Jianyu Miao
Transformed $\ell_1$ Regularization for Learning Sparse Deep Neural Networks
Jan 04, 2019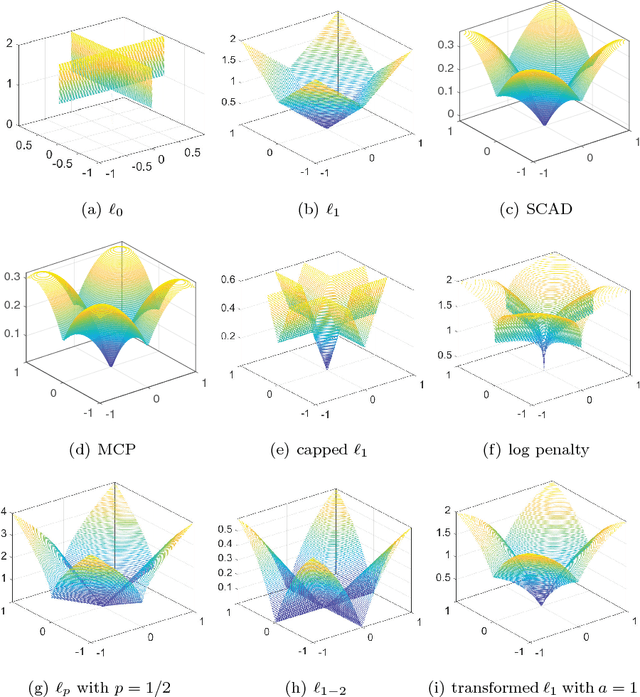

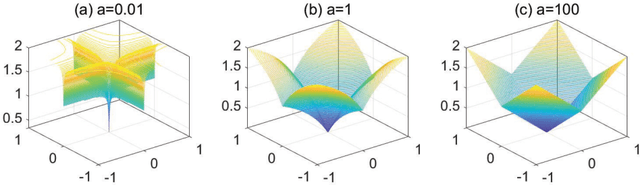
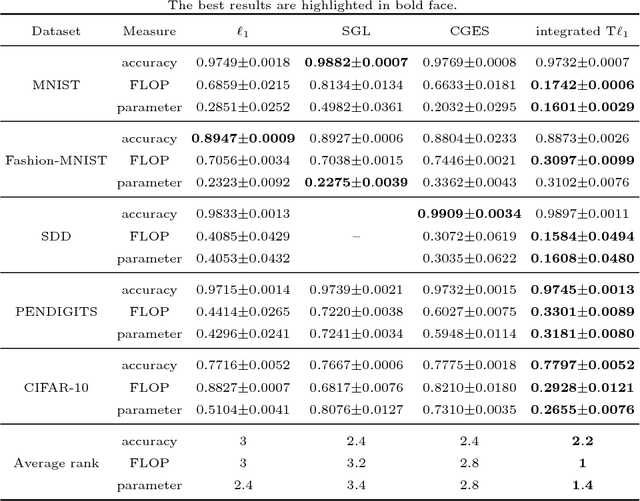
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved extraordinary success in numerous areas. However, to attain this success, DNNs often carry a large number of weight parameters, leading to heavy costs of memory and computation resources. Overfitting is also likely to happen in such network when the training data are insufficient. These shortcomings severely hinder the application of DNNs in resource-constrained platforms. In fact, many network weights are known to be redundant and can be removed from the network without much loss of performance. To this end, we introduce a new non-convex integrated transformed $\ell_1$ regularizer to promote sparsity for DNNs, which removes both redundant connections and unnecessary neurons simultaneously. To be specific, we apply the transformed $\ell_1$ to the matrix space of network weights and utilize it to remove redundant connections. Besides, group sparsity is also employed as an auxiliary to remove unnecessary neurons. An efficient stochastic proximal gradient algorithm is presented to solve the new model at the same time. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to utilize a non-convex regularizer in sparse optimization based method to promote sparsity for DNNs. Experiments on several public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Beyond Attributes: Adversarial Erasing Embedding Network for Zero-shot Learning
Nov 20, 2018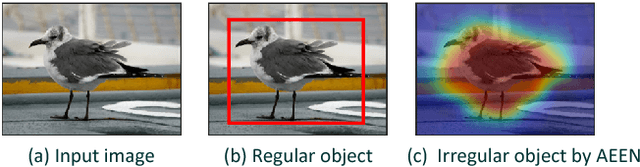
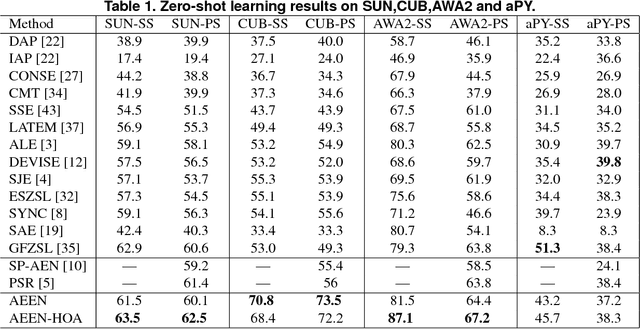
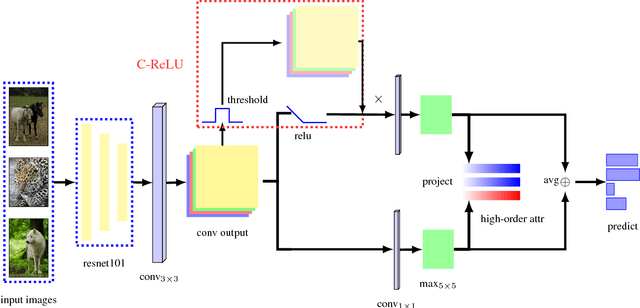
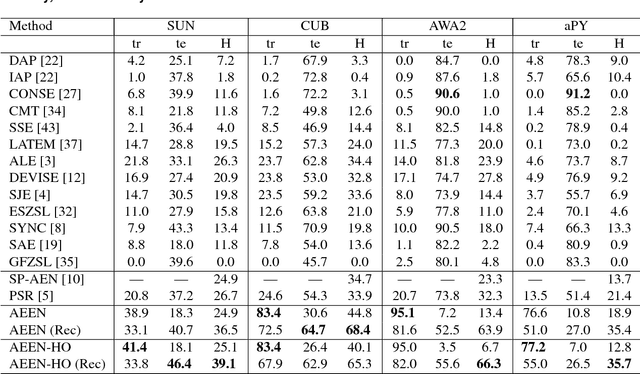
Abstract:In this paper, an adversarial erasing embedding network with the guidance of high-order attributes (AEEN-HOA) is proposed for going further to solve the challenging ZSL/GZSL task. AEEN-HOA consists of two branches, i.e., the upper stream is capable of erasing some initially discovered regions, then the high-order attribute supervision is incorporated to characterize the relationship between the class attributes. Meanwhile, the bottom stream is trained by taking the current background regions to train the same attribute. As far as we know, it is the first time of introducing the erasing operations into the ZSL task. In addition, we first propose a class attribute activation map for the visualization of ZSL output, which shows the relationship between class attribute feature and attention map. Experiments on four standard benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of AEEN-HOA framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge