Weiyi Lu
Shiva-DiT: Residual-Based Differentiable Top-$k$ Selection for Efficient Diffusion Transformers
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) incur prohibitive computational costs due to the quadratic scaling of self-attention. Existing pruning methods fail to simultaneously satisfy differentiability, efficiency, and the strict static budgets required for hardware overhead. To address this, we propose Shiva-DiT, which effectively reconciles these conflicting requirements via Residual-Based Differentiable Top-$k$ Selection. By leveraging a residual-aware straight-through estimator, our method enforces deterministic token counts for static compilation while preserving end-to-end learnability through residual gradient estimation. Furthermore, we introduce a Context-Aware Router and Adaptive Ratio Policy to autonomously learn an adaptive pruning schedule. Experiments on mainstream models, including SD3.5, demonstrate that Shiva-DiT establishes a new Pareto frontier, achieving a 1.54$\times$ wall-clock speedup with superior fidelity compared to existing baselines, effectively eliminating ragged tensor overheads.
Semantic Codebooks as Effective Priors for Neural Speech Compression
Dec 25, 2025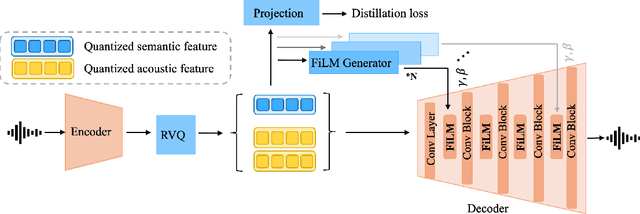
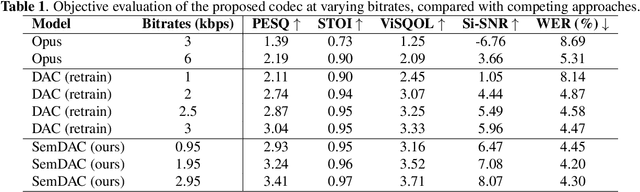
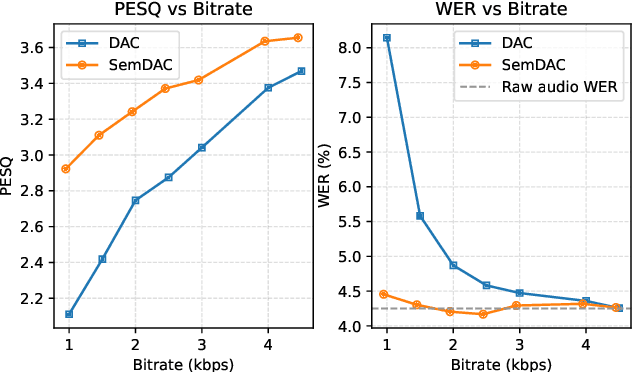
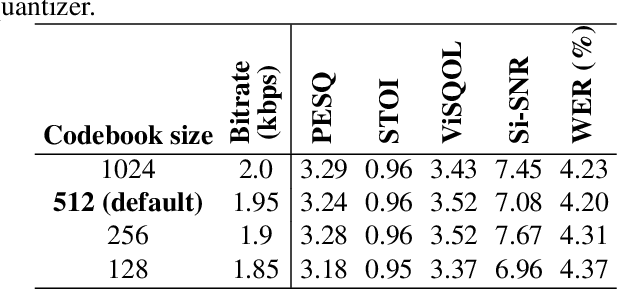
Abstract:Speech codecs are traditionally optimized for waveform fidelity, allocating bits to preserve acoustic detail even when much of it can be inferred from linguistic structure. This leads to inefficient compression and suboptimal performance on downstream recognition tasks. We propose SemDAC, a semantic-aware neural audio codec that leverages semantic codebooks as effective priors for speech compression. In SemDAC, the first quantizer in a residual vector quantization (RVQ) stack is distilled from HuBERT features to produce semantic tokens that capture phonetic content, while subsequent quantizers model residual acoustics. A FiLM-conditioned decoder reconstructs audio conditioned on the semantic tokens, improving efficiency in the use of acoustic codebooks. Despite its simplicity, this design proves highly effective: SemDAC outperforms DAC across perceptual metrics and achieves lower WER when running Whisper on reconstructed speech, all while operating at substantially lower bitrates (e.g., 0.95 kbps vs. 2.5 kbps for DAC). These results demonstrate that semantic codebooks provide an effective inductive bias for neural speech compression, producing compact yet recognition-friendly representations.
InstGenIE: Generative Image Editing Made Efficient with Mask-aware Caching and Scheduling
May 27, 2025
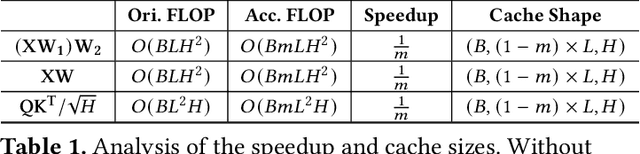
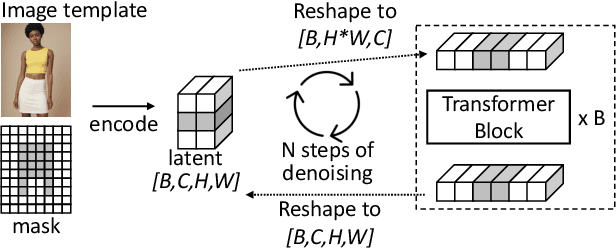
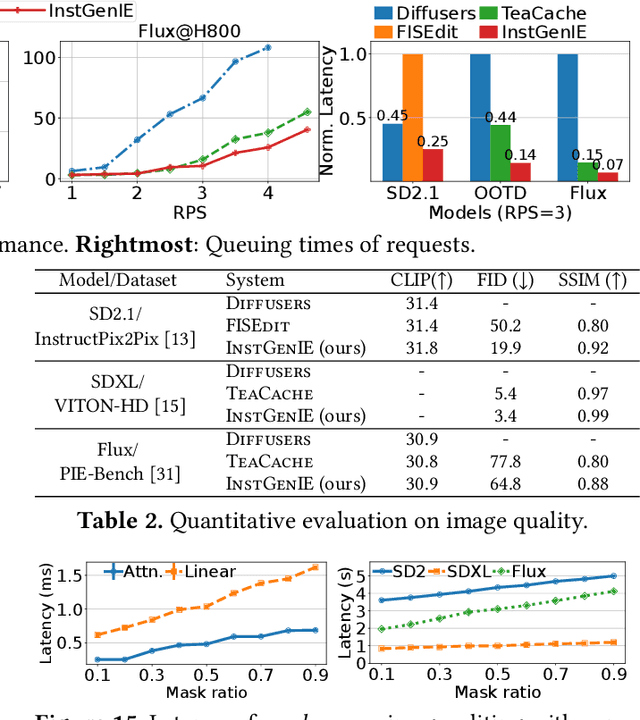
Abstract:Generative image editing using diffusion models has become a prevalent application in today's AI cloud services. In production environments, image editing typically involves a mask that specifies the regions of an image template to be edited. The use of masks provides direct control over the editing process and introduces sparsity in the model inference. In this paper, we present InstGenIE, a system that efficiently serves image editing requests. The key insight behind InstGenIE is that image editing only modifies the masked regions of image templates while preserving the original content in the unmasked areas. Driven by this insight, InstGenIE judiciously skips redundant computations associated with the unmasked areas by reusing cached intermediate activations from previous inferences. To mitigate the high cache loading overhead, InstGenIE employs a bubble-free pipeline scheme that overlaps computation with cache loading. Additionally, to reduce queuing latency in online serving while improving the GPU utilization, InstGenIE proposes a novel continuous batching strategy for diffusion model serving, allowing newly arrived requests to join the running batch in just one step of denoising computation, without waiting for the entire batch to complete. As heterogeneous masks induce imbalanced loads, InstGenIE also develops a load balancing strategy that takes into account the loads of both computation and cache loading. Collectively, InstGenIE outperforms state-of-the-art diffusion serving systems for image editing, achieving up to 3x higher throughput and reducing average request latency by up to 14.7x while ensuring image quality.
SwiftDiffusion: Efficient Diffusion Model Serving with Add-on Modules
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:This paper documents our characterization study and practices for serving text-to-image requests with stable diffusion models in production. We first comprehensively analyze inference request traces for commercial text-to-image applications. It commences with our observation that add-on modules, i.e., ControlNets and LoRAs, that augment the base stable diffusion models, are ubiquitous in generating images for commercial applications. Despite their efficacy, these add-on modules incur high loading overhead, prolong the serving latency, and swallow up expensive GPU resources. Driven by our characterization study, we present SwiftDiffusion, a system that efficiently generates high-quality images using stable diffusion models and add-on modules. To achieve this, SwiftDiffusion reconstructs the existing text-to-image serving workflow by identifying the opportunities for parallel computation and distributing ControlNet computations across multiple GPUs. Further, SwiftDiffusion thoroughly analyzes the dynamics of image generation and develops techniques to eliminate the overhead associated with LoRA loading and patching while preserving the image quality. Last, SwiftDiffusion proposes specialized optimizations in the backbone architecture of the stable diffusion models, which are also compatible with the efficient serving of add-on modules. Compared to state-of-the-art text-to-image serving systems, SwiftDiffusion reduces serving latency by up to 5x and improves serving throughput by up to 2x without compromising image quality.
DynaMaR: Dynamic Prompt with Mask Token Representation
Jun 07, 2022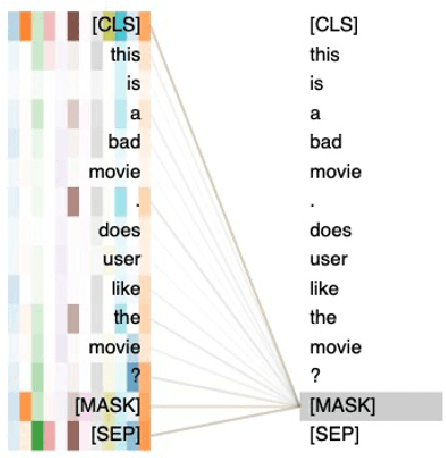
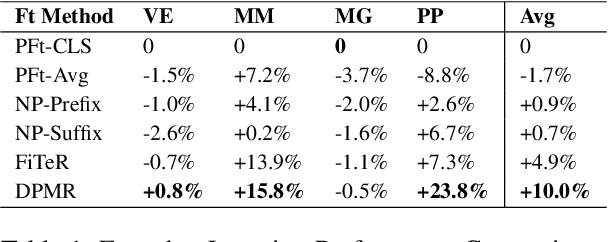
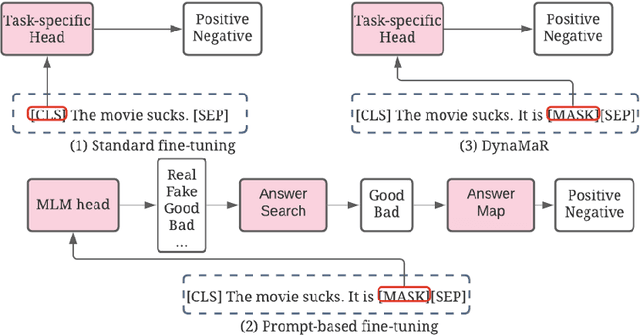
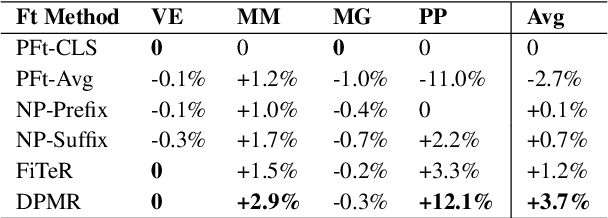
Abstract:Recent research has shown that large language models pretrained using unsupervised approaches can achieve significant performance improvement on many downstream tasks. Typically when adapting these language models to downstream tasks, like a classification or regression task, we employ a fine-tuning paradigm in which the sentence representation from the language model is input to a task-specific head; the model is then fine-tuned end-to-end. However, with the emergence of models like GPT-3, prompt-based fine-tuning has been proven to be a successful approach for few-shot tasks. Inspired by this work, we study discrete prompt technologies in practice. There are two issues that arise with the standard prompt approach. First, it can overfit on the prompt template. Second, it requires manual effort to formulate the downstream task as a language model problem. In this paper, we propose an improvement to prompt-based fine-tuning that addresses these two issues. We refer to our approach as DynaMaR -- Dynamic Prompt with Mask Token Representation. Results show that DynaMaR can achieve an average improvement of 10% in few-shot settings and improvement of 3.7% in data-rich settings over the standard fine-tuning approach on four e-commerce applications.
Accurate Protein Structure Prediction by Embeddings and Deep Learning Representations
Nov 09, 2019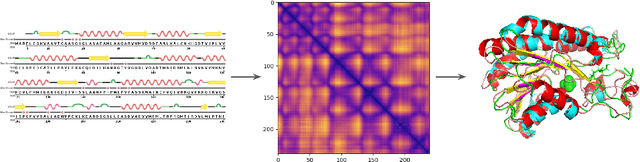
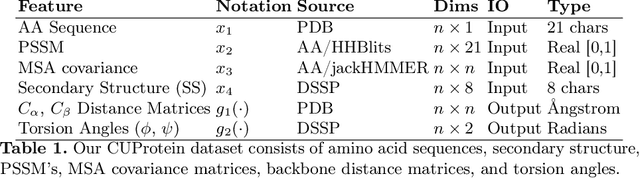

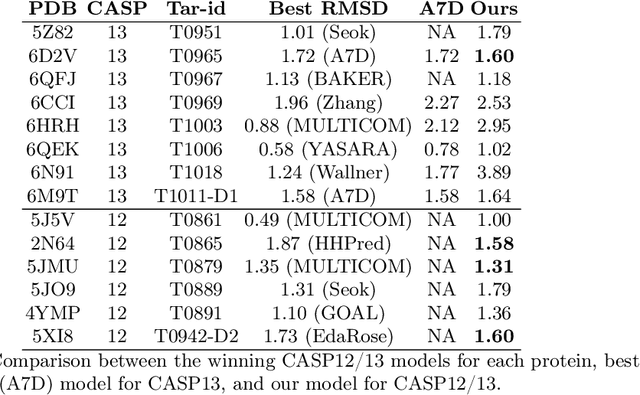
Abstract:Proteins are the major building blocks of life, and actuators of almost all chemical and biophysical events in living organisms. Their native structures in turn enable their biological functions which have a fundamental role in drug design. This motivates predicting the structure of a protein from its sequence of amino acids, a fundamental problem in computational biology. In this work, we demonstrate state-of-the-art protein structure prediction (PSP) results using embeddings and deep learning models for prediction of backbone atom distance matrices and torsion angles. We recover 3D coordinates of backbone atoms and reconstruct full atom protein by optimization. We create a new gold standard dataset of proteins which is comprehensive and easy to use. Our dataset consists of amino acid sequences, Q8 secondary structures, position specific scoring matrices, multiple sequence alignment co-evolutionary features, backbone atom distance matrices, torsion angles, and 3D coordinates. We evaluate the quality of our structure prediction by RMSD on the latest Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction (CASP) test data and demonstrate competitive results with the winning teams and AlphaFold in CASP13 and supersede the results of the winning teams in CASP12. We make our data, models, and code publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge