles (RV) using gated myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (MPS) heavily relies on the precise extraction of right ventricular contours. In this paper, we present a new deep learning model integrating both the spatial and temporal features in SPECT images to perform the segmentation of RV epicardium and endocardium. Methods. By integrating the spatial features from each cardiac frame of gated MPS and the temporal features from the sequential cardiac frames of the gated MPS, we develop a Spatial-Temporal V-Net (S-T-V-Net) for automatic extraction of RV endocardial and epicardial contours. In the S-T-V-Net, a V-Net is employed to hierarchically extract spatial features, and convolutional long-term short-term memory (ConvLSTM) units are added to the skip-connection pathway to extract the temporal features. The input of the S-T-V-Net is an ECG-gated sequence of the SPECT images and the output is the probability map of the endocardial or epicardial masks. A Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) loss which penalizes the discrepancy between the model prediction and the ground truth is adopted to optimize the segmentation model. Results. Our segmentation model was trained and validated on a retrospective dataset with 34 subjects, and the cardiac cycle of each subject was divided into 8 gates. The proposed ST-V-Net achieved a DSC of 0.7924 and 0.8227 for the RV endocardium and epicardium, respectively. The mean absolute error, the mean squared error, and the Pearson correlation coefficient of the RV ejection fraction between the ground truth and the model prediction are 0.0907, 0.0130 and 0.8411. Conclusion. The results demonstrate that the proposed ST-V-Net is an effective model for RV segmentation. It has great promise for clinical use in RV functional assessment.
Flexible Compositional Learning of Structured Visual Concepts
May 20, 2021



Abstract:Humans are highly efficient learners, with the ability to grasp the meaning of a new concept from just a few examples. Unlike popular computer vision systems, humans can flexibly leverage the compositional structure of the visual world, understanding new concepts as combinations of existing concepts. In the current paper, we study how people learn different types of visual compositions, using abstract visual forms with rich relational structure. We find that people can make meaningful compositional generalizations from just a few examples in a variety of scenarios, and we develop a Bayesian program induction model that provides a close fit to the behavioral data. Unlike past work examining special cases of compositionality, our work shows how a single computational approach can account for many distinct types of compositional generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge