Xiaolong Shen
Controllable 3D Face Generation with Conditional Style Code Diffusion
Jan 11, 2024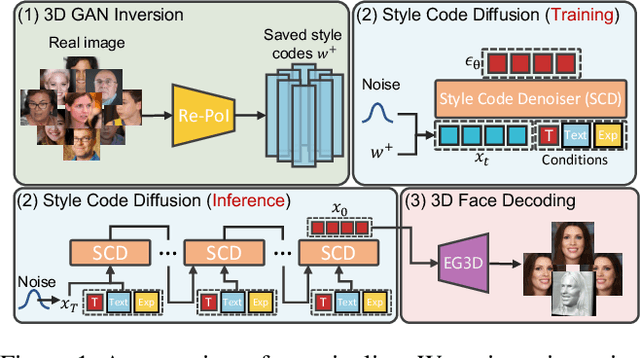


Abstract:Generating photorealistic 3D faces from given conditions is a challenging task. Existing methods often rely on time-consuming one-by-one optimization approaches, which are not efficient for modeling the same distribution content, e.g., faces. Additionally, an ideal controllable 3D face generation model should consider both facial attributes and expressions. Thus we propose a novel approach called TEx-Face(TExt & Expression-to-Face) that addresses these challenges by dividing the task into three components, i.e., 3D GAN Inversion, Conditional Style Code Diffusion, and 3D Face Decoding. For 3D GAN inversion, we introduce two methods which aim to enhance the representation of style codes and alleviate 3D inconsistencies. Furthermore, we design a style code denoiser to incorporate multiple conditions into the style code and propose a data augmentation strategy to address the issue of insufficient paired visual-language data. Extensive experiments conducted on FFHQ, CelebA-HQ, and CelebA-Dialog demonstrate the promising performance of our TEx-Face in achieving the efficient and controllable generation of photorealistic 3D faces. The code will be available at https://github.com/sxl142/TEx-Face.
Global-to-Local Modeling for Video-based 3D Human Pose and Shape Estimation
Mar 26, 2023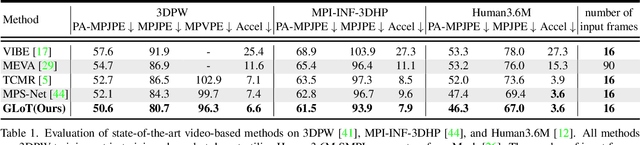
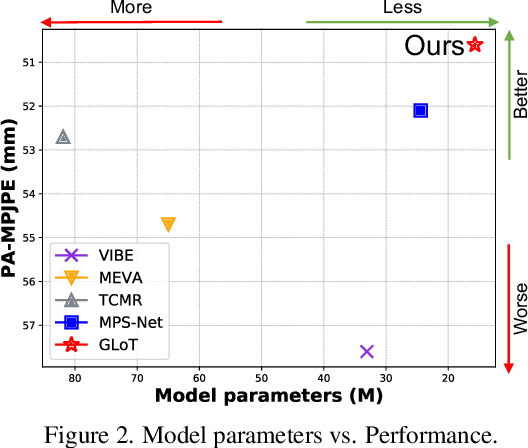
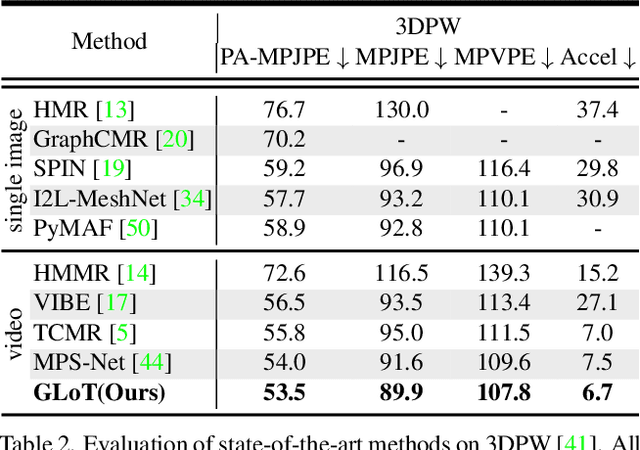

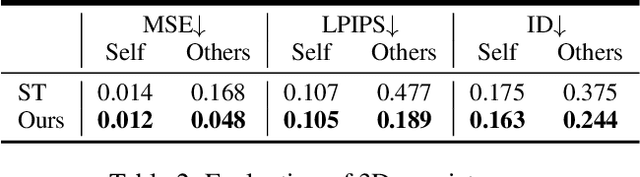
Abstract:Video-based 3D human pose and shape estimations are evaluated by intra-frame accuracy and inter-frame smoothness. Although these two metrics are responsible for different ranges of temporal consistency, existing state-of-the-art methods treat them as a unified problem and use monotonous modeling structures (e.g., RNN or attention-based block) to design their networks. However, using a single kind of modeling structure is difficult to balance the learning of short-term and long-term temporal correlations, and may bias the network to one of them, leading to undesirable predictions like global location shift, temporal inconsistency, and insufficient local details. To solve these problems, we propose to structurally decouple the modeling of long-term and short-term correlations in an end-to-end framework, Global-to-Local Transformer (GLoT). First, a global transformer is introduced with a Masked Pose and Shape Estimation strategy for long-term modeling. The strategy stimulates the global transformer to learn more inter-frame correlations by randomly masking the features of several frames. Second, a local transformer is responsible for exploiting local details on the human mesh and interacting with the global transformer by leveraging cross-attention. Moreover, a Hierarchical Spatial Correlation Regressor is further introduced to refine intra-frame estimations by decoupled global-local representation and implicit kinematic constraints. Our GLoT surpasses previous state-of-the-art methods with the lowest model parameters on popular benchmarks, i.e., 3DPW, MPI-INF-3DHP, and Human3.6M. Codes are available at https://github.com/sxl142/GLoT.
StepNet: Spatial-temporal Part-aware Network for Sign Language Recognition
Dec 25, 2022
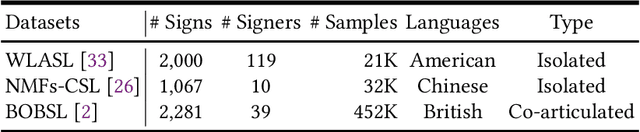

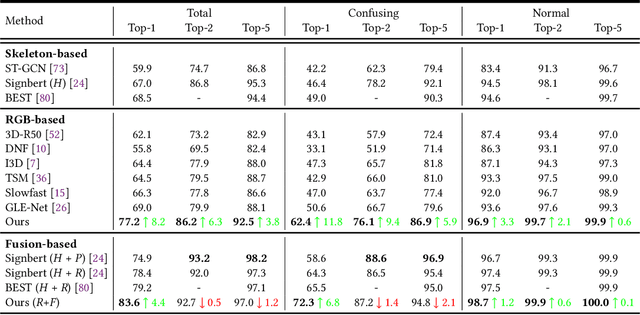
Abstract:Sign language recognition (SLR) aims to overcome the communication barrier for the people with deafness or the people with hard hearing. Most existing approaches can be typically divided into two lines, i.e., Skeleton-based and RGB-based methods, but both the two lines of methods have their limitations. RGB-based approaches usually overlook the fine-grained hand structure, while Skeleton-based methods do not take the facial expression into account. In attempts to address both limitations, we propose a new framework named Spatial-temporal Part-aware network (StepNet), based on RGB parts. As the name implies, StepNet consists of two modules: Part-level Spatial Modeling and Part-level Temporal Modeling. Particularly, without using any keypoint-level annotations, Part-level Spatial Modeling implicitly captures the appearance-based properties, such as hands and faces, in the feature space. On the other hand, Part-level Temporal Modeling captures the pertinent properties over time by implicitly mining the long-short term context. Extensive experiments show that our StepNet, thanks to Spatial-temporal modules, achieves competitive Top-1 Per-instance accuracy on three widely-used SLR benchmarks, i.e., 56.89% on WLASL, 77.2% on NMFs-CSL, and 77.1% on BOBSL. Moreover, the proposed method is compatible with the optical flow input, and can yield higher performance if fused. We hope that this work can serve as a preliminary step for the people with deafness.
Exploring Frame Segmentation Networks for Temporal Action Localization
Feb 14, 2019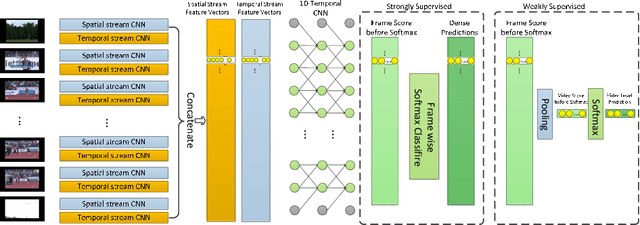
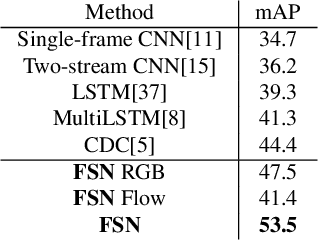
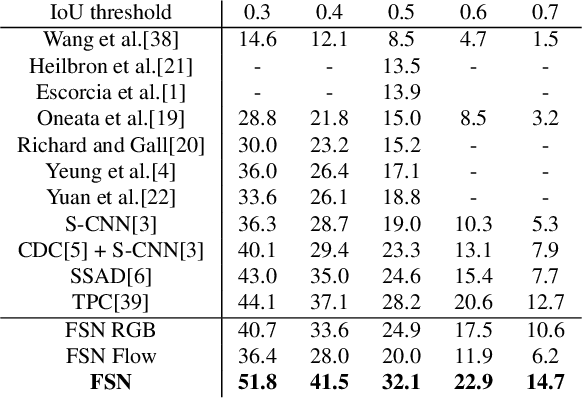
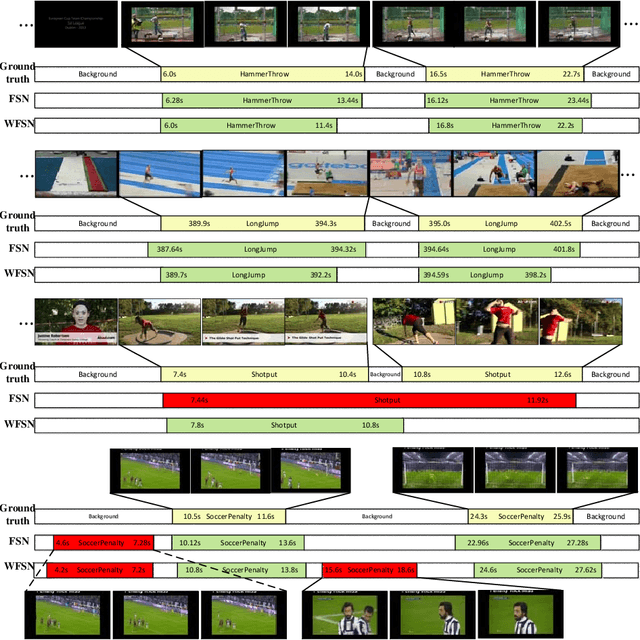
Abstract:Temporal action localization is an important task of computer vision. Though many methods have been proposed, it still remains an open question how to predict the temporal location of action segments precisely. Most state-of-the-art works train action classifiers on video segments pre-determined by action proposal. However, recent work found that a desirable model should move beyond segment-level and make dense predictions at a fine granularity in time to determine precise temporal boundaries. In this paper, we propose a Frame Segmentation Network (FSN) that places a temporal CNN on top of the 2D spatial CNNs. Spatial CNNs are responsible for abstracting semantics in spatial dimension while temporal CNN is responsible for introducing temporal context information and performing dense predictions. The proposed FSN can make dense predictions at frame-level for a video clip using both spatial and temporal context information. FSN is trained in an end-to-end manner, so the model can be optimized in spatial and temporal domain jointly. We also adapt FSN to use it in weakly supervised scenario (WFSN), where only video level labels are provided when training. Experiment results on public dataset show that FSN achieves superior performance in both frame-level action localization and temporal action localization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge