Yafei Ou
Experience-Driven Multi-Agent Systems Are Training-free Context-aware Earth Observers
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent advances have enabled large language model (LLM) agents to solve complex tasks by orchestrating external tools. However, these agents often struggle in specialized, tool-intensive domains that demand long-horizon execution, tight coordination across modalities, and strict adherence to implicit tool constraints. Earth Observation (EO) tasks exemplify this challenge due to the multi-modal and multi-temporal data inputs, as well as the requirements of geo-knowledge constraints (spectrum library, spatial reasoning, etc): many high-level plans can be derailed by subtle execution errors that propagate through a pipeline and invalidate final results. A core difficulty is that existing agents lack a mechanism to learn fine-grained, tool-level expertise from interaction. Without such expertise, they cannot reliably configure tool parameters or recover from mid-execution failures, limiting their effectiveness in complex EO workflows. To address this, we introduce \textbf{GeoEvolver}, a self-evolving multi-agent system~(MAS) that enables LLM agents to acquire EO expertise through structured interaction without any parameter updates. GeoEvolver decomposes each query into independent sub-goals via a retrieval-augmented multi-agent orchestrator, then explores diverse tool-parameter configurations at the sub-goal level. Successful patterns and root-cause attribution from failures are then distilled in an evolving memory bank that provides in-context demonstrations for future queries. Experiments on three tool-integrated EO benchmarks show that GeoEvolver consistently improves end-to-end task success, with an average gain of 12\% across multiple LLM backbones, demonstrating that EO expertise can emerge progressively from efficient, fine-grained interactions with the environment.
CRESSim-MPM: A Material Point Method Library for Surgical Soft Body Simulation with Cutting and Suturing
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:A number of recent studies have focused on developing surgical simulation platforms to train machine learning (ML) agents or models with synthetic data for surgical assistance. While existing platforms excel at tasks such as rigid body manipulation and soft body deformation, they struggle to simulate more complex soft body behaviors like cutting and suturing. A key challenge lies in modeling soft body fracture and splitting using the finite-element method (FEM), which is the predominant approach in current platforms. Additionally, the two-way suture needle/thread contact inside a soft body is further complicated when using FEM. In this work, we use the material point method (MPM) for such challenging simulations and propose new rigid geometries and soft-rigid contact methods specifically designed for them. We introduce CRESSim-MPM, a GPU-accelerated MPM library that integrates multiple MPM solvers and incorporates surgical geometries for cutting and suturing, serving as a specialized physics engine for surgical applications. It is further integrated into Unity, requiring minimal modifications to existing projects for soft body simulation. We demonstrate the simulator's capabilities in real-time simulation of cutting and suturing on soft tissue and provide an initial performance evaluation of different MPM solvers when simulating varying numbers of particles.
Layer Separation: Adjustable Joint Space Width Images Synthesis in Conventional Radiography
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation and progressive structural damage. Joint space width (JSW) is a critical indicator in conventional radiography for evaluating disease progression, which has become a prominent research topic in computer-aided diagnostic (CAD) systems. However, deep learning-based radiological CAD systems for JSW analysis face significant challenges in data quality, including data imbalance, limited variety, and annotation difficulties. This work introduced a challenging image synthesis scenario and proposed Layer Separation Networks (LSN) to accurately separate the soft tissue layer, the upper bone layer, and the lower bone layer in conventional radiographs of finger joints. Using these layers, the adjustable JSW images can be synthesized to address data quality challenges and achieve ground truth (GT) generation. Experimental results demonstrated that LSN-based synthetic images closely resemble real radiographs, and significantly enhanced the performance in downstream tasks. The code and dataset will be available.
Learning Autonomous Surgical Irrigation and Suction with the da Vinci Research Kit Using Reinforcement Learning
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:The irrigation-suction process is a common procedure to rinse and clean up the surgical field in minimally invasive surgery (MIS). In this process, surgeons first irrigate liquid, typically saline, into the surgical scene for rinsing and diluting the contaminant, and then suction the liquid out of the surgical field. While recent advances have shown promising results in the application of reinforcement learning (RL) for automating surgical subtasks, fewer studies have explored the automation of fluid-related tasks. In this work, we explore the automation of both steps in the irrigation-suction procedure and train two vision-based RL agents to complete irrigation and suction autonomously. To achieve this, a platform is developed for creating simulated surgical robot learning environments and for training agents, and two simulated learning environments are built for irrigation and suction with visually plausible fluid rendering capabilities. With techniques such as domain randomization (DR) and carefully designed reward functions, two agents are trained in the simulator and transferred to the real world. Individual evaluations of both agents show satisfactory real-world results. With an initial amount of around 5 grams of contaminants, the irrigation agent ultimately achieved an average of 2.21 grams remaining after a manual suction. As a comparison, fully manual operation by a human results in 1.90 grams remaining. The suction agent achieved 2.64 and 2.24 grams of liquid remaining across two trial groups with more than 20 and 30 grams of initial liquid in the container. Fully autonomous irrigation-suction trials reduce the contaminant in the container from around 5 grams to an average of 2.42 grams, although yielding a higher total weight remaining (4.40) due to residual liquid not suctioned. Further information about the project is available at https://tbs-ualberta.github.io/CRESSim/.
BLS-GAN: A Deep Layer Separation Framework for Eliminating Bone Overlap in Conventional Radiographs
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:Conventional radiography is the widely used imaging technology in diagnosing, monitoring, and prognosticating musculoskeletal (MSK) diseases because of its easy availability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. In conventional radiographs, bone overlaps are prevalent, and can impede the accurate assessment of bone characteristics by radiologists or algorithms, posing significant challenges to conventional and computer-aided diagnoses. This work initiated the study of a challenging scenario - bone layer separation in conventional radiographs, in which separate overlapped bone regions enable the independent assessment of the bone characteristics of each bone layer and lay the groundwork for MSK disease diagnosis and its automation. This work proposed a Bone Layer Separation GAN (BLS-GAN) framework that can produce high-quality bone layer images with reasonable bone characteristics and texture. This framework introduced a reconstructor based on conventional radiography imaging principles, which achieved efficient reconstruction and mitigates the recurrent calculations and training instability issues caused by soft tissue in the overlapped regions. Additionally, pre-training with synthetic images was implemented to enhance the stability of both the training process and the results. The generated images passed the visual Turing test, and improved performance in downstream tasks. This work affirms the feasibility of extracting bone layer images from conventional radiographs, which holds promise for leveraging bone layer separation technology to facilitate more comprehensive analytical research in MSK diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis. Code and dataset will be made available.
From Decision to Action in Surgical Autonomy: Multi-Modal Large Language Models for Robot-Assisted Blood Suction
Aug 14, 2024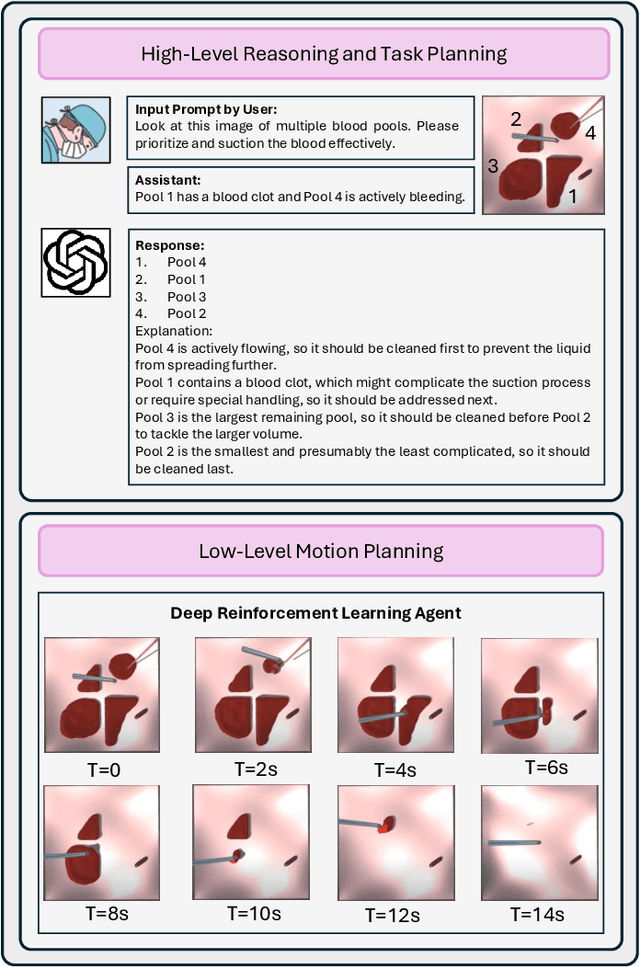
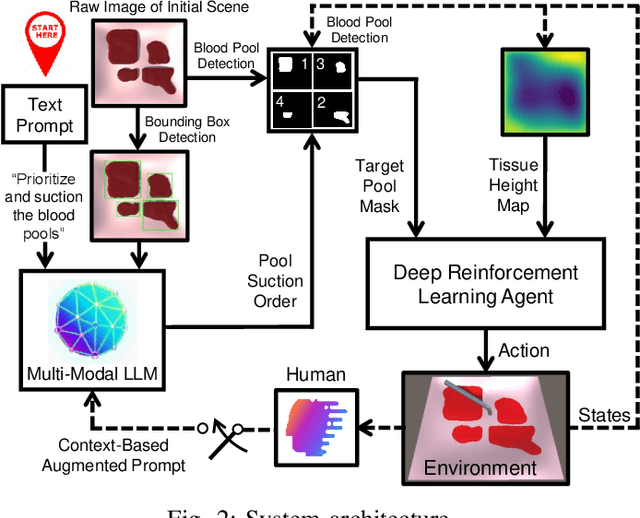
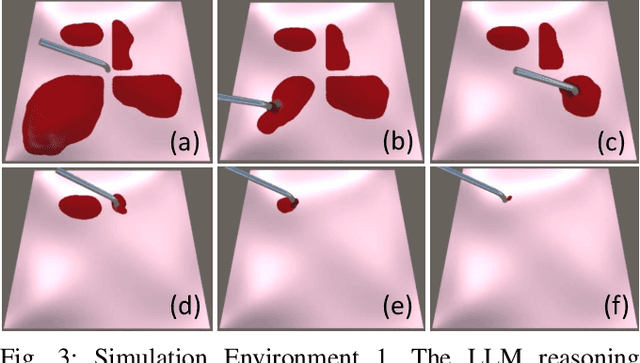

Abstract:The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has impacted research in robotics and automation. While progress has been made in integrating LLMs into general robotics tasks, a noticeable void persists in their adoption in more specific domains such as surgery, where critical factors such as reasoning, explainability, and safety are paramount. Achieving autonomy in robotic surgery, which entails the ability to reason and adapt to changes in the environment, remains a significant challenge. In this work, we propose a multi-modal LLM integration in robot-assisted surgery for autonomous blood suction. The reasoning and prioritization are delegated to the higher-level task-planning LLM, and the motion planning and execution are handled by the lower-level deep reinforcement learning model, creating a distributed agency between the two components. As surgical operations are highly dynamic and may encounter unforeseen circumstances, blood clots and active bleeding were introduced to influence decision-making. Results showed that using a multi-modal LLM as a higher-level reasoning unit can account for these surgical complexities to achieve a level of reasoning previously unattainable in robot-assisted surgeries. These findings demonstrate the potential of multi-modal LLMs to significantly enhance contextual understanding and decision-making in robotic-assisted surgeries, marking a step toward autonomous surgical systems.
Tri-VQA: Triangular Reasoning Medical Visual Question Answering for Multi-Attribute Analysis
Jun 21, 2024



Abstract:The intersection of medical Visual Question Answering (Med-VQA) is a challenging research topic with advantages including patient engagement and clinical expert involvement for second opinions. However, existing Med-VQA methods based on joint embedding fail to explain whether their provided results are based on correct reasoning or coincidental answers, which undermines the credibility of VQA answers. In this paper, we investigate the construction of a more cohesive and stable Med-VQA structure. Motivated by causal effect, we propose a novel Triangular Reasoning VQA (Tri-VQA) framework, which constructs reverse causal questions from the perspective of "Why this answer?" to elucidate the source of the answer and stimulate more reasonable forward reasoning processes. We evaluate our method on the Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) multi-attribute annotated dataset from five centers, and test it on medical VQA datasets. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our approach over existing methods. Our codes and pre-trained models are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Tri_VQA.
MDA: An Interpretable Multi-Modal Fusion with Missing Modalities and Intrinsic Noise
Jun 15, 2024


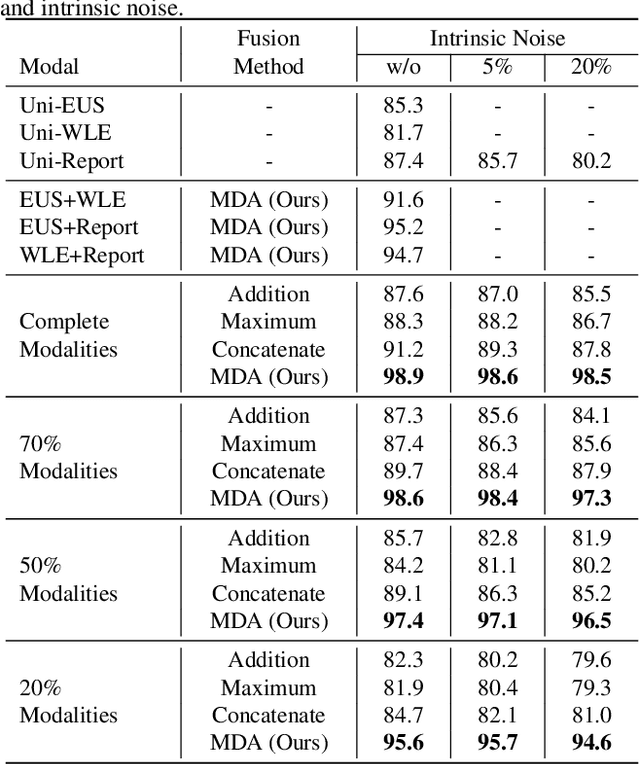
Abstract:Multi-modal fusion is crucial in medical data research, enabling a comprehensive understanding of diseases and improving diagnostic performance by combining diverse modalities. However, multi-modal fusion faces challenges, including capturing interactions between modalities, addressing missing modalities, handling erroneous modal information, and ensuring interpretability. Many existing researchers tend to design different solutions for these problems, often overlooking the commonalities among them. This paper proposes a novel multi-modal fusion framework that achieves adaptive adjustment over the weights of each modality by introducing the Modal-Domain Attention (MDA). It aims to facilitate the fusion of multi-modal information while allowing for the inclusion of missing modalities or intrinsic noise, thereby enhancing the representation of multi-modal data. We provide visualizations of accuracy changes and MDA weights by observing the process of modal fusion, offering a comprehensive analysis of its interpretability. Extensive experiments on various gastrointestinal disease benchmarks, the proposed MDA maintains high accuracy even in the presence of missing modalities and intrinsic noise. One thing worth mentioning is that the visualization of MDA is highly consistent with the conclusions of existing clinical studies on the dependence of different diseases on various modalities. Code and dataset will be made available.
A Realistic Surgical Simulator for Non-Rigid and Contact-Rich Manipulation in Surgeries with the da Vinci Research Kit
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Realistic real-time surgical simulators play an increasingly important role in surgical robotics research, such as surgical robot learning and automation, and surgical skills assessment. Although there are a number of existing surgical simulators for research, they generally lack the ability to simulate the diverse types of objects and contact-rich manipulation tasks typically present in surgeries, such as tissue cutting and blood suction. In this work, we introduce CRESSim, a realistic surgical simulator based on PhysX 5 for the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) that enables simulating various contact-rich surgical tasks involving different surgical instruments, soft tissue, and body fluids. The real-world dVRK console and the master tool manipulator (MTM) robots are incorporated into the system to allow for teleoperation through virtual reality (VR). To showcase the advantages and potentials of the simulator, we present three examples of surgical tasks, including tissue grasping and deformation, blood suction, and tissue cutting. These tasks are performed using the simulated surgical instruments, including the large needle driver, suction irrigator, and curved scissor, through VR-based teleoperation.
Halo Reduction in Display Systems through Smoothed Local Histogram Equalization and Human Visual System Modeling
Feb 09, 2024


Abstract:Halo artifacts significantly impact display quality. We propose a method to reduce halos in Local Histogram Equalization (LHE) algorithms by separately addressing dark and light variants. This approach results in visually natural images by exploring the relationship between lateral inhibition and halo artifacts in the human visual system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge