Wei Min
Modelling graph dynamics in fraud detection with "Attention"
Apr 22, 2022Abstract:At online retail platforms, detecting fraudulent accounts and transactions is crucial to improve customer experience, minimize loss, and avoid unauthorized transactions. Despite the variety of different models for deep learning on graphs, few approaches have been proposed for dealing with graphs that are both heterogeneous and dynamic. In this paper, we propose DyHGN (Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network) and its variants to capture both temporal and heterogeneous information. We first construct dynamic heterogeneous graphs from registration and transaction data from eBay. Then, we build models with diachronic entity embedding and heterogeneous graph transformer. We also use model explainability techniques to understand the behaviors of DyHGN-* models. Our findings reveal that modelling graph dynamics with heterogeneous inputs need to be conducted with "attention" depending on the data structure, distribution, and computation cost.
Explainable Deep Behavioral Sequence Clustering for Transaction Fraud Detection
Jan 12, 2021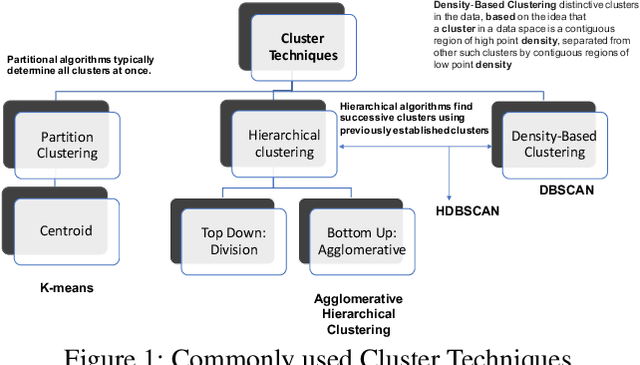
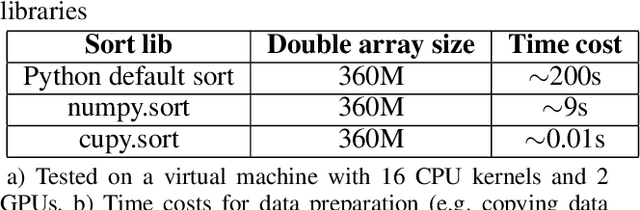
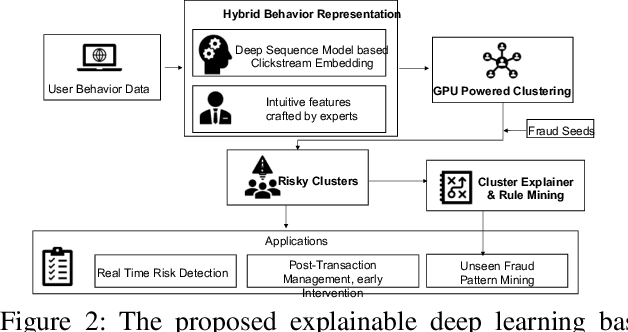
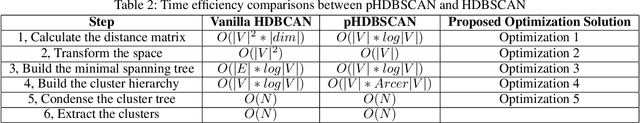
Abstract:In e-commerce industry, user behavior sequence data has been widely used in many business units such as search and merchandising to improve their products. However, it is rarely used in financial services not only due to its 3V characteristics - i.e. Volume, Velocity and Variety - but also due to its unstructured nature. In this paper, we propose a Financial Service scenario Deep learning based Behavior data representation method for Clustering (FinDeepBehaviorCluster) to detect fraudulent transactions. To utilize the behavior sequence data, we treat click stream data as event sequence, use time attention based Bi-LSTM to learn the sequence embedding in an unsupervised fashion, and combine them with intuitive features generated by risk experts to form a hybrid feature representation. We also propose a GPU powered HDBSCAN (pHDBSCAN) algorithm, which is an engineering optimization for the original HDBSCAN algorithm based on FAISS project, so that clustering can be carried out on hundreds of millions of transactions within a few minutes. The computation efficiency of the algorithm has increased 500 times compared with the original implementation, which makes flash fraud pattern detection feasible. Our experimental results show that the proposed FinDeepBehaviorCluster framework is able to catch missed fraudulent transactions with considerable business values. In addition, rule extraction method is applied to extract patterns from risky clusters using intuitive features, so that narrative descriptions can be attached to the risky clusters for case investigation, and unknown risk patterns can be mined for real-time fraud detection. In summary, FinDeepBehaviorCluster as a complementary risk management strategy to the existing real-time fraud detection engine, can further increase our fraud detection and proactive risk defense capabilities.
Suspicious Massive Registration Detection via Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks
Dec 20, 2020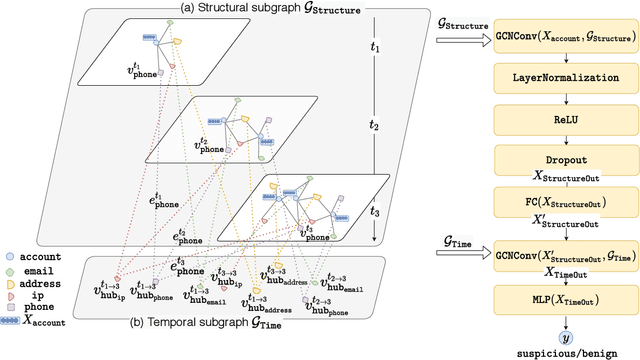
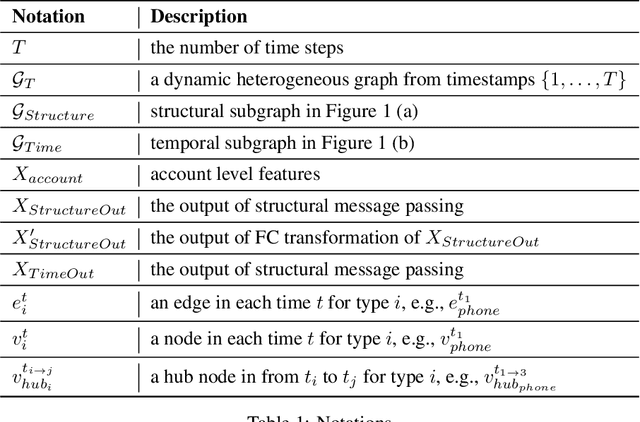
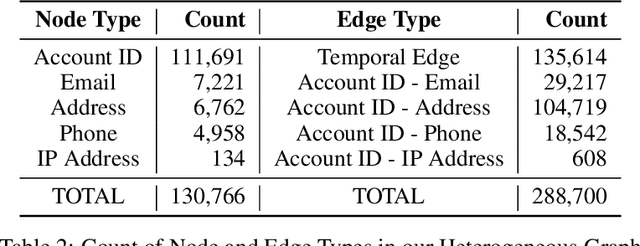

Abstract:Massive account registration has raised concerns on risk management in e-commerce companies, especially when registration increases rapidly within a short time frame. To monitor these registrations constantly and minimize the potential loss they might incur, detecting massive registration and predicting their riskiness are necessary. In this paper, we propose a Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network framework to capture suspicious massive registrations (DHGReg). We first construct a dynamic heterogeneous graph from the registration data, which is composed of a structural subgraph and a temporal subgraph. Then, we design an efficient architecture to predict suspicious/benign accounts. Our proposed model outperforms the baseline models and is computationally efficient in processing a dynamic heterogeneous graph constructed from a real-world dataset. In practice, the DHGReg framework would benefit the detection of suspicious registration behaviors at an early stage.
xFraud: Explainable Fraud Transaction Detection on Heterogeneous Graphs
Nov 24, 2020



Abstract:At online retail platforms, it is crucial to actively detect risks of fraudulent transactions to improve our customer experience, minimize loss, and prevent unauthorized chargebacks. Traditional rule-based methods and simple feature-based models are either inefficient or brittle and uninterpretable. The graph structure that exists among the heterogeneous typed entities of the transaction logs is informative and difficult to fake. To utilize the heterogeneous graph relationships and enrich the explainability, we present xFraud, an explainable Fraud transaction prediction system. xFraud is composed of a predictor which learns expressive representations for malicious transaction detection from the heterogeneous transaction graph via a self-attentive heterogeneous graph neural network, and an explainer that generates meaningful and human understandable explanations from graphs to facilitate further process in business unit. In our experiments with xFraud on two real transaction networks with up to ten millions transactions, we are able to achieve an area under a curve (AUC) score that outperforms baseline models and graph embedding methods. In addition, we show how the explainer could benefit the understanding towards model predictions and enhance model trustworthiness for real-world fraud transaction cases.
Sequential Behavioral Data Processing Using Deep Learning and the Markov Transition Field in Online Fraud Detection
Aug 16, 2018
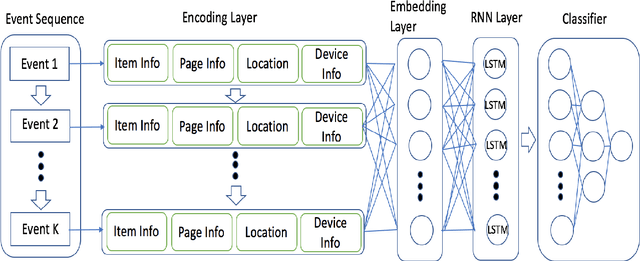
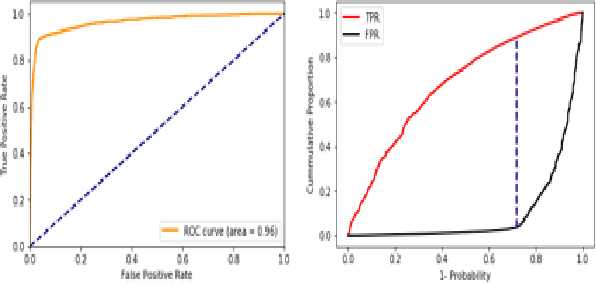
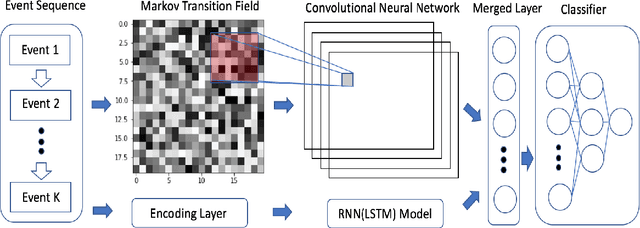
Abstract:Due to the popularity of the Internet and smart mobile devices, more and more financial transactions and activities have been digitalized. Compared to traditional financial fraud detection strategies using credit-related features, customers are generating a large amount of unstructured behavioral data every second. In this paper, we propose an Recurrent Neural Netword (RNN) based deep-learning structure integrated with Markov Transition Field (MTF) for predicting online fraud behaviors using customer's interactions with websites or smart-phone apps as a series of states. In practice, we tested and proved that the proposed network structure for processing sequential behavioral data could significantly boost fraud predictive ability comparing with the multilayer perceptron network and distance based classifier with Dynamic Time Warping(DTW) as distance metric.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge