Xinchun Yu
Extended k-u Fading Model in mmWave Communication: Statistical Properties and Performance Evaluations
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:This study proposes a small-scale fading model, named the extended k-u model, which incorporates the imbalance of multipath clusters by adding a new parameter based on the original k-u model. The extended k-u model outperforms the k-u model in characterizing small-scale fading in the millimeter-wave (mmWave) band and has more accurate modeling capability than the extended n-u model in scenarios with line-of-sight (LoS) paths. And it is mathematically more tractable than the a-k-n-u model. Experiments are conducted for mmWave communication scenarios with LoS paths, covering the outdoor 28 GHz band, the indoor 65 GHz band, and the indoor 92 GHz band. The results demonstrate that the extended k-u model achieves a smaller mean square error in fitting the measured data compared to both the k-u model and the extended n-u model across all scenarios. In addition, through theoretical derivations, closed-form expressions are obtained for the key statistical characteristics of the extended k-u model, including the probability density function, cumulative distribution function, moments of arbitrary order, and moment generating function. Based on these statistics, this study further derives and analyzes the expressions for some performance metrics of the communication system, including the amount of fading, the probability of outage, and the average bit error rate.
Sample-efficient diffusion-based control of complex nonlinear systems
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Complex nonlinear system control faces challenges in achieving sample-efficient, reliable performance. While diffusion-based methods have demonstrated advantages over classical and reinforcement learning approaches in long-term control performance, they are limited by sample efficiency. This paper presents SEDC (Sample-Efficient Diffusion-based Control), a novel diffusion-based control framework addressing three core challenges: high-dimensional state-action spaces, nonlinear system dynamics, and the gap between non-optimal training data and near-optimal control solutions. Through three innovations - Decoupled State Diffusion, Dual-Mode Decomposition, and Guided Self-finetuning - SEDC achieves 39.5\%-49.4\% better control accuracy than baselines while using only 10\% of the training samples, as validated across three complex nonlinear dynamic systems. Our approach represents a significant advancement in sample-efficient control of complex nonlinear systems. The implementation of the code can be found at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DIFOCON-C019.
UVCG: Leveraging Temporal Consistency for Universal Video Protection
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:The security risks of AI-driven video editing have garnered significant attention. Although recent studies indicate that adding perturbations to images can protect them from malicious edits, directly applying image-based methods to perturb each frame in a video becomes ineffective, as video editing techniques leverage the consistency of inter-frame information to restore individually perturbed content. To address this challenge, we leverage the temporal consistency of video content to propose a straightforward and efficient, yet highly effective and broadly applicable approach, Universal Video Consistency Guard (UVCG). UVCG embeds the content of another video(target video) within a protected video by introducing continuous, imperceptible perturbations which has the ability to force the encoder of editing models to map continuous inputs to misaligned continuous outputs, thereby inhibiting the generation of videos consistent with the intended textual prompts. Additionally leveraging similarity in perturbations between adjacent frames, we improve the computational efficiency of perturbation generation by employing a perturbation-reuse strategy. We applied UVCG across various versions of Latent Diffusion Models (LDM) and assessed its effectiveness and generalizability across multiple LDM-based editing pipelines. The results confirm the effectiveness, transferability, and efficiency of our approach in safeguarding video content from unauthorized modifications.
Knowledge-Guided Prompt Learning for Request Quality Assurance in Public Code Review
Oct 29, 2024

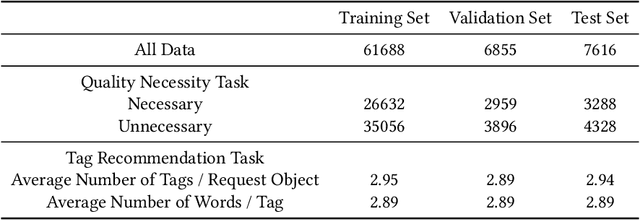
Abstract:Public Code Review (PCR) is an assistant to the internal code review of the development team, in the form of a public Software Question Answering (SQA) community, to help developers access high-quality and efficient review services. Current methods on PCR mainly focus on the reviewer's perspective, including finding a capable reviewer, predicting comment quality, and recommending/generating review comments. However, it is not well studied that how to satisfy the review necessity requests posted by developers which can increase their visibility, which in turn acts as a prerequisite for better review responses. To this end, we propose a Knowledge-guided Prompt learning for Public Code Review (KP-PCR) to achieve developer-based code review request quality assurance (i.e., predicting request necessity and recommending tags subtask). Specifically, we reformulate the two subtasks via 1) text prompt tuning which converts both of them into a Masked Language Model (MLM) by constructing prompt templates using hard prompt; 2) knowledge and code prefix tuning which introduces external knowledge by soft prompt, and uses data flow diagrams to characterize code snippets. Finally, both of the request necessity prediction and tag recommendation subtasks output predicted results through an answer engineering module. In addition, we further analysis the time complexity of our KP-PCR that has lightweight prefix based the operation of introducing knowledge. Experimental results on the PCR dataset for the period 2011-2023 demonstrate that our KP-PCR outperforms baselines by 8.3%-28.8% in the request necessity prediction and by 0.1%-29.5% in the tag recommendation. The code implementation is released at https://github.com/WUT-IDEA/KP-PCR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge