Wenyi Tang
A Decentralized Retrieval Augmented Generation System with Source Reliabilities Secured on Blockchain
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Existing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems typically use a centralized architecture, causing a high cost of data collection, integration, and management, as well as privacy concerns. There is a great need for a decentralized RAG system that enables foundation models to utilize information directly from data owners who maintain full control over their sources. However, decentralization brings a challenge: the numerous independent data sources vary significantly in reliability, which can diminish retrieval accuracy and response quality. To address this, our decentralized RAG system has a novel reliability scoring mechanism that dynamically evaluates each source based on the quality of responses it contributes to generate and prioritizes high-quality sources during retrieval. To ensure transparency and trust, the scoring process is securely managed through blockchain-based smart contracts, creating verifiable and tamper-proof reliability records without relying on a central authority. We evaluate our decentralized system with two Llama models (3B and 8B) in two simulated environments where six data sources have different levels of reliability. Our system achieves a +10.7\% performance improvement over its centralized counterpart in the real world-like unreliable data environments. Notably, it approaches the upper-bound performance of centralized systems under ideally reliable data environments. The decentralized infrastructure enables secure and trustworthy scoring management, achieving approximately 56\% marginal cost savings through batched update operations. Our code and system are open-sourced at github.com/yining610/Reliable-dRAG.
RAUCG: Retrieval-Augmented Unsupervised Counter Narrative Generation for Hate Speech
Oct 09, 2023
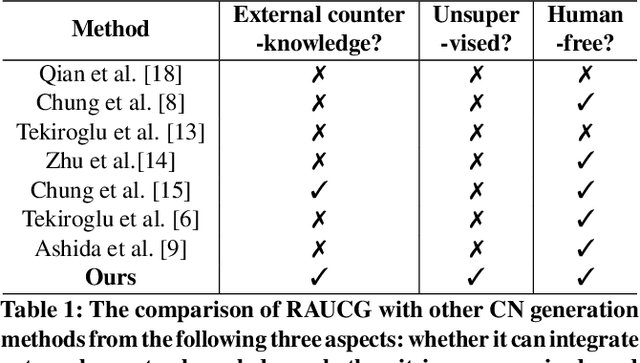

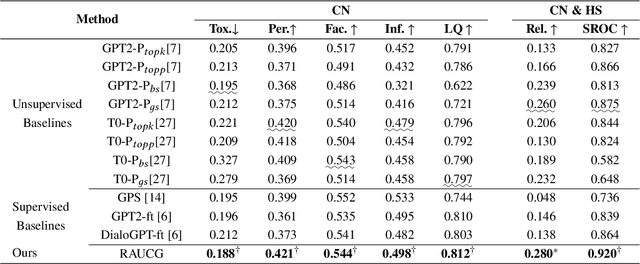
Abstract:The Counter Narrative (CN) is a promising approach to combat online hate speech (HS) without infringing on freedom of speech. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in automatically generating CNs using natural language generation techniques. However, current automatic CN generation methods mainly rely on expert-authored datasets for training, which are time-consuming and labor-intensive to acquire. Furthermore, these methods cannot directly obtain and extend counter-knowledge from external statistics, facts, or examples. To address these limitations, we propose Retrieval-Augmented Unsupervised Counter Narrative Generation (RAUCG) to automatically expand external counter-knowledge and map it into CNs in an unsupervised paradigm. Specifically, we first introduce an SSF retrieval method to retrieve counter-knowledge from the multiple perspectives of stance consistency, semantic overlap rate, and fitness for HS. Then we design an energy-based decoding mechanism by quantizing knowledge injection, countering and fluency constraints into differentiable functions, to enable the model to build mappings from counter-knowledge to CNs without expert-authored CN data. Lastly, we comprehensively evaluate model performance in terms of language quality, toxicity, persuasiveness, relevance, and success rate of countering HS, etc. Experimental results show that RAUCG outperforms strong baselines on all metrics and exhibits stronger generalization capabilities, achieving significant improvements of +2.0% in relevance and +4.5% in success rate of countering metrics. Moreover, RAUCG enabled GPT2 to outperform T0 in all metrics, despite the latter being approximately eight times larger than the former. Warning: This paper may contain offensive or upsetting content!
Detecting Offensive Language on Social Networks: An End-to-end Detection Method based on Graph Attention Networks
Mar 04, 2022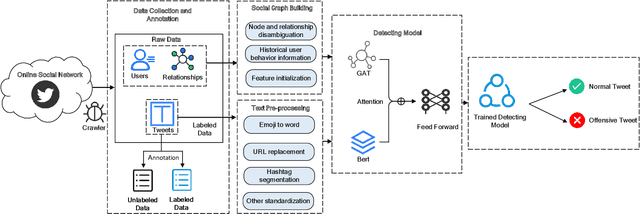
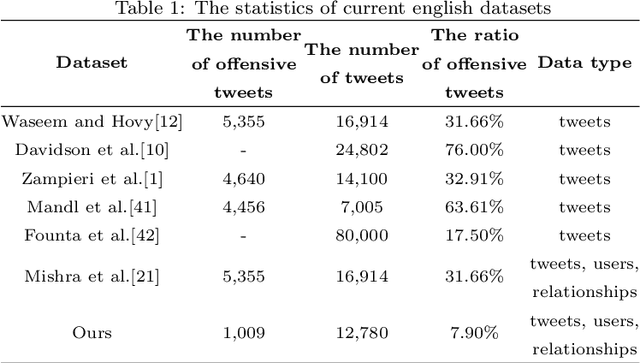
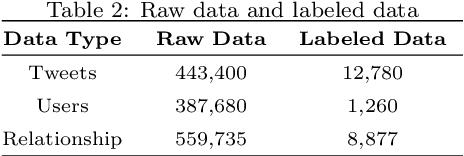
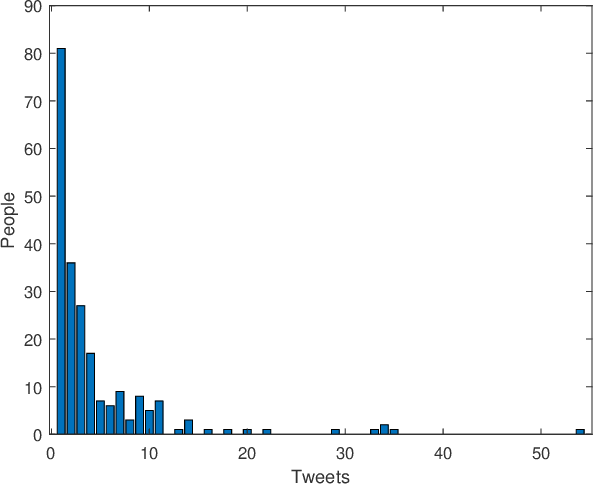
Abstract:The pervasiveness of offensive language on the social network has caused adverse effects on society, such as abusive behavior online. It is urgent to detect offensive language and curb its spread. Existing research shows that methods with community structure features effectively improve the performance of offensive language detection. However, the existing models deal with community structure independently, which seriously affects the effectiveness of detection models. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end method based on community structure and text features for offensive language detection (CT-OLD). Specifically, the community structure features are directly captured by the graph attention network layer, and the text embeddings are taken from the last hidden layer of BERT. Attention mechanisms and position encoding are used to fuse these features. Meanwhile, we add user opinion to the community structure for representing user features. The user opinion is represented by user historical behavior information, which outperforms that represented by text information. Besides the above point, the distribution of users and tweets is unbalanced in the popular datasets, which limits the generalization ability of the model. To address this issue, we construct and release a dataset with reasonable user distribution. Our method outperforms baselines with the F1 score of 89.94%. The results show that the end-to-end model effectively learns the potential information of community structure and text, and user historical behavior information is more suitable for user opinion representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge