Weidan Cao
WatchGuardian: Enabling User-Defined Personalized Just-in-Time Intervention on Smartwatch
Feb 09, 2025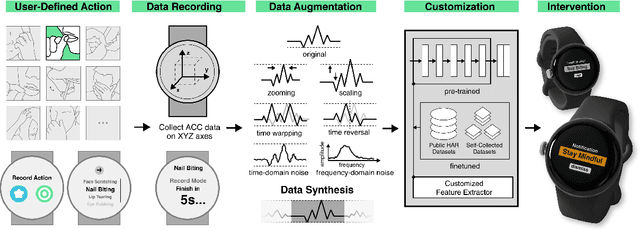
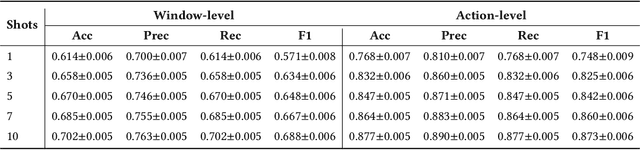
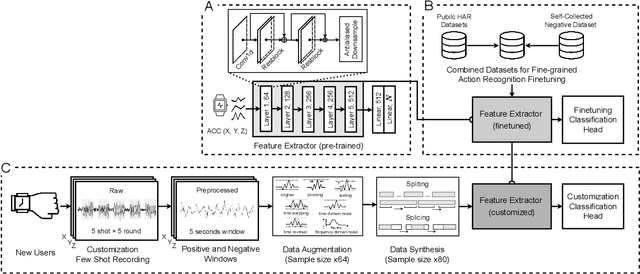
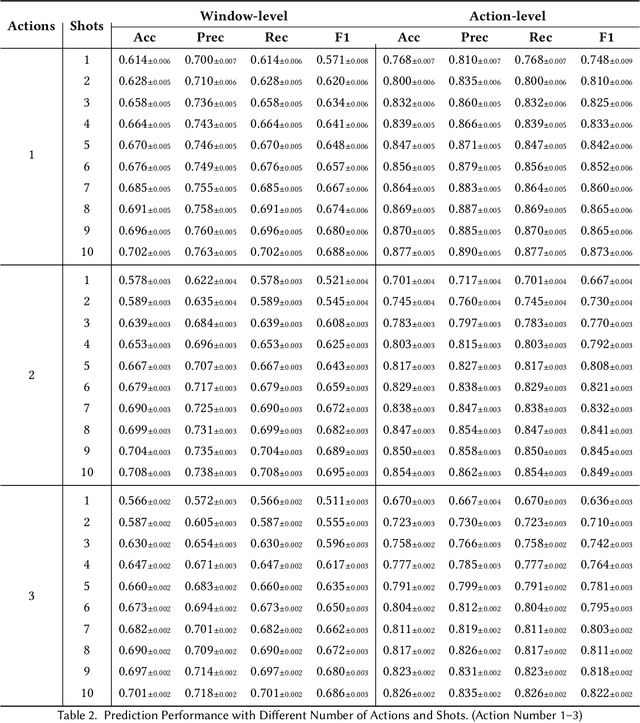
Abstract:While just-in-time interventions (JITIs) have effectively targeted common health behaviors, individuals often have unique needs to intervene in personal undesirable actions that can negatively affect physical, mental, and social well-being. We present WatchGuardian, a smartwatch-based JITI system that empowers users to define custom interventions for these personal actions with a small number of samples. For the model to detect new actions based on limited new data samples, we developed a few-shot learning pipeline that finetuned a pre-trained inertial measurement unit (IMU) model on public hand-gesture datasets. We then designed a data augmentation and synthesis process to train additional classification layers for customization. Our offline evaluation with 26 participants showed that with three, five, and ten examples, our approach achieved an average accuracy of 76.8%, 84.7%, and 87.7%, and an F1 score of 74.8%, 84.2%, and 87.2% We then conducted a four-hour intervention study to compare WatchGuardian against a rule-based intervention. Our results demonstrated that our system led to a significant reduction by 64.0 +- 22.6% in undesirable actions, substantially outperforming the baseline by 29.0%. Our findings underscore the effectiveness of a customizable, AI-driven JITI system for individuals in need of behavioral intervention in personal undesirable actions. We envision that our work can inspire broader applications of user-defined personalized intervention with advanced AI solutions.
SepsisCalc: Integrating Clinical Calculators into Early Sepsis Prediction via Dynamic Temporal Graph Construction
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Sepsis is an organ dysfunction caused by a deregulated immune response to an infection. Early sepsis prediction and identification allow for timely intervention, leading to improved clinical outcomes. Clinical calculators (e.g., the six-organ dysfunction assessment of SOFA) play a vital role in sepsis identification within clinicians' workflow, providing evidence-based risk assessments essential for sepsis diagnosis. However, artificial intelligence (AI) sepsis prediction models typically generate a single sepsis risk score without incorporating clinical calculators for assessing organ dysfunctions, making the models less convincing and transparent to clinicians. To bridge the gap, we propose to mimic clinicians' workflow with a novel framework SepsisCalc to integrate clinical calculators into the predictive model, yielding a clinically transparent and precise model for utilization in clinical settings. Practically, clinical calculators usually combine information from multiple component variables in Electronic Health Records (EHR), and might not be applicable when the variables are (partially) missing. We mitigate this issue by representing EHRs as temporal graphs and integrating a learning module to dynamically add the accurately estimated calculator to the graphs. Experimental results on real-world datasets show that the proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods on sepsis prediction tasks. Moreover, we developed a system to identify organ dysfunctions and potential sepsis risks, providing a human-AI interaction tool for deployment, which can help clinicians understand the prediction outputs and prepare timely interventions for the corresponding dysfunctions, paving the way for actionable clinical decision-making support for early intervention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge