Xing Ma
Disentangle Object and Non-object Infrared Features via Language Guidance
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Infrared object detection focuses on identifying and locating objects in complex environments (\eg, dark, snow, and rain) where visible imaging cameras are disabled by poor illumination. However, due to low contrast and weak edge information in infrared images, it is challenging to extract discriminative object features for robust detection. To deal with this issue, we propose a novel vision-language representation learning paradigm for infrared object detection. An additional textual supervision with rich semantic information is explored to guide the disentanglement of object and non-object features. Specifically, we propose a Semantic Feature Alignment (SFA) module to align the object features with the corresponding text features. Furthermore, we develop an Object Feature Disentanglement (OFD) module that disentangles text-aligned object features and non-object features by minimizing their correlation. Finally, the disentangled object features are entered into the detection head. In this manner, the detection performance can be remarkably enhanced via more discriminative and less noisy features. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior performance on two benchmarks: M\textsuperscript{3}FD (83.7\% mAP), FLIR (86.1\% mAP). Our code will be publicly available once the paper is accepted.
Reasoner for Real-World Event Detection: Scaling Reinforcement Learning via Adaptive Perplexity-Aware Sampling Strategy
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Detecting abnormal events in real-world customer service dialogues is highly challenging due to the complexity of business data and the dynamic nature of customer interactions. Moreover, models must demonstrate strong out-of-domain (OOD) generalization to enable rapid adaptation across different business scenarios and maximize commercial value. In this work, we propose a novel Adaptive Perplexity-Aware Reinforcement Learning (APARL) framework that leverages the advanced reasoning capabilities of large language models for abnormal event detection. APARL introduces a dual-loop dynamic curriculum learning architecture, enabling the model to progressively focus on more challenging samples as its proficiency increases. This design effectively addresses performance bottlenecks and significantly enhances OOD transferability. Extensive evaluations on food delivery dialogue tasks show that our model achieves significantly enhanced adaptability and robustness, attaining the highest F1 score with an average improvement of 17.19\%, and an average improvement of 9.59\% in OOD transfer tests. This method provides a superior solution for industrial deployment of anomaly detection models, contributing to improved operational efficiency and commercial benefits.
When to Continue Thinking: Adaptive Thinking Mode Switching for Efficient Reasoning
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) achieve remarkable performance via long reasoning chains, but often incur excessive computational overhead due to redundant reasoning, especially on simple tasks. In this work, we systematically quantify the upper bounds of LRMs under both Long-Thinking and No-Thinking modes, and uncover the phenomenon of "Internal Self-Recovery Mechanism" where models implicitly supplement reasoning during answer generation. Building on this insight, we propose Adaptive Self-Recovery Reasoning (ASRR), a framework that suppresses unnecessary reasoning and enables implicit recovery. By introducing accuracy-aware length reward regulation, ASRR adaptively allocates reasoning effort according to problem difficulty, achieving high efficiency with negligible performance sacrifice. Experiments across multiple benchmarks and models show that, compared with GRPO, ASRR reduces reasoning budget by up to 32.5% (1.5B) and 25.7% (7B) with minimal accuracy loss (1.2% and 0.6% pass@1), and significantly boosts harmless rates on safety benchmarks (up to +21.7%). Our results highlight the potential of ASRR for enabling efficient, adaptive, and safer reasoning in LRMs.
Discovering Customer-Service Dialog System with Semi-Supervised Learning and Coarse-to-Fine Intent Detection
Dec 23, 2022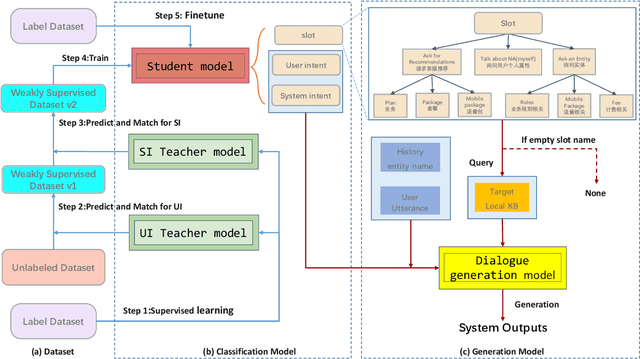
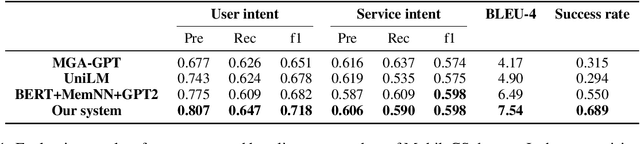
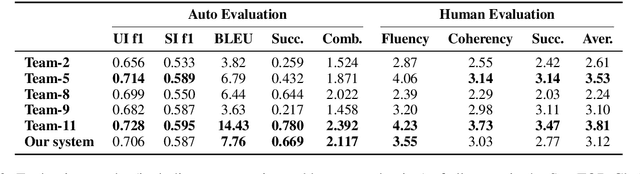
Abstract:Task-oriented dialog(TOD) aims to assist users in achieving specific goals through multi-turn conversation. Recently, good results have been obtained based on large pre-trained models. However, the labeled-data scarcity hinders the efficient development of TOD systems at scale. In this work, we constructed a weakly supervised dataset based on a teacher/student paradigm that leverages a large collection of unlabelled dialogues. Furthermore, we built a modular dialogue system and integrated coarse-to-fine grained classification for user intent detection. Experiments show that our method can reach the dialog goal with a higher success rate and generate more coherent responses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge