Wen-Shu Fan
Exploring Dark Knowledge under Various Teacher Capacities and Addressing Capacity Mismatch
May 21, 2024Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) could transfer the ``dark knowledge" of a well-performed yet large neural network to a weaker but lightweight one. From the view of output logits and softened probabilities, this paper goes deeper into the dark knowledge provided by teachers with different capacities. Two fundamental observations are: (1) a larger teacher tends to produce probability vectors that are less distinct between non-ground-truth classes; (2) teachers with different capacities are basically consistent in their cognition of relative class affinity. Abundant experimental studies verify these observations and in-depth empirical explanations are provided. The difference in dark knowledge leads to the peculiar phenomenon named ``capacity mismatch" that a more accurate teacher does not necessarily perform as well as a smaller teacher when teaching the same student network. Enlarging the distinctness between non-ground-truth class probabilities for larger teachers could address the capacity mismatch problem. This paper explores multiple simple yet effective ways to achieve this goal and verify their success by comparing them with popular KD methods that solve the capacity mismatch.
Asymmetric Temperature Scaling Makes Larger Networks Teach Well Again
Oct 11, 2022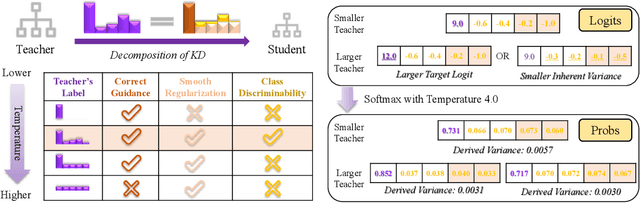
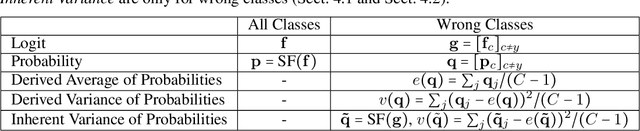
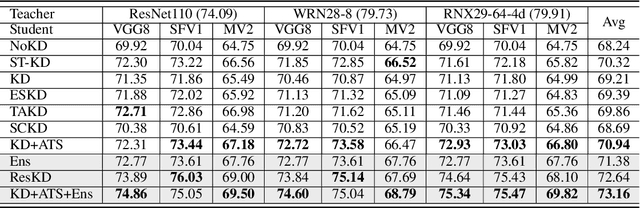
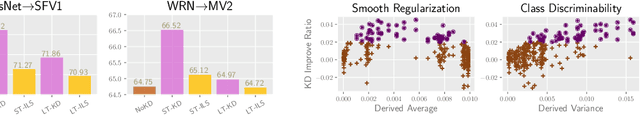
Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) aims at transferring the knowledge of a well-performed neural network (the {\it teacher}) to a weaker one (the {\it student}). A peculiar phenomenon is that a more accurate model doesn't necessarily teach better, and temperature adjustment can neither alleviate the mismatched capacity. To explain this, we decompose the efficacy of KD into three parts: {\it correct guidance}, {\it smooth regularization}, and {\it class discriminability}. The last term describes the distinctness of {\it wrong class probabilities} that the teacher provides in KD. Complex teachers tend to be over-confident and traditional temperature scaling limits the efficacy of {\it class discriminability}, resulting in less discriminative wrong class probabilities. Therefore, we propose {\it Asymmetric Temperature Scaling (ATS)}, which separately applies a higher/lower temperature to the correct/wrong class. ATS enlarges the variance of wrong class probabilities in the teacher's label and makes the students grasp the absolute affinities of wrong classes to the target class as discriminative as possible. Both theoretical analysis and extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of ATS. The demo developed in Mindspore is available at \url{https://gitee.com/lxcnju/ats-mindspore} and will be available at \url{https://gitee.com/mindspore/models/tree/master/research/cv/ats}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge