Xiaobin Xu
Evidential Deep Active Learning for Semi-Supervised Classification
May 27, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised classification based on active learning has made significant progress, but the existing methods often ignore the uncertainty estimation (or reliability) of the prediction results during the learning process, which makes it questionable whether the selected samples can effectively update the model. Hence, this paper proposes an evidential deep active learning approach for semi-supervised classification (EDALSSC). EDALSSC builds a semi-supervised learning framework to simultaneously quantify the uncertainty estimation of labeled and unlabeled data during the learning process. The uncertainty estimation of the former is associated with evidential deep learning, while that of the latter is modeled by combining ignorance information and conflict information of the evidence from the perspective of the T-conorm operator. Furthermore, this article constructs a heuristic method to dynamically balance the influence of evidence and the number of classes on uncertainty estimation to ensure that it does not produce counter-intuitive results in EDALSSC. For the sample selection strategy, EDALSSC selects the sample with the greatest uncertainty estimation that is calculated in the form of a sum when the training loss increases in the latter half of the learning process. Experimental results demonstrate that EDALSSC outperforms existing semi-supervised and supervised active learning approaches on image classification datasets.
Adaptive Group Collaborative Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm
Dec 02, 2021
Abstract:As an effective algorithm for solving complex optimization problems, artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm has shown to be competitive, but the same as other population-based algorithms, it is poor at balancing the abilities of global searching in the whole solution space (named as exploration) and quick searching in local solution space which is defined as exploitation. For improving the performance of ABC, an adaptive group collaborative ABC (AgABC) algorithm is introduced where the population in different phases is divided to specific groups and different search strategies with different abilities are assigned to the members in groups, and the member or strategy which obtains the best solution will be employed for further searching. Experimental results on benchmark functions show that the proposed algorithm with dynamic mechanism is superior to other algorithms in searching accuracy and stability. Furthermore, numerical experiments show that the proposed method can generate the optimal solution for the complex scheduling problem.
An improved bearing fault detection strategy based on artificial bee colony algorithm
Dec 02, 2021
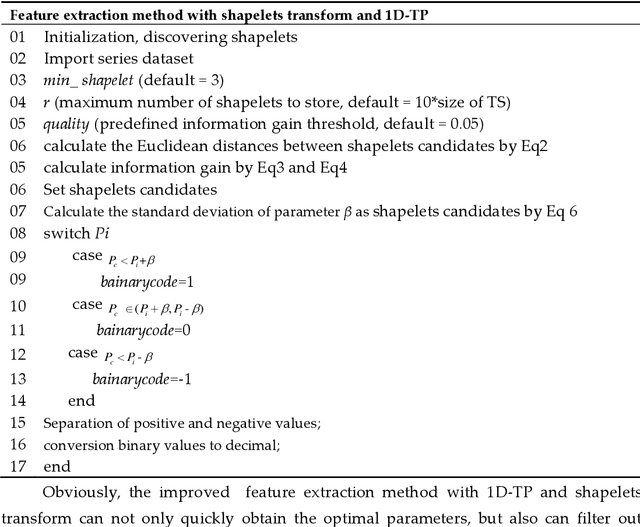


Abstract:The operating state of bearing directly affects the performance of rotating machinery and how to accurately and decisively extract features from the original vibration signal and recognize the faulty parts as early as possible is very critical. In this study, the one-dimensional ternary model which has been proved to be an effective statistical method in feature selection is introduced and shapelets transformation is proposed to calculate the parameter of it which is also the standard deviation of the transformed shaplets that is usually selected by trial and error. Moreover, XGBoost is used to recognize the faults from the obtained features, and an improved artificial bee colony algorithm(ABC) where the evolution is guided by the importance indices of different search space is proposed to optimize the parameters of XGBoost. Here the value of importance index is related to the probability of optimal solutions in certain space, thus the problem of easily falling into local optimality in traditional ABC could be avoided.The experimental results based on the failure vibration signal samples show that the average accuracy of fault signal recognition can reach 97% which is much higher than the ones corresponding to other extraction strategies, thus the ability of extraction could be improved. And with the improved artificial bee colony algorithm which is used to optimize the parameters of XGBoost, the classification accuracy could be improved from 97.02% to about 98.60% compared with the traditional classification strategy
Fine-grained ECG Classification Based on Deep CNN and Online Decision Fusion
Jan 19, 2019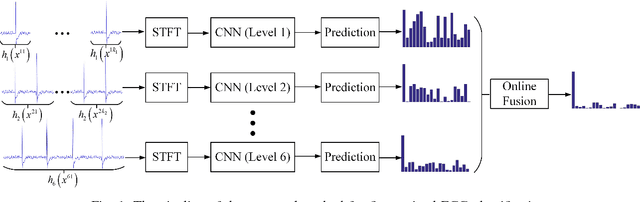

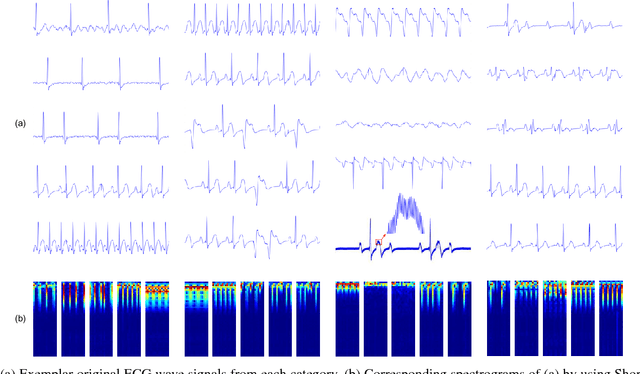
Abstract:Early recognition of abnormal rhythm in ECG signals is crucial for monitoring or diagnosing patients' cardiac conditions and increasing the success rate of the treatment. Classifying abnormal rhythms into fine-grained categories is very challenging due to the the broad taxonomy of rhythms, noises and lack of real-world data and annotations from large number of patients. This paper presents a new ECG classification method based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNN) and online decision fusion. Different from previous methods which utilize hand-crafted features or learn features from the original signal domain, the proposed DCNN based method learns features and classifiers from the time-frequency domain in an end-to-end manner. First, the ECG wave signal is transformed to time-frequency domain by using Short-Time Fourier Transform. Next, specific DCNN models are trained on ECG samples of specific length. Finally, an online decision fusion method is proposed to fuse past and current decisions from different models into a more accurate one. Experimental results on both synthetic and real-world ECG datasets convince the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method.
3D Hand Pose Tracking and Estimation Using Stereo Matching
Oct 23, 2016



Abstract:3D hand pose tracking/estimation will be very important in the next generation of human-computer interaction. Most of the currently available algorithms rely on low-cost active depth sensors. However, these sensors can be easily interfered by other active sources and require relatively high power consumption. As a result, they are currently not suitable for outdoor environments and mobile devices. This paper aims at tracking/estimating hand poses using passive stereo which avoids these limitations. A benchmark with 18,000 stereo image pairs and 18,000 depth images captured from different scenarios and the ground-truth 3D positions of palm and finger joints (obtained from the manual label) is thus proposed. This paper demonstrates that the performance of the state-of-the art tracking/estimation algorithms can be maintained with most stereo matching algorithms on the proposed benchmark, as long as the hand segmentation is correct. As a result, a novel stereo-based hand segmentation algorithm specially designed for hand tracking/estimation is proposed. The quantitative evaluation demonstrates that the proposed algorithm is suitable for the state-of-the-art hand pose tracking/estimation algorithms and the tracking quality is comparable to the use of active depth sensors under different challenging scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge