Weiran Liu
Reliable and Private Utility Signaling for Data Markets
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:The explosive growth of data has highlighted its critical role in driving economic growth through data marketplaces, which enable extensive data sharing and access to high-quality datasets. To support effective trading, signaling mechanisms provide participants with information about data products before transactions, enabling informed decisions and facilitating trading. However, due to the inherent free-duplication nature of data, commonly practiced signaling methods face a dilemma between privacy and reliability, undermining the effectiveness of signals in guiding decision-making. To address this, this paper explores the benefits and develops a non-TCP-based construction for a desirable signaling mechanism that simultaneously ensures privacy and reliability. We begin by formally defining the desirable utility signaling mechanism and proving its ability to prevent suboptimal decisions for both participants and facilitate informed data trading. To design a protocol to realize its functionality, we propose leveraging maliciously secure multi-party computation (MPC) to ensure the privacy and robustness of signal computation and introduce an MPC-based hash verification scheme to ensure input reliability. In multi-seller scenarios requiring fair data valuation, we further explore the design and optimization of the MPC-based KNN-Shapley method with improved efficiency. Rigorous experiments demonstrate the efficiency and practicality of our approach.
SecureV2X: An Efficient and Privacy-Preserving System for Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Applications
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving and V2X technologies have developed rapidly in the past decade, leading to improved safety and efficiency in modern transportation. These systems interact with extensive networks of vehicles, roadside infrastructure, and cloud resources to support their machine learning capabilities. However, the widespread use of machine learning in V2X systems raises issues over the privacy of the data involved. This is particularly concerning for smart-transit and driver safety applications which can implicitly reveal user locations or explicitly disclose medical data such as EEG signals. To resolve these issues, we propose SecureV2X, a scalable, multi-agent system for secure neural network inferences deployed between the server and each vehicle. Under this setting, we study two multi-agent V2X applications: secure drowsiness detection, and secure red-light violation detection. Our system achieves strong performance relative to baselines, and scales efficiently to support a large number of secure computation interactions simultaneously. For instance, SecureV2X is $9.4 \times$ faster, requires $143\times$ fewer computational rounds, and involves $16.6\times$ less communication on drowsiness detection compared to other secure systems. Moreover, it achieves a runtime nearly $100\times$ faster than state-of-the-art benchmarks in object detection tasks for red light violation detection.
Rectifying Privacy and Efficacy Measurements in Machine Unlearning: A New Inference Attack Perspective
Jun 16, 2025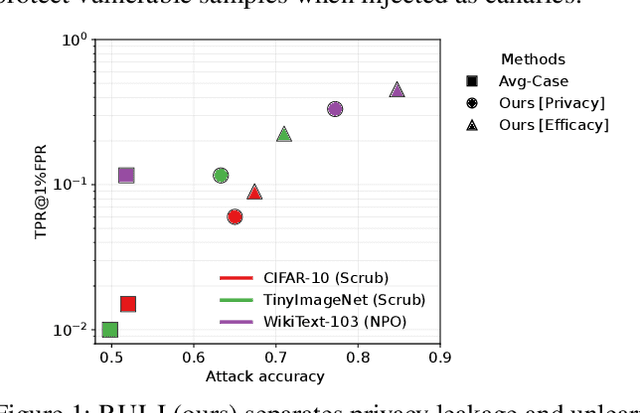
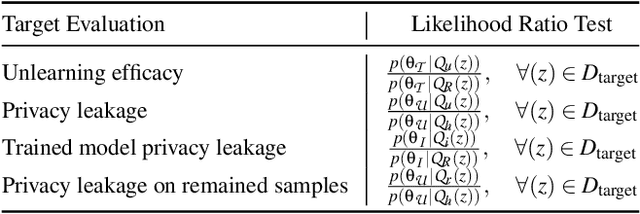
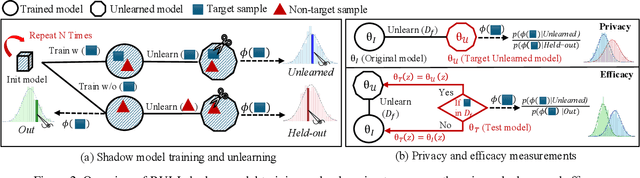
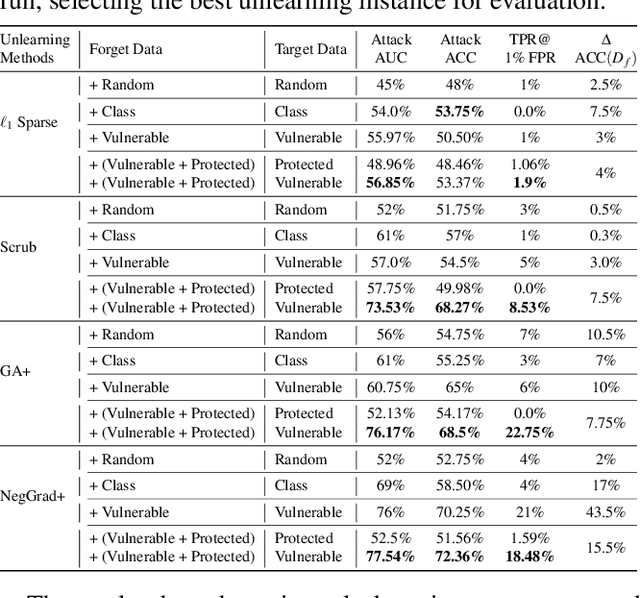
Abstract:Machine unlearning focuses on efficiently removing specific data from trained models, addressing privacy and compliance concerns with reasonable costs. Although exact unlearning ensures complete data removal equivalent to retraining, it is impractical for large-scale models, leading to growing interest in inexact unlearning methods. However, the lack of formal guarantees in these methods necessitates the need for robust evaluation frameworks to assess their privacy and effectiveness. In this work, we first identify several key pitfalls of the existing unlearning evaluation frameworks, e.g., focusing on average-case evaluation or targeting random samples for evaluation, incomplete comparisons with the retraining baseline. Then, we propose RULI (Rectified Unlearning Evaluation Framework via Likelihood Inference), a novel framework to address critical gaps in the evaluation of inexact unlearning methods. RULI introduces a dual-objective attack to measure both unlearning efficacy and privacy risks at a per-sample granularity. Our findings reveal significant vulnerabilities in state-of-the-art unlearning methods, where RULI achieves higher attack success rates, exposing privacy risks underestimated by existing methods. Built on a game-based foundation and validated through empirical evaluations on both image and text data (spanning tasks from classification to generation), RULI provides a rigorous, scalable, and fine-grained methodology for evaluating unlearning techniques.
The WMDP Benchmark: Measuring and Reducing Malicious Use With Unlearning
Mar 06, 2024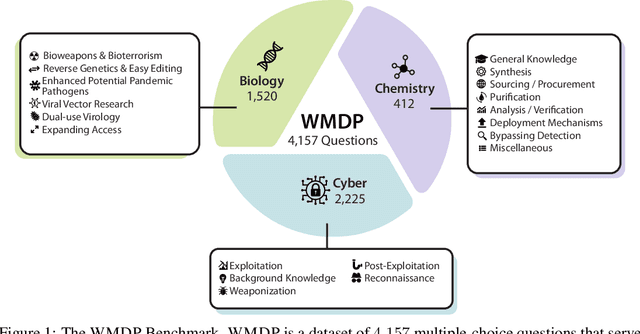
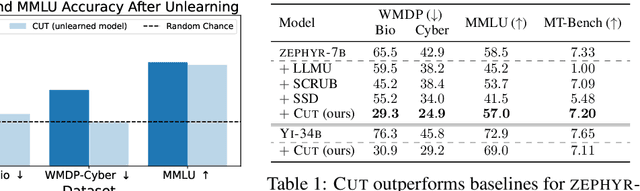
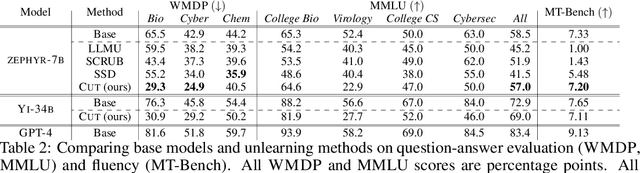
Abstract:The White House Executive Order on Artificial Intelligence highlights the risks of large language models (LLMs) empowering malicious actors in developing biological, cyber, and chemical weapons. To measure these risks of malicious use, government institutions and major AI labs are developing evaluations for hazardous capabilities in LLMs. However, current evaluations are private, preventing further research into mitigating risk. Furthermore, they focus on only a few, highly specific pathways for malicious use. To fill these gaps, we publicly release the Weapons of Mass Destruction Proxy (WMDP) benchmark, a dataset of 4,157 multiple-choice questions that serve as a proxy measurement of hazardous knowledge in biosecurity, cybersecurity, and chemical security. WMDP was developed by a consortium of academics and technical consultants, and was stringently filtered to eliminate sensitive information prior to public release. WMDP serves two roles: first, as an evaluation for hazardous knowledge in LLMs, and second, as a benchmark for unlearning methods to remove such hazardous knowledge. To guide progress on unlearning, we develop CUT, a state-of-the-art unlearning method based on controlling model representations. CUT reduces model performance on WMDP while maintaining general capabilities in areas such as biology and computer science, suggesting that unlearning may be a concrete path towards reducing malicious use from LLMs. We release our benchmark and code publicly at https://wmdp.ai
OpBoost: A Vertical Federated Tree Boosting Framework Based on Order-Preserving Desensitization
Oct 04, 2022
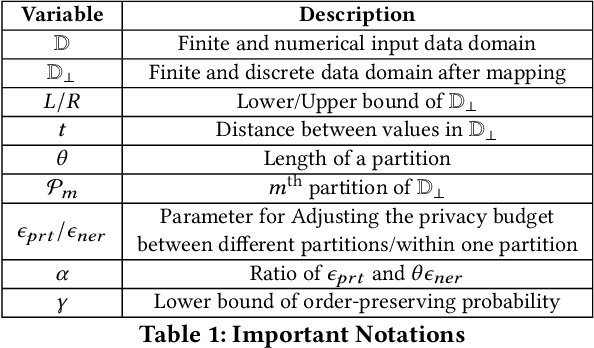
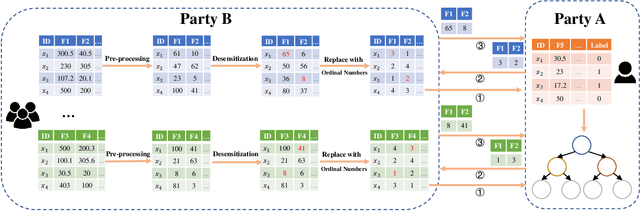
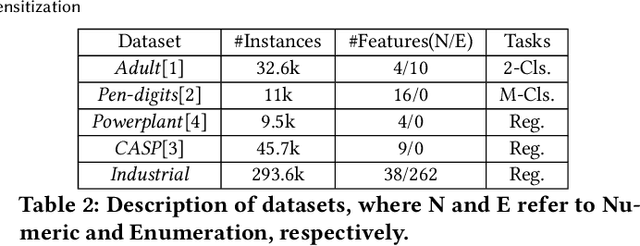
Abstract:Vertical Federated Learning (FL) is a new paradigm that enables users with non-overlapping attributes of the same data samples to jointly train a model without directly sharing the raw data. Nevertheless, recent works show that it's still not sufficient to prevent privacy leakage from the training process or the trained model. This paper focuses on studying the privacy-preserving tree boosting algorithms under the vertical FL. The existing solutions based on cryptography involve heavy computation and communication overhead and are vulnerable to inference attacks. Although the solution based on Local Differential Privacy (LDP) addresses the above problems, it leads to the low accuracy of the trained model. This paper explores to improve the accuracy of the widely deployed tree boosting algorithms satisfying differential privacy under vertical FL. Specifically, we introduce a framework called OpBoost. Three order-preserving desensitization algorithms satisfying a variant of LDP called distance-based LDP (dLDP) are designed to desensitize the training data. In particular, we optimize the dLDP definition and study efficient sampling distributions to further improve the accuracy and efficiency of the proposed algorithms. The proposed algorithms provide a trade-off between the privacy of pairs with large distance and the utility of desensitized values. Comprehensive evaluations show that OpBoost has a better performance on prediction accuracy of trained models compared with existing LDP approaches on reasonable settings. Our code is open source.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge