Xiao-Bo Jin
The Demon is in Ambiguity: Revisiting Situation Recognition with Single Positive Multi-Label Learning
Aug 29, 2025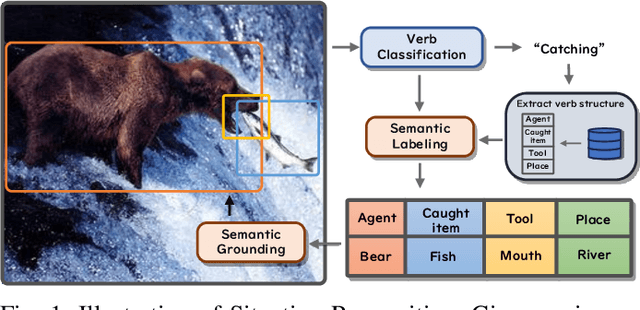
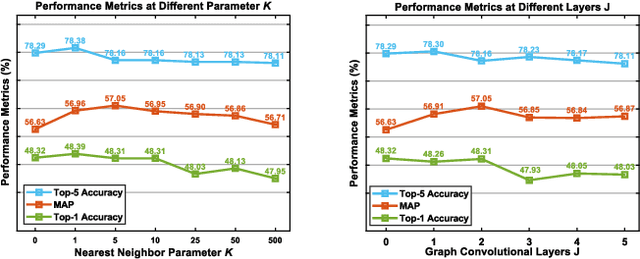
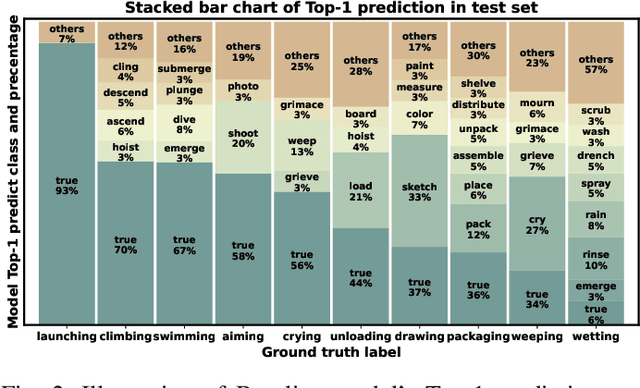
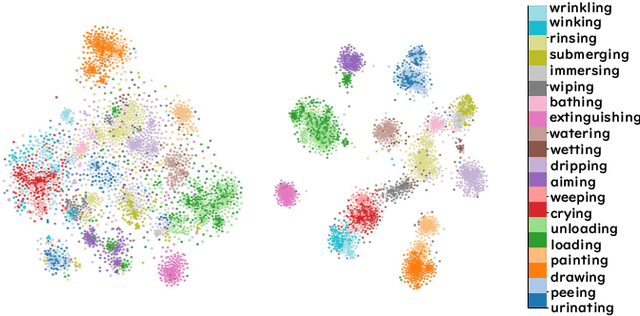
Abstract:Context recognition (SR) is a fundamental task in computer vision that aims to extract structured semantic summaries from images by identifying key events and their associated entities. Specifically, given an input image, the model must first classify the main visual events (verb classification), then identify the participating entities and their semantic roles (semantic role labeling), and finally localize these entities in the image (semantic role localization). Existing methods treat verb classification as a single-label problem, but we show through a comprehensive analysis that this formulation fails to address the inherent ambiguity in visual event recognition, as multiple verb categories may reasonably describe the same image. This paper makes three key contributions: First, we reveal through empirical analysis that verb classification is inherently a multi-label problem due to the ubiquitous semantic overlap between verb categories. Second, given the impracticality of fully annotating large-scale datasets with multiple labels, we propose to reformulate verb classification as a single positive multi-label learning (SPMLL) problem - a novel perspective in SR research. Third, we design a comprehensive multi-label evaluation benchmark for SR that is carefully designed to fairly evaluate model performance in a multi-label setting. To address the challenges of SPMLL, we futher develop the Graph Enhanced Verb Multilayer Perceptron (GE-VerbMLP), which combines graph neural networks to capture label correlations and adversarial training to optimize decision boundaries. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that our approach achieves more than 3\% MAP improvement while remaining competitive on traditional top-1 and top-5 accuracy metrics.
F-SE-LSTM: A Time Series Anomaly Detection Method with Frequency Domain Information
Dec 03, 2024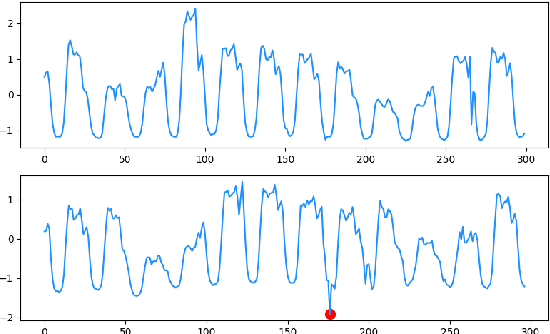
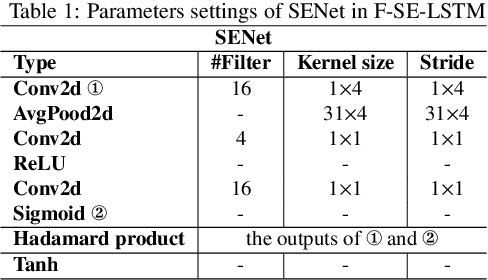
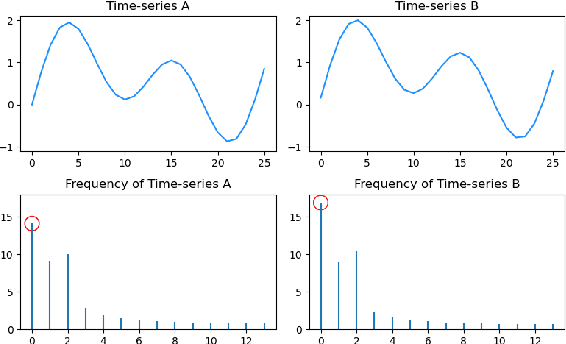
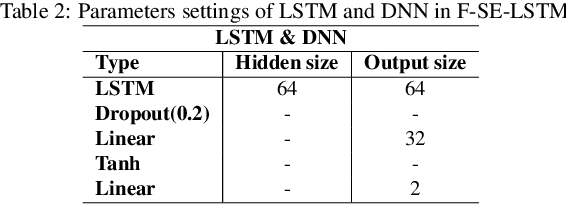
Abstract:With the development of society, time series anomaly detection plays an important role in network and IoT services. However, most existing anomaly detection methods directly analyze time series in the time domain and cannot distinguish some relatively hidden anomaly sequences. We attempt to analyze the impact of frequency on time series from a frequency domain perspective, thus proposing a new time series anomaly detection method called F-SE-LSTM. This method utilizes two sliding windows and fast Fourier transform (FFT) to construct a frequency matrix. Simultaneously, Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks (SENet) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) are employed to extract frequency-related features within and between periods. Through comparative experiments on multiple datasets such as Yahoo Webscope S5 and Numenta Anomaly Benchmark, the results demonstrate that the frequency matrix constructed by F-SE-LSTM exhibits better discriminative ability than ordinary time domain and frequency domain data. Furthermore, F-SE-LSTM outperforms existing state-of-the-art deep learning anomaly detection methods in terms of anomaly detection capability and execution efficiency.
Context Does Matter: End-to-end Panoptic Narrative Grounding with Deformable Attention Refined Matching Network
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:Panoramic Narrative Grounding (PNG) is an emerging visual grounding task that aims to segment visual objects in images based on dense narrative captions. The current state-of-the-art methods first refine the representation of phrase by aggregating the most similar $k$ image pixels, and then match the refined text representations with the pixels of the image feature map to generate segmentation results. However, simply aggregating sampled image features ignores the contextual information, which can lead to phrase-to-pixel mis-match. In this paper, we propose a novel learning framework called Deformable Attention Refined Matching Network (DRMN), whose main idea is to bring deformable attention in the iterative process of feature learning to incorporate essential context information of different scales of pixels. DRMN iteratively re-encodes pixels with the deformable attention network after updating the feature representation of the top-$k$ most similar pixels. As such, DRMN can lead to accurate yet discriminative pixel representations, purify the top-$k$ most similar pixels, and consequently alleviate the phrase-to-pixel mis-match substantially.Experimental results show that our novel design significantly improves the matching results between text phrases and image pixels. Concretely, DRMN achieves new state-of-the-art performance on the PNG benchmark with an average recall improvement 3.5%. The codes are available in: https://github.com/JaMesLiMers/DRMN.
Beyond Attributes: Adversarial Erasing Embedding Network for Zero-shot Learning
Nov 20, 2018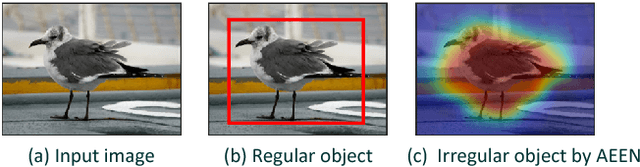
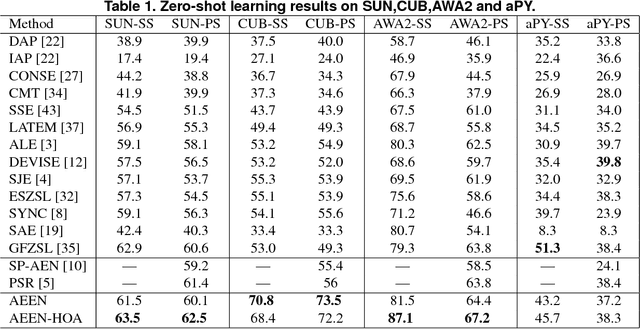
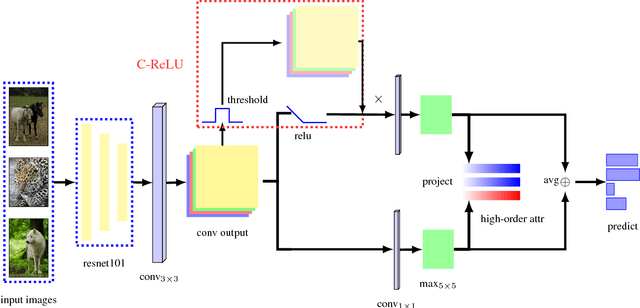
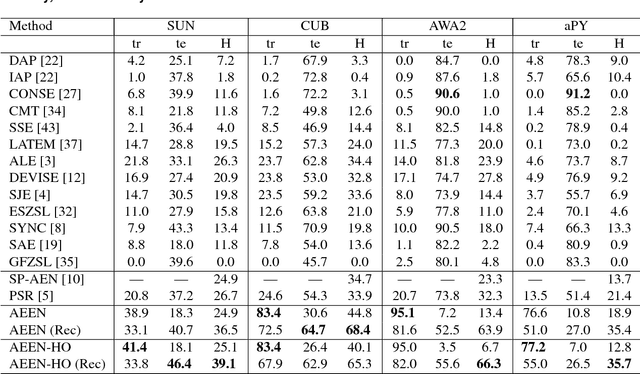
Abstract:In this paper, an adversarial erasing embedding network with the guidance of high-order attributes (AEEN-HOA) is proposed for going further to solve the challenging ZSL/GZSL task. AEEN-HOA consists of two branches, i.e., the upper stream is capable of erasing some initially discovered regions, then the high-order attribute supervision is incorporated to characterize the relationship between the class attributes. Meanwhile, the bottom stream is trained by taking the current background regions to train the same attribute. As far as we know, it is the first time of introducing the erasing operations into the ZSL task. In addition, we first propose a class attribute activation map for the visualization of ZSL output, which shows the relationship between class attribute feature and attention map. Experiments on four standard benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of AEEN-HOA framework.
Stochastic Conjugate Gradient Algorithm with Variance Reduction
Oct 16, 2018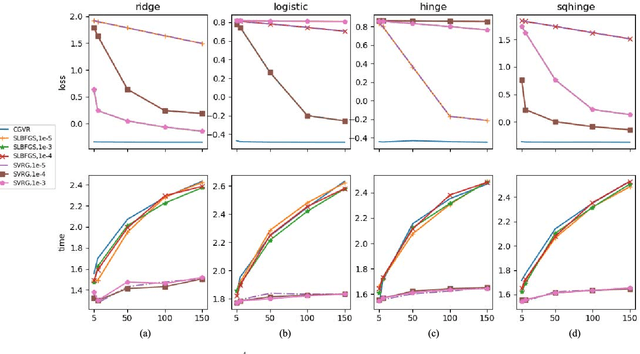
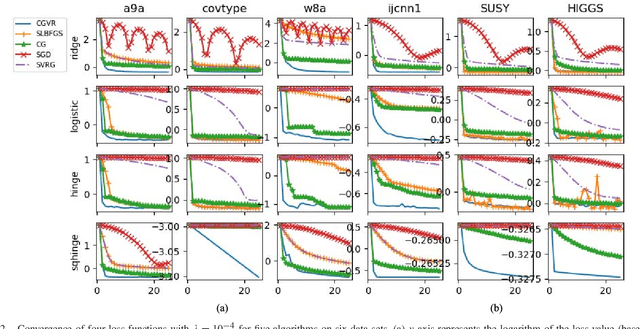
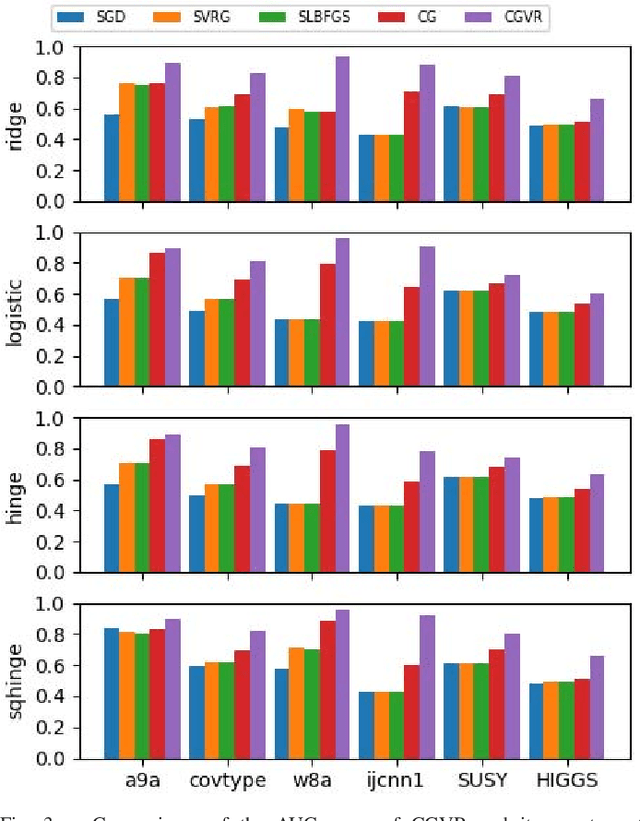
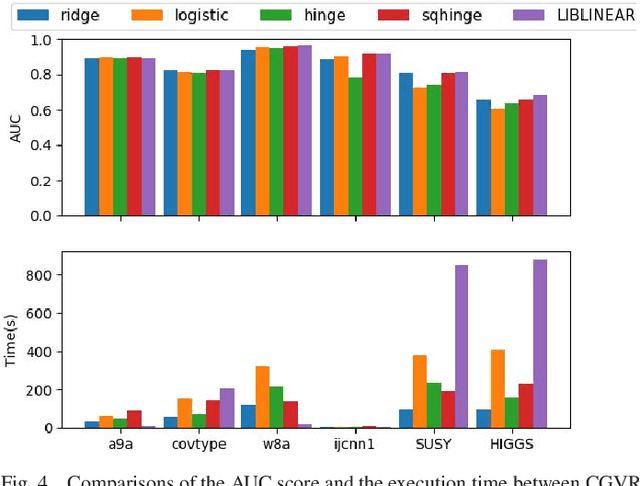
Abstract:Conjugate gradient (CG) methods are a class of important methods for solving linear equations and nonlinear optimization problems. In this paper, we propose a new stochastic CG algorithm with variance reduction and we prove its linear convergence with the Fletcher and Reeves method for strongly convex and smooth functions. We experimentally demonstrate that the CG with variance reduction algorithm converges faster than its counterparts for four learning models, which may be convex, nonconvex or nonsmooth. In addition, its area under the curve performance on six large-scale data sets is comparable to that of the LIBLINEAR solver for the L2-regularized L2-loss but with a significant improvement in computational efficiency
* 10 pages, 4 figures, appeared in IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND LEARNING SYSTEMS, CGVR algorithm is available on github: https://github.com/xbjin/cgvr
Qualitative detection of oil adulteration with machine learning approaches
May 14, 2013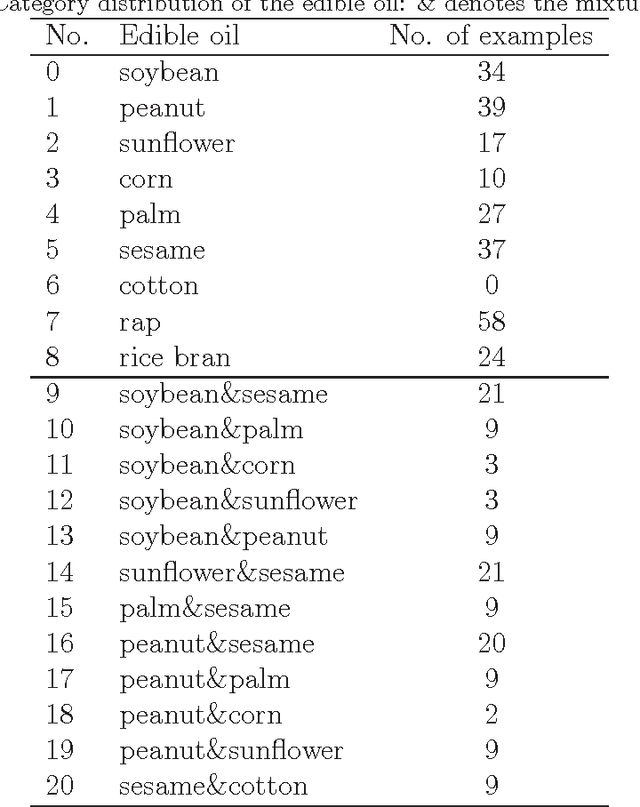
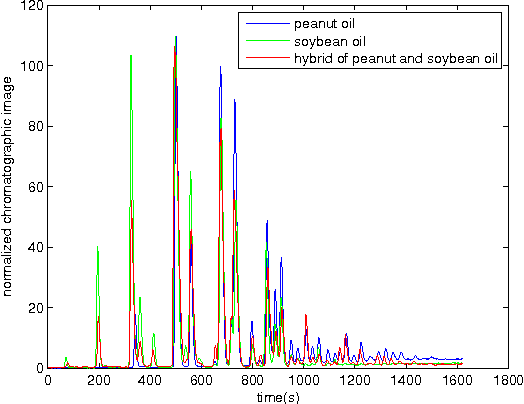
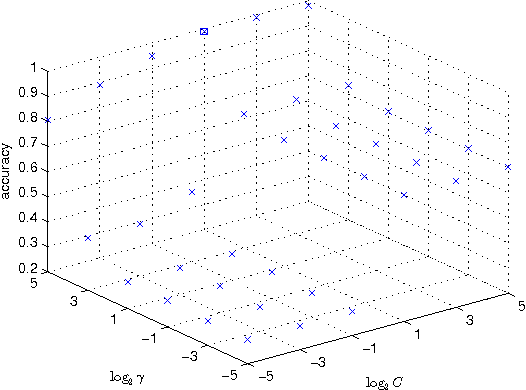
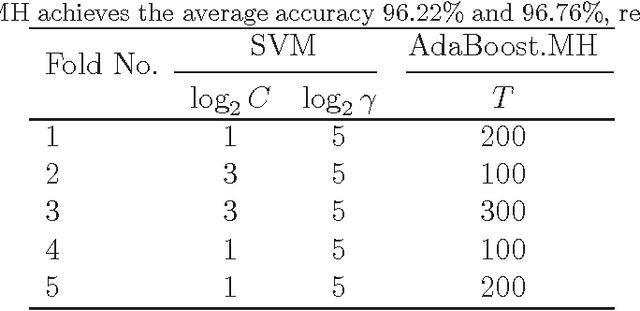
Abstract:The study focused on the machine learning analysis approaches to identify the adulteration of 9 kinds of edible oil qualitatively and answered the following three questions: Is the oil sample adulterant? How does it constitute? What is the main ingredient of the adulteration oil? After extracting the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) data on triglyceride from 370 oil samples, we applied the adaptive boosting with multi-class Hamming loss (AdaBoost.MH) to distinguish the oil adulteration in contrast with the support vector machine (SVM). Further, we regarded the adulterant oil and the pure oil samples as ones with multiple labels and with only one label, respectively. Then multi-label AdaBoost.MH and multi-label learning vector quantization (ML-LVQ) model were built to determine the ingredients and their relative ratio in the adulteration oil. The experimental results on six measures show that ML-LVQ achieves better performance than multi-label AdaBoost.MH.
Linear NDCG and Pair-wise Loss
Mar 11, 2013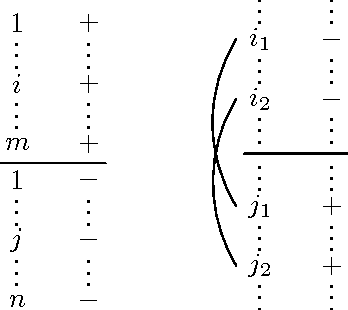
Abstract:Linear NDCG is used for measuring the performance of the Web content quality assessment in ECML/PKDD Discovery Challenge 2010. In this paper, we will prove that the DCG error equals a new pair-wise loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge