Wenzhen Zhu
DocBed: A Multi-Stage OCR Solution for Documents with Complex Layouts
Feb 03, 2022



Abstract:Digitization of newspapers is of interest for many reasons including preservation of history, accessibility and search ability, etc. While digitization of documents such as scientific articles and magazines is prevalent in literature, one of the main challenges for digitization of newspaper lies in its complex layout (e.g. articles spanning multiple columns, text interrupted by images) analysis, which is necessary to preserve human read-order. This work provides a major breakthrough in the digitization of newspapers on three fronts: first, releasing a dataset of 3000 fully-annotated, real-world newspaper images from 21 different U.S. states representing an extensive variety of complex layouts for document layout analysis; second, proposing layout segmentation as a precursor to existing optical character recognition (OCR) engines, where multiple state-of-the-art image segmentation models and several post-processing methods are explored for document layout segmentation; third, providing a thorough and structured evaluation protocol for isolated layout segmentation and end-to-end OCR.
Invariant Information Bottleneck for Domain Generalization
Jun 14, 2021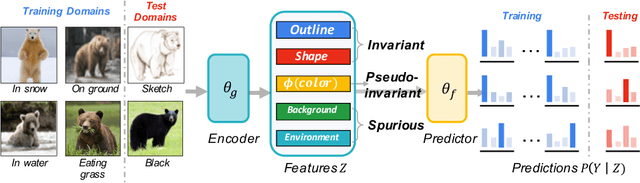
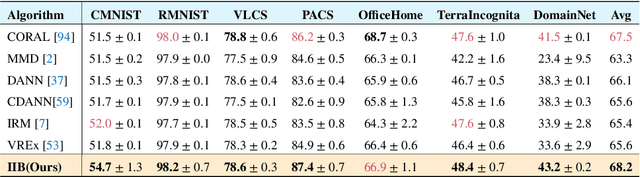
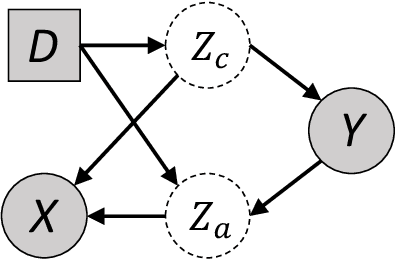
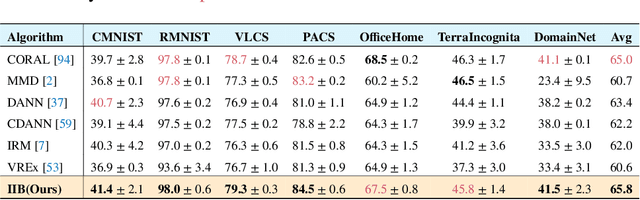
Abstract:The main challenge for domain generalization (DG) is to overcome the potential distributional shift between multiple training domains and unseen test domains. One popular class of DG algorithms aims to learn representations that have an invariant causal relation across the training domains. However, certain features, called \emph{pseudo-invariant features}, may be invariant in the training domain but not the test domain and can substantially decreases the performance of existing algorithms. To address this issue, we propose a novel algorithm, called Invariant Information Bottleneck (IIB), that learns a minimally sufficient representation that is invariant across training and testing domains. By minimizing the mutual information between the representation and inputs, IIB alleviates its reliance on pseudo-invariant features, which is desirable for DG. To verify the effectiveness of the IIB principle, we conduct extensive experiments on large-scale DG benchmarks. The results show that IIB outperforms invariant learning baseline (e.g. IRM) by an average of 2.8\% and 3.8\% accuracy over two evaluation metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge