Wenjie Song
MobRT: A Digital Twin-Based Framework for Scalable Learning in Mobile Manipulation
Oct 06, 2025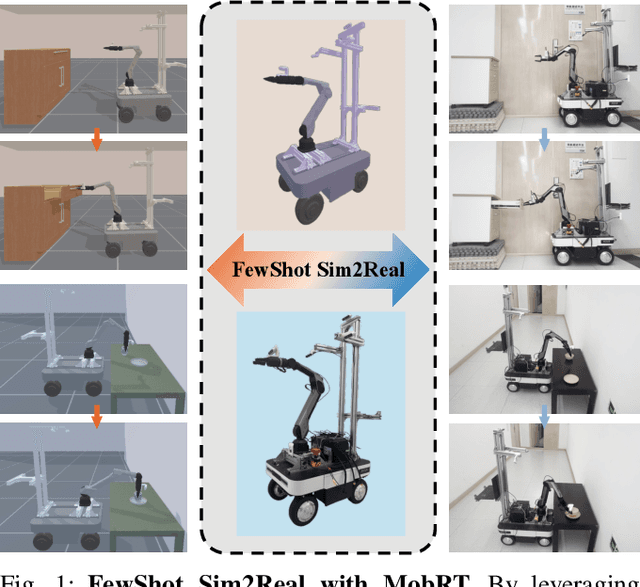
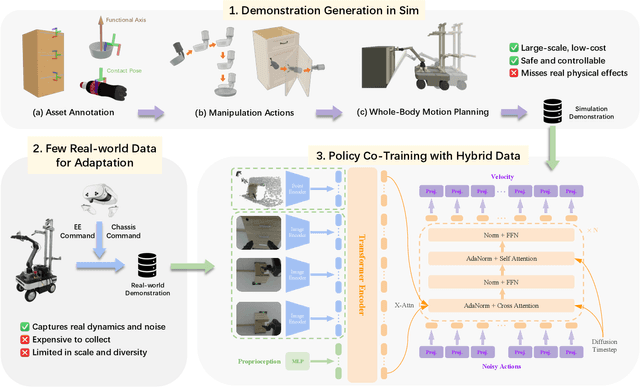
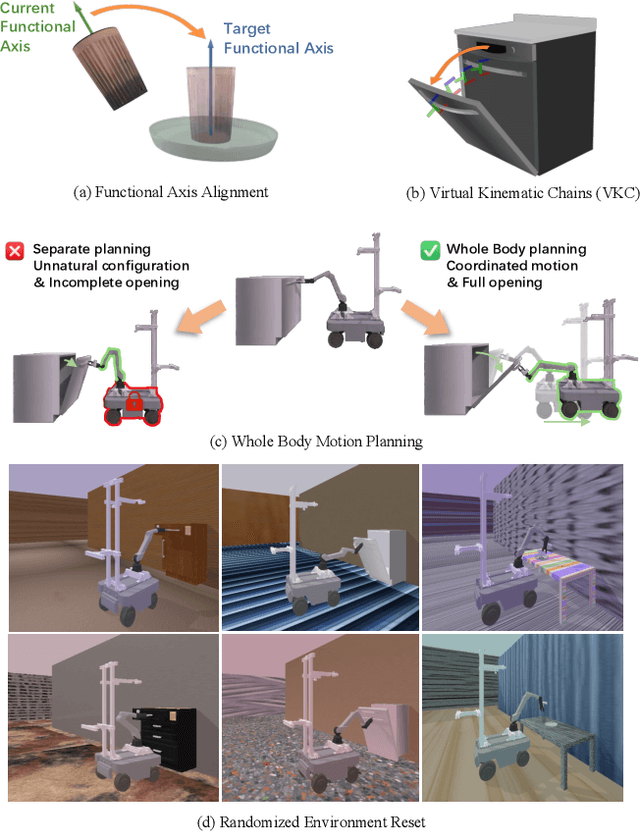
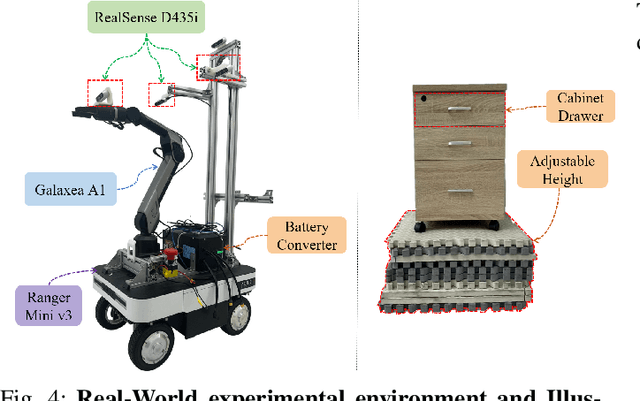
Abstract:Recent advances in robotics have been largely driven by imitation learning, which depends critically on large-scale, high-quality demonstration data. However, collecting such data remains a significant challenge-particularly for mobile manipulators, which must coordinate base locomotion and arm manipulation in high-dimensional, dynamic, and partially observable environments. Consequently, most existing research remains focused on simpler tabletop scenarios, leaving mobile manipulation relatively underexplored. To bridge this gap, we present \textit{MobRT}, a digital twin-based framework designed to simulate two primary categories of complex, whole-body tasks: interaction with articulated objects (e.g., opening doors and drawers) and mobile-base pick-and-place operations. \textit{MobRT} autonomously generates diverse and realistic demonstrations through the integration of virtual kinematic control and whole-body motion planning, enabling coherent and physically consistent execution. We evaluate the quality of \textit{MobRT}-generated data across multiple baseline algorithms, establishing a comprehensive benchmark and demonstrating a strong correlation between task success and the number of generated trajectories. Experiments integrating both simulated and real-world demonstrations confirm that our approach markedly improves policy generalization and performance, achieving robust results in both simulated and real-world environments.
Object Navigation with Structure-Semantic Reasoning-Based Multi-level Map and Multimodal Decision-Making LLM
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:The zero-shot object navigation (ZSON) in unknown open-ended environments coupled with semantically novel target often suffers from the significant decline in performance due to the neglect of high-dimensional implicit scene information and the long-range target searching task. To address this, we proposed an active object navigation framework with Environmental Attributes Map (EAM) and MLLM Hierarchical Reasoning module (MHR) to improve its success rate and efficiency. EAM is constructed by reasoning observed environments with SBERT and predicting unobserved ones with Diffusion, utilizing human space regularities that underlie object-room correlations and area adjacencies. MHR is inspired by EAM to perform frontier exploration decision-making, avoiding the circuitous trajectories in long-range scenarios to improve path efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that the EAM module achieves 64.5\% scene mapping accuracy on MP3D dataset, while the navigation task attains SPLs of 28.4\% and 26.3\% on HM3D and MP3D benchmarks respectively - representing absolute improvements of 21.4\% and 46.0\% over baseline methods.
Residual Feature-Reutilization Inception Network for Image Classification
Dec 27, 2024Abstract:Capturing feature information effectively is of great importance in the field of computer vision. With the development of convolutional neural networks (CNNs), concepts like residual connection and multiple scales promote continual performance gains in diverse deep learning vision tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel CNN architecture that it consists of residual feature-reutilization inceptions (ResFRI) or split-residual feature-reutilization inceptions (Split-ResFRI). And it is composed of four convolutional combinations of different structures connected by specially designed information interaction passages, which are utilized to extract multi-scale feature information and effectively increase the receptive field of the model. Moreover, according to the network structure designed above, Split-ResFRI can adjust the segmentation ratio of the input information, thereby reducing the number of parameters and guaranteeing the model performance. Specifically, in experiments based on popular vision datasets, such as CIFAR10 ($97.94$\%), CIFAR100 ($85.91$\%) and Tiny Imagenet ($70.54$\%), we obtain state-of-the-art results compared with other modern models under the premise that the model size is approximate and no additional data is used.
Contrastive Loss Based Frame-wise Feature disentanglement for Polyphonic Sound Event Detection
Jan 11, 2024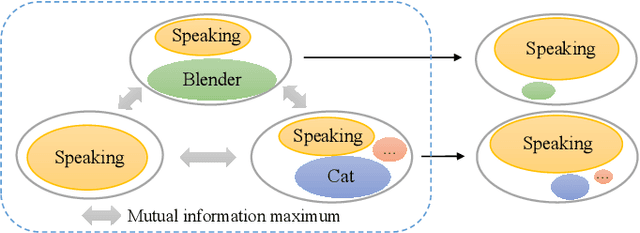
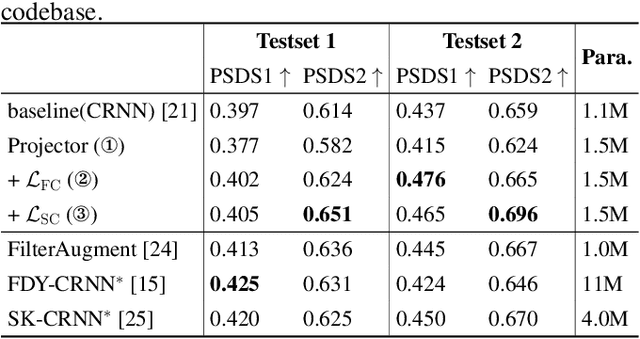
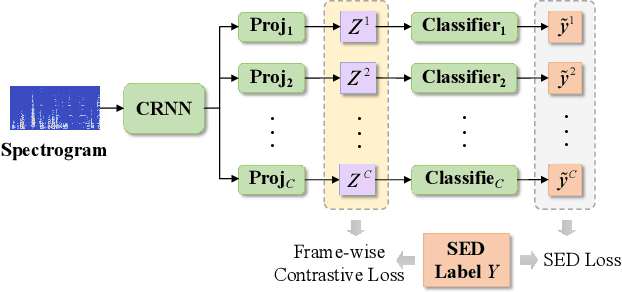
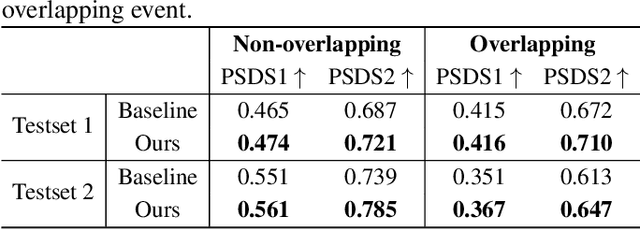
Abstract:Overlapping sound events are ubiquitous in real-world environments, but existing end-to-end sound event detection (SED) methods still struggle to detect them effectively. A critical reason is that these methods represent overlapping events using shared and entangled frame-wise features, which degrades the feature discrimination. To solve the problem, we propose a disentangled feature learning framework to learn a category-specific representation. Specifically, we employ different projectors to learn the frame-wise features for each category. To ensure that these feature does not contain information of other categories, we maximize the common information between frame-wise features within the same category and propose a frame-wise contrastive loss. In addition, considering that the labeled data used by the proposed method is limited, we propose a semi-supervised frame-wise contrastive loss that can leverage large amounts of unlabeled data to achieve feature disentanglement. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Robust Estimation of Similarity Transformation for Visual Object Tracking with Correlation Filters
Dec 14, 2017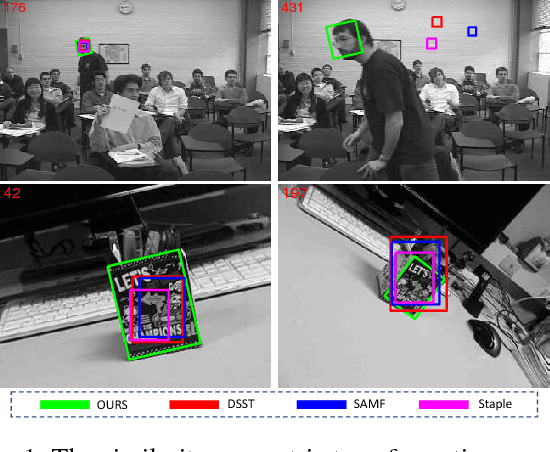
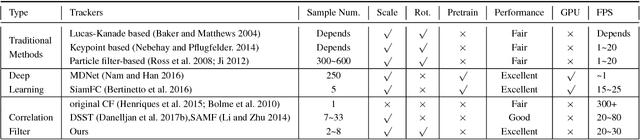
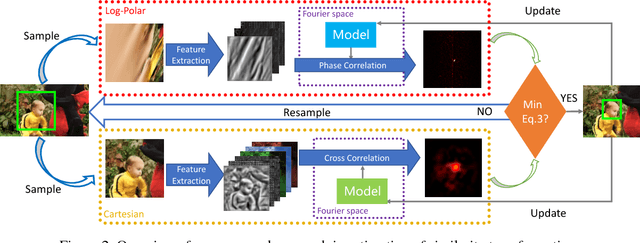

Abstract:Most of existing correlation filter-based tracking approaches only estimate simple axis-aligned bounding boxes, and very few of them is capable of recovering the underlying similarity transformation. To a large extent, such limitation restricts the applications of such trackers for a wide range of scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel correlation filter-based tracker with robust estimation of similarity transformation on the large displacements to tackle this challenging problem. In order to efficiently search in such a large 4-DoF space in real-time, we formulate the problem into two 2-DoF sub-problems and apply an efficient Block Coordinates Descent solver to optimize the estimation result. Specifically, we employ an efficient phase correlation scheme to deal with both scale and rotation changes simultaneously in log-polar coordinates. Moreover, a fast variant of correlation filter is used to predict the translational motion individually. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed tracker achieves very promising prediction performance compared with the state-of-the-art visual object tracking methods while still retaining the advantages of efficiency and simplicity in conventional correlation filter-based tracking methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge