Xinyu Nan
AI-Driven Automated Tool for Abdominal CT Body Composition Analysis in Gastrointestinal Cancer Management
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:The incidence of gastrointestinal cancers remains significantly high, particularly in China, emphasizing the importance of accurate prognostic assessments and effective treatment strategies. Research shows a strong correlation between abdominal muscle and fat tissue composition and patient outcomes. However, existing manual methods for analyzing abdominal tissue composition are time-consuming and costly, limiting clinical research scalability. To address these challenges, we developed an AI-driven tool for automated analysis of abdominal CT scans to effectively identify and segment muscle, subcutaneous fat, and visceral fat. Our tool integrates a multi-view localization model and a high-precision 2D nnUNet-based segmentation model, demonstrating a localization accuracy of 90% and a Dice Score Coefficient of 0.967 for segmentation. Furthermore, it features an interactive interface that allows clinicians to refine the segmentation results, ensuring high-quality outcomes effectively. Our tool offers a standardized method for effectively extracting critical abdominal tissues, potentially enhancing the management and treatment for gastrointestinal cancers. The code is available at https://github.com/NanXinyu/AI-Tool4Abdominal-Seg.git}{https://github.com/NanXinyu/AI-Tool4Abdominal-Seg.git.
PropSAM: A Propagation-Based Model for Segmenting Any 3D Objects in Multi-Modal Medical Images
Aug 25, 2024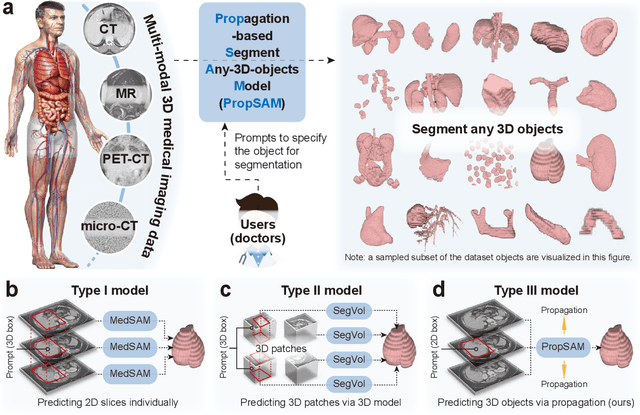
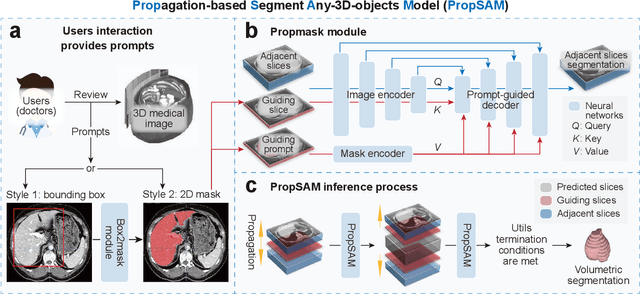
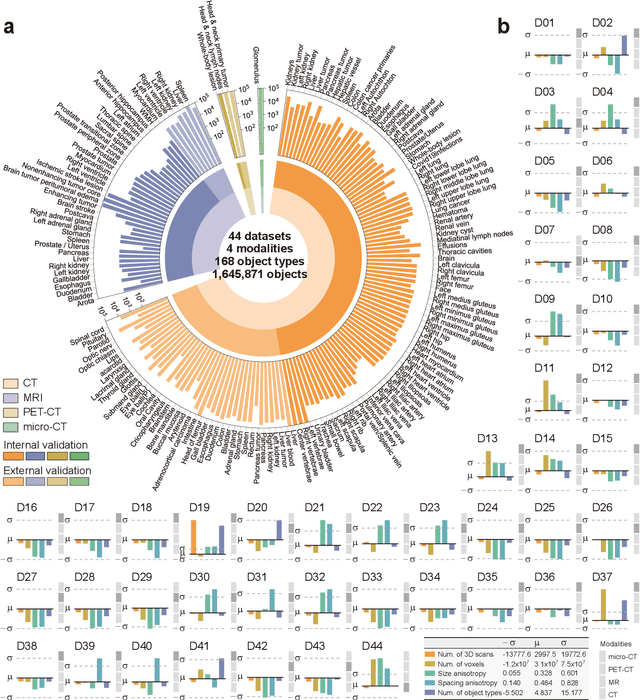
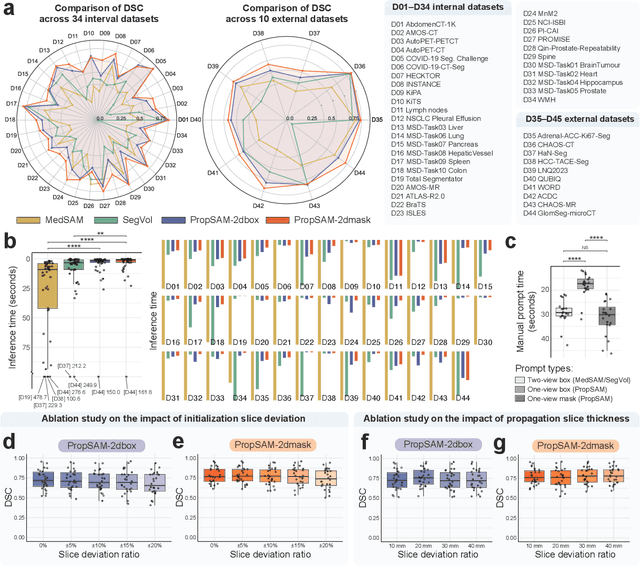
Abstract:Volumetric segmentation is crucial for medical imaging but is often constrained by labor-intensive manual annotations and the need for scenario-specific model training. Furthermore, existing general segmentation models are inefficient due to their design and inferential approaches. Addressing this clinical demand, we introduce PropSAM, a propagation-based segmentation model that optimizes the use of 3D medical structure information. PropSAM integrates a CNN-based UNet for intra-slice processing with a Transformer-based module for inter-slice propagation, focusing on structural and semantic continuities to enhance segmentation across various modalities. Distinctively, PropSAM operates on a one-view prompt, such as a 2D bounding box or sketch mask, unlike conventional models that require two-view prompts. It has demonstrated superior performance, significantly improving the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) across 44 medical datasets and various imaging modalities, outperforming models like MedSAM and SegVol with an average DSC improvement of 18.1%. PropSAM also maintains stable predictions despite prompt deviations and varying propagation configurations, confirmed by one-way ANOVA tests with P>0.5985 and P>0.6131, respectively. Moreover, PropSAM's efficient architecture enables faster inference speeds (Wilcoxon rank-sum test, P<0.001) and reduces user interaction time by 37.8% compared to two-view prompt models. Its ability to handle irregular and complex objects with robust performance further demonstrates its potential in clinical settings, facilitating more automated and reliable medical imaging analyses with minimal retraining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge