Xudong Yan
MaxSup: Overcoming Representation Collapse in Label Smoothing
Feb 18, 2025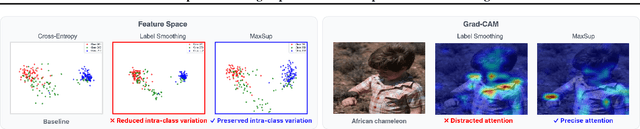
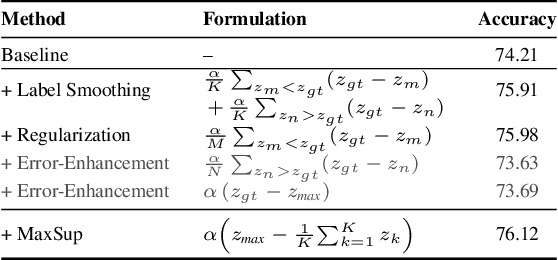
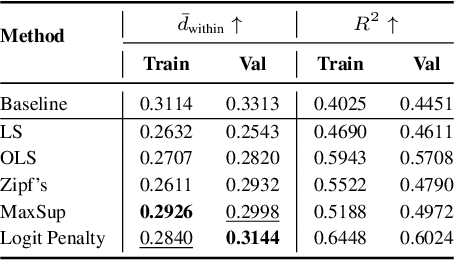
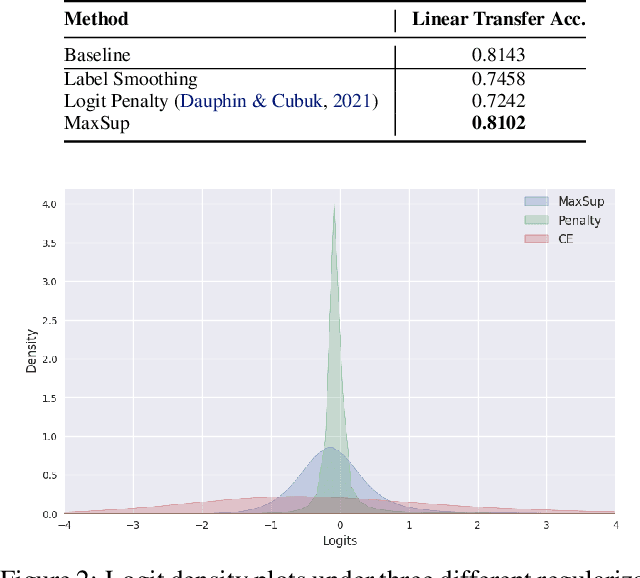
Abstract:Label Smoothing (LS) is widely adopted to curb overconfidence in neural network predictions and enhance generalization. However, previous research shows that LS can force feature representations into excessively tight clusters, eroding intra-class distinctions. More recent findings suggest that LS also induces overconfidence in misclassifications, yet the precise mechanism remained unclear. In this work, we decompose the loss term introduced by LS, revealing two key components: (i) a regularization term that functions only when the prediction is correct, and (ii) an error-enhancement term that emerges under misclassifications. This latter term compels the model to reinforce incorrect predictions with exaggerated certainty, further collapsing the feature space. To address these issues, we propose Max Suppression (MaxSup), which uniformly applies the intended regularization to both correct and incorrect predictions by penalizing the top-1 logit instead of the ground-truth logit. Through feature analyses, we show that MaxSup restores intra-class variation and sharpens inter-class boundaries. Extensive experiments on image classification and downstream tasks confirm that MaxSup is a more robust alternative to LS. Code is available at: https://github.com/ZhouYuxuanYX/Maximum-Suppression-Regularization.
Leveraging MLLM Embeddings and Attribute Smoothing for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:Compositional zero-shot learning (CZSL) aims to recognize novel compositions of attributes and objects learned from seen compositions. Previous works disentangle attribute and object by extracting shared and exclusive parts between image pairs sharing the same attribute (object), as well as aligning them with pretrained word embeddings to improve unseen attribute-object recognition. Despite the significant achievements of existing efforts, they are hampered by three limitations: (1) the efficacy of disentanglement is compromised due to the influence of the background and the intricate entanglement of attribute with object in the same parts. (2) existing word embeddings fail to capture complex multimodal semantic information. (3) overconfidence exhibited by existing models in seen compositions hinders their generalization to novel compositions. Being aware of these, we propose a novel framework named Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) embeddings and attribute smoothing guided disentanglement (TRIDENT) for CZSL. First, we leverage feature adaptive aggregation modules to mitigate the impact of background, and utilize learnable condition masks to capture multigranularity features for disentanglement. Then, the last hidden states of MLLM are employed as word embeddings for their superior representation capabilities. Moreover, we propose attribute smoothing with auxiliary attributes generated by Large Language Model (LLM) for seen compositions, addressing the issue of overconfidence by encouraging the model to learn more attributes in one given composition. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TRIDENT achieves state-of-the-art performance on three benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge