Weihua Shan
Collaborative Route Planning of UAVs, Workers and Cars for Crowdsensing in Disaster Response
Aug 21, 2023
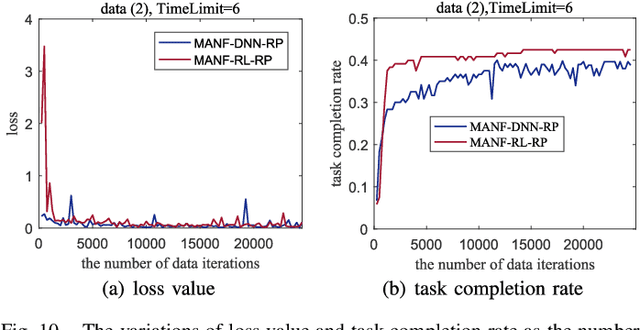
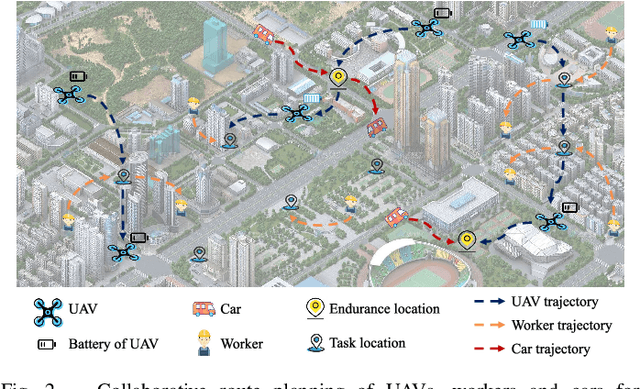
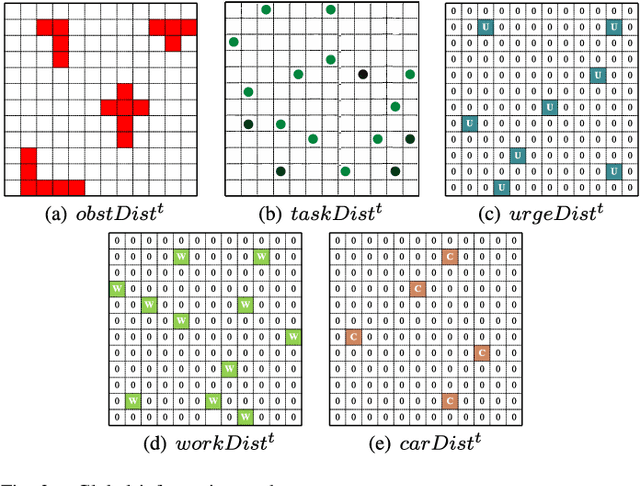
Abstract:Efficiently obtaining the up-to-date information in the disaster-stricken area is the key to successful disaster response. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), workers and cars can collaborate to accomplish sensing tasks, such as data collection, in disaster-stricken areas. In this paper, we explicitly address the route planning for a group of agents, including UAVs, workers, and cars, with the goal of maximizing the task completion rate. We propose MANF-RL-RP, a heterogeneous multi-agent route planning algorithm that incorporates several efficient designs, including global-local dual information processing and a tailored model structure for heterogeneous multi-agent systems. Global-local dual information processing encompasses the extraction and dissemination of spatial features from global information, as well as the partitioning and filtering of local information from individual agents. Regarding the construction of the model structure for heterogeneous multi-agent, we perform the following work. We design the same data structure to represent the states of different agents, prove the Markovian property of the decision-making process of agents to simplify the model structure, and also design a reasonable reward function to train the model. Finally, we conducted detailed experiments based on the rich simulation data. In comparison to the baseline algorithms, namely Greedy-SC-RP and MANF-DNN-RP, MANF-RL-RP has exhibited a significant improvement in terms of task completion rate.
Human 3D Avatar Modeling with Implicit Neural Representation: A Brief Survey
Jun 06, 2023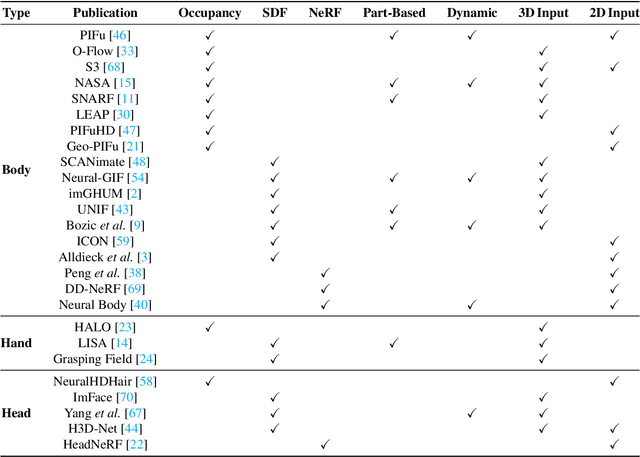
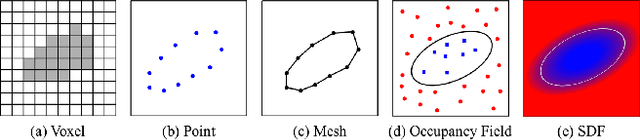
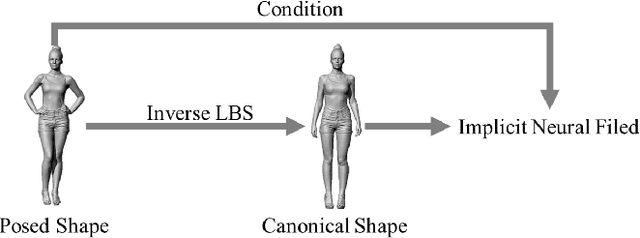
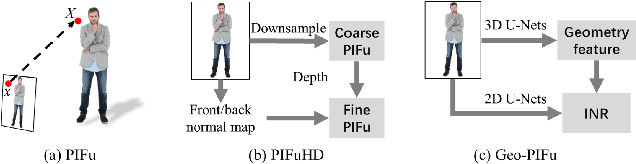
Abstract:A human 3D avatar is one of the important elements in the metaverse, and the modeling effect directly affects people's visual experience. However, the human body has a complex topology and diverse details, so it is often expensive, time-consuming, and laborious to build a satisfactory model. Recent studies have proposed a novel method, implicit neural representation, which is a continuous representation method and can describe objects with arbitrary topology at arbitrary resolution. Researchers have applied implicit neural representation to human 3D avatar modeling and obtained more excellent results than traditional methods. This paper comprehensively reviews the application of implicit neural representation in human body modeling. First, we introduce three implicit representations of occupancy field, SDF, and NeRF, and make a classification of the literature investigated in this paper. Then the application of implicit modeling methods in the body, hand, and head are compared and analyzed respectively. Finally, we point out the shortcomings of current work and provide available suggestions for researchers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge