Wenjuan Zhong
A Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Gesture Recognition from High-Density Electromyography
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Accurate hand gesture prediction is crucial for effective upper-limb prosthetic limbs control. As the high flexibility and multiple degrees of freedom exhibited by human hands, there has been a growing interest in integrating deep networks with high-density surface electromyography (HD-sEMG) grids to enhance gesture recognition capabilities. However, many existing methods fall short in fully exploit the specific spatial topology and temporal dependencies present in HD-sEMG data. Additionally, these studies are often limited number of gestures and lack generality. Hence, this study introduces a novel gesture recognition method, named STGCN-GR, which leverages spatio-temporal graph convolution networks for HD-sEMG-based human-machine interfaces. Firstly, we construct muscle networks based on functional connectivity between channels, creating a graph representation of HD-sEMG recordings. Subsequently, a temporal convolution module is applied to capture the temporal dependences in the HD-sEMG series and a spatial graph convolution module is employed to effectively learn the intrinsic spatial topology information among distinct HD-sEMG channels. We evaluate our proposed model on a public HD-sEMG dataset comprising a substantial number of gestures (i.e., 65). Our results demonstrate the remarkable capability of the STGCN-GR method, achieving an impressive accuracy of 91.07% in predicting gestures, which surpasses state-of-the-art deep learning methods applied to the same dataset.
Predicting Continuous Locomotion Modes via Multidimensional Feature Learning from sEMG
Nov 13, 2023



Abstract:Walking-assistive devices require adaptive control methods to ensure smooth transitions between various modes of locomotion. For this purpose, detecting human locomotion modes (e.g., level walking or stair ascent) in advance is crucial for improving the intelligence and transparency of such robotic systems. This study proposes Deep-STF, a unified end-to-end deep learning model designed for integrated feature extraction in spatial, temporal, and frequency dimensions from surface electromyography (sEMG) signals. Our model enables accurate and robust continuous prediction of nine locomotion modes and 15 transitions at varying prediction time intervals, ranging from 100 to 500 ms. In addition, we introduced the concept of 'stable prediction time' as a distinct metric to quantify prediction efficiency. This term refers to the duration during which consistent and accurate predictions of mode transitions are made, measured from the time of the fifth correct prediction to the occurrence of the critical event leading to the task transition. This distinction between stable prediction time and prediction time is vital as it underscores our focus on the precision and reliability of mode transition predictions. Experimental results showcased Deep-STP's cutting-edge prediction performance across diverse locomotion modes and transitions, relying solely on sEMG data. When forecasting 100 ms ahead, Deep-STF surpassed CNN and other machine learning techniques, achieving an outstanding average prediction accuracy of 96.48%. Even with an extended 500 ms prediction horizon, accuracy only marginally decreased to 93.00%. The averaged stable prediction times for detecting next upcoming transitions spanned from 28.15 to 372.21 ms across the 100-500 ms time advances.
Gait Cycle-Inspired Learning Strategy for Continuous Prediction of Knee Joint Trajectory from sEMG
Jul 25, 2023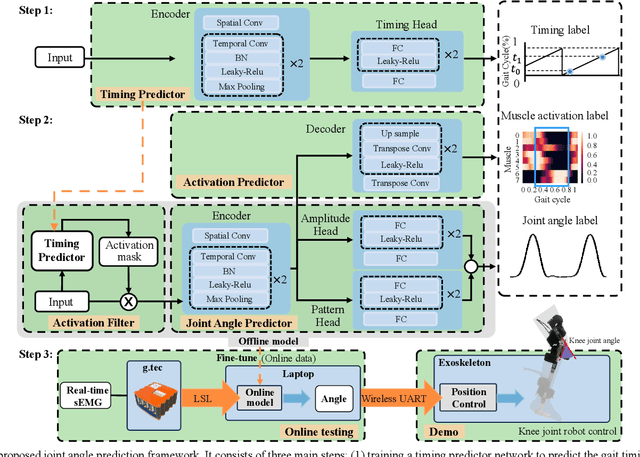
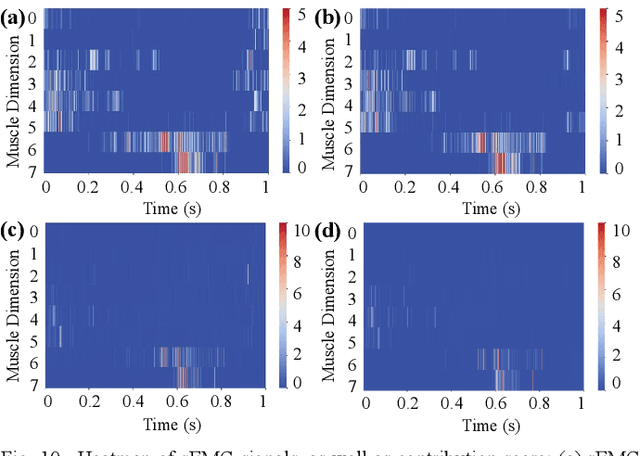
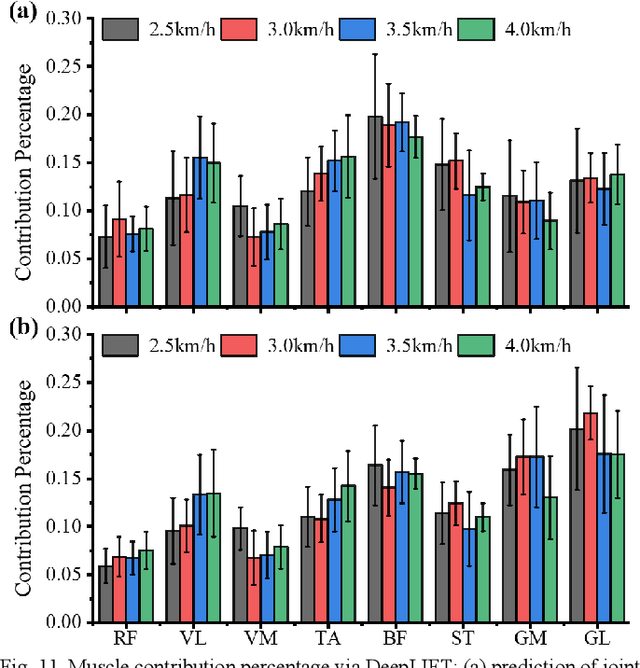
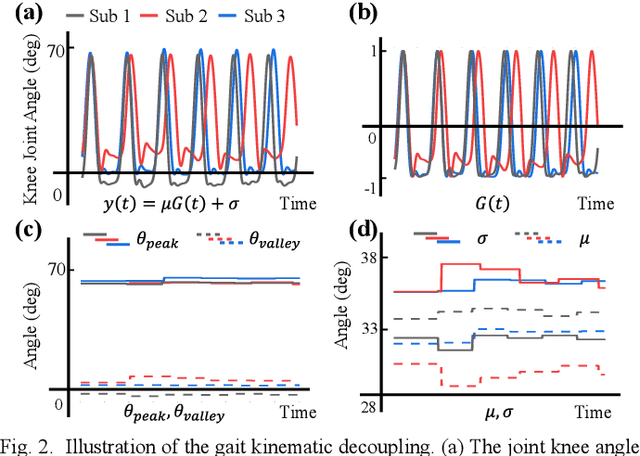
Abstract:Predicting lower limb motion intent is vital for controlling exoskeleton robots and prosthetic limbs. Surface electromyography (sEMG) attracts increasing attention in recent years as it enables ahead-of-time prediction of motion intentions before actual movement. However, the estimation performance of human joint trajectory remains a challenging problem due to the inter- and intra-subject variations. The former is related to physiological differences (such as height and weight) and preferred walking patterns of individuals, while the latter is mainly caused by irregular and gait-irrelevant muscle activity. This paper proposes a model integrating two gait cycle-inspired learning strategies to mitigate the challenge for predicting human knee joint trajectory. The first strategy is to decouple knee joint angles into motion patterns and amplitudes former exhibit low variability while latter show high variability among individuals. By learning through separate network entities, the model manages to capture both the common and personalized gait features. In the second, muscle principal activation masks are extracted from gait cycles in a prolonged walk. These masks are used to filter out components unrelated to walking from raw sEMG and provide auxiliary guidance to capture more gait-related features. Experimental results indicate that our model could predict knee angles with the average root mean square error (RMSE) of 3.03(0.49) degrees and 50ms ahead of time. To our knowledge this is the best performance in relevant literatures that has been reported, with reduced RMSE by at least 9.5%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge