Xinzi He
M^3-GloDets: Multi-Region and Multi-Scale Analysis of Fine-Grained Diseased Glomerular Detection
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Accurate detection of diseased glomeruli is fundamental to progress in renal pathology and underpins the delivery of reliable clinical diagnoses. Although recent advances in computer vision have produced increasingly sophisticated detection algorithms, the majority of research efforts have focused on normal glomeruli or instances of global sclerosis, leaving the wider spectrum of diseased glomerular subtypes comparatively understudied. This disparity is not without consequence; the nuanced and highly variable morphological characteristics that define these disease variants frequently elude even the most advanced computational models. Moreover, ongoing debate surrounds the choice of optimal imaging magnifications and region-of-view dimensions for fine-grained glomerular analysis, adding further complexity to the pursuit of accurate classification and robust segmentation. To bridge these gaps, we present M^3-GloDet, a systematic framework designed to enable thorough evaluation of detection models across a broad continuum of regions, scales, and classes. Within this framework, we evaluate both long-standing benchmark architectures and recently introduced state-of-the-art models that have achieved notable performance, using an experimental design that reflects the diversity of region-of-interest sizes and imaging resolutions encountered in routine digital renal pathology. As the results, we found that intermediate patch sizes offered the best balance between context and efficiency. Additionally, moderate magnifications enhanced generalization by reducing overfitting. Through systematic comparison of these approaches on a multi-class diseased glomerular dataset, our aim is to advance the understanding of model strengths and limitations, and to offer actionable insights for the refinement of automated detection strategies and clinical workflows in the digital pathology domain.
BrainMorph: A Foundational Keypoint Model for Robust and Flexible Brain MRI Registration
May 22, 2024Abstract:We present a keypoint-based foundation model for general purpose brain MRI registration, based on the recently-proposed KeyMorph framework. Our model, called BrainMorph, serves as a tool that supports multi-modal, pairwise, and scalable groupwise registration. BrainMorph is trained on a massive dataset of over 100,000 3D volumes, skull-stripped and non-skull-stripped, from nearly 16,000 unique healthy and diseased subjects. BrainMorph is robust to large misalignments, interpretable via interrogating automatically-extracted keypoints, and enables rapid and controllable generation of many plausible transformations with different alignment types and different degrees of nonlinearity at test-time. We demonstrate the superiority of BrainMorph in solving 3D rigid, affine, and nonlinear registration on a variety of multi-modal brain MRI scans of healthy and diseased subjects, in both the pairwise and groupwise setting. In particular, we show registration accuracy and speeds that surpass current state-of-the-art methods, especially in the context of large initial misalignments and large group settings. All code and models are available at https://github.com/alanqrwang/brainmorph.
Neural Pre-Processing: A Learning Framework for End-to-end Brain MRI Pre-processing
Mar 21, 2023



Abstract:Head MRI pre-processing involves converting raw images to an intensity-normalized, skull-stripped brain in a standard coordinate space. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end weakly supervised learning approach, called Neural Pre-processing (NPP), for solving all three sub-tasks simultaneously via a neural network, trained on a large dataset without individual sub-task supervision. Because the overall objective is highly under-constrained, we explicitly disentangle geometric-preserving intensity mapping (skull-stripping and intensity normalization) and spatial transformation (spatial normalization). Quantitative results show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art methods which tackle only a single sub-task. Our ablation experiments demonstrate the importance of the architecture design we chose for NPP. Furthermore, NPP affords the user the flexibility to control each of these tasks at inference time. The code and model are freely-available at \url{https://github.com/Novestars/Neural-Pre-processing}.
Recursive Refinement Network for Deformable Lung Registration between Exhale and Inhale CT Scans
Jun 14, 2021
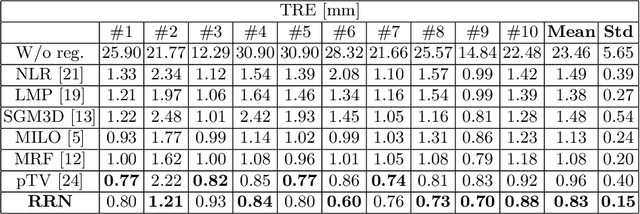
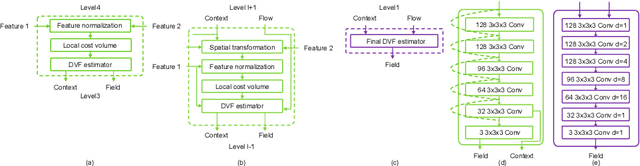
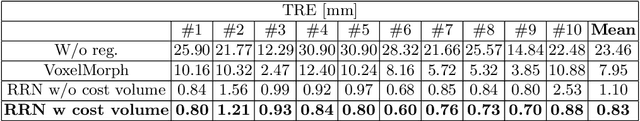
Abstract:Unsupervised learning-based medical image registration approaches have witnessed rapid development in recent years. We propose to revisit a commonly ignored while simple and well-established principle: recursive refinement of deformation vector fields across scales. We introduce a recursive refinement network (RRN) for unsupervised medical image registration, to extract multi-scale features, construct normalized local cost correlation volume and recursively refine volumetric deformation vector fields. RRN achieves state of the art performance for 3D registration of expiratory-inspiratory pairs of CT lung scans. On DirLab COPDGene dataset, RRN returns an average Target Registration Error (TRE) of 0.83 mm, which corresponds to a 13% error reduction from the best result presented in the leaderboard. In addition to comparison with conventional methods, RRN leads to 89% error reduction compared to deep-learning-based peer approaches.
PTNet: A High-Resolution Infant MRI Synthesizer Based on Transformer
May 28, 2021
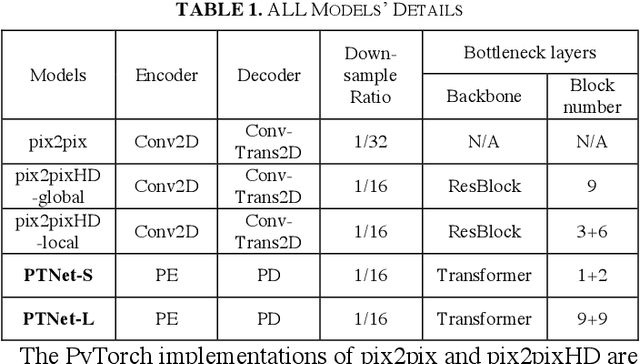
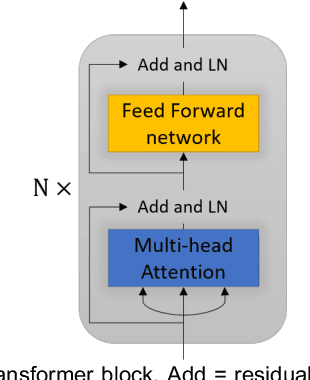
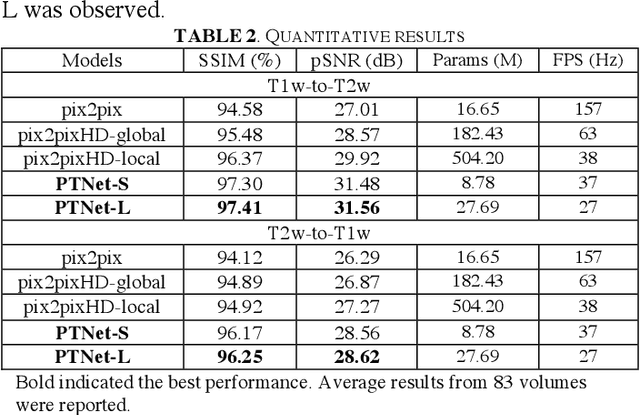
Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) noninvasively provides critical information about how human brain structures develop across stages of life. Developmental scientists are particularly interested in the first few years of neurodevelopment. Despite the success of MRI collection and analysis for adults, it is a challenge for researchers to collect high-quality multimodal MRIs from developing infants mainly because of their irregular sleep pattern, limited attention, inability to follow instructions to stay still, and a lack of analysis approaches. These challenges often lead to a significant reduction of usable data. To address this issue, researchers have explored various solutions to replace corrupted scans through synthesizing realistic MRIs. Among them, the convolution neural network (CNN) based generative adversarial network has demonstrated promising results and achieves state-of-the-art performance. However, adversarial training is unstable and may need careful tuning of regularization terms to stabilize the training. In this study, we introduced a novel MRI synthesis framework - Pyramid Transformer Net (PTNet). PTNet consists of transformer layers, skip-connections, and multi-scale pyramid representation. Compared with the most widely used CNN-based conditional GAN models (namely pix2pix and pix2pixHD), our model PTNet shows superior performance in terms of synthesis accuracy and model size. Notably, PTNet does not require any type of adversarial training and can be easily trained using the simple mean squared error loss.
SANet:Superpixel Attention Network for Skin Lesion Attributes Detection
Oct 20, 2019



Abstract:The accurate detection of lesion attributes is meaningful for both the computeraid diagnosis system and dermatologists decisions. However, unlike lesion segmentation and melenoma classification, there are few deep learning methods and literatures focusing on this task. Currently, the lesion attribute detection still remains challenging due to the extremely unbalanced class distribution and insufficient samples, as well as large intraclass and low interclass variations. To solve these problems, we propose a deep learning framework named superpixel attention network (SANet). Firstly, we segment input images into small regions and shuffle the obtained regions by the random shuttle mechanism (RSM). Secondly, we apply the SANet to capture discriminative features and reconstruct input images. Specifically, SANet contains two sub modules: superpixel average pooling and superpixel at tention module. We introduce a superpixel average pooling to reformulate the superpixel classification problem as a superpixel segmentation problem and a SAMis utilized to focus on discriminative superpixel regions and feature channels. Finally, we design a novel but effective loss, namely global balancing loss to address the serious data imbalance in ISIC 2018 Task 2 lesion attributes detection dataset. The proposed method achieves quite good performance on the ISIC 2018 Task 2 challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge