Zhurong Wang
Multi-task CNN Behavioral Embedding Model For Transaction Fraud Detection
Nov 29, 2024

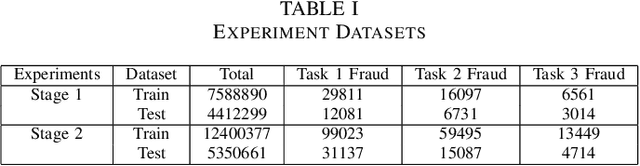
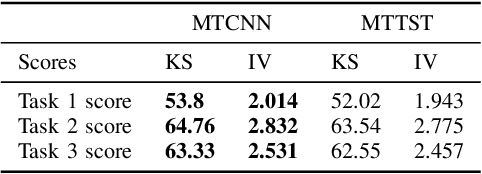
Abstract:The burgeoning e-Commerce sector requires advanced solutions for the detection of transaction fraud. With an increasing risk of financial information theft and account takeovers, deep learning methods have become integral to the embedding of behavior sequence data in fraud detection. However, these methods often struggle to balance modeling capabilities and efficiency and incorporate domain knowledge. To address these issues, we introduce the multitask CNN behavioral Embedding Model for Transaction Fraud Detection. Our contributions include 1) introducing a single-layer CNN design featuring multirange kernels which outperform LSTM and Transformer models in terms of scalability and domain-focused inductive bias, and 2) the integration of positional encoding with CNN to introduce sequence-order signals enhancing overall performance, and 3) implementing multitask learning with randomly assigned label weights, thus removing the need for manual tuning. Testing on real-world data reveals our model's enhanced performance of downstream transaction models and comparable competitiveness with the Transformer Time Series (TST) model.
Behavioral graph fraud detection in E-commerce
Oct 13, 2022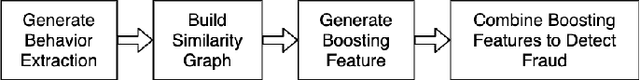
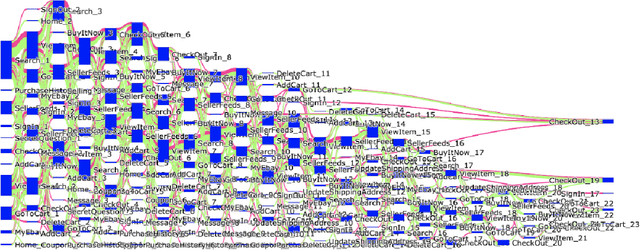
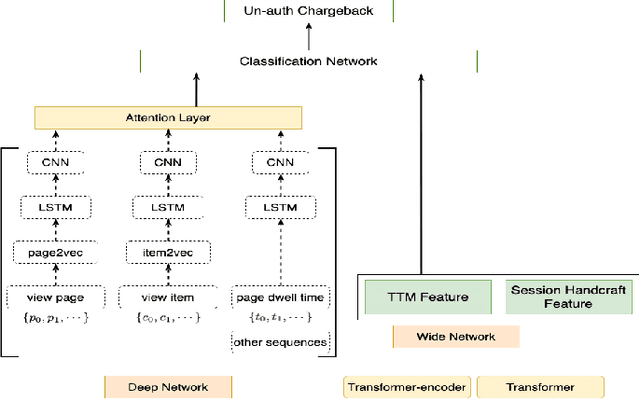
Abstract:In e-commerce industry, graph neural network methods are the new trends for transaction risk modeling.The power of graph algorithms lie in the capability to catch transaction linking network information, which is very hard to be captured by other algorithms.However, in most existing approaches, transaction or user connections are defined by hard link strategies on shared properties, such as same credit card, same device, same ip address, same shipping address, etc. Those types of strategies will result in sparse linkages by entities with strong identification characteristics (ie. device) and over-linkages by entities that could be widely shared (ie. ip address), making it more difficult to learn useful information from graph. To address aforementioned problems, we present a novel behavioral biometric based method to establish transaction linkings based on user behavioral similarities, then train an unsupervised GNN to extract embedding features for downstream fraud prediction tasks. To our knowledge, this is the first time similarity based soft link has been used in graph embedding applications. To speed up similarity calculation, we apply an in-house GPU based HDBSCAN clustering method to remove highly concentrated and isolated nodes before graph construction. Our experiments show that embedding features learned from similarity based behavioral graph have achieved significant performance increase to the baseline fraud detection model in various business scenarios. In new guest buyer transaction scenario, this segment is a challenge for traditional method, we can make precision increase from 0.82 to 0.86 at the same recall of 0.27, which means we can decrease false positive rate using this method.
Explainable Deep Behavioral Sequence Clustering for Transaction Fraud Detection
Jan 12, 2021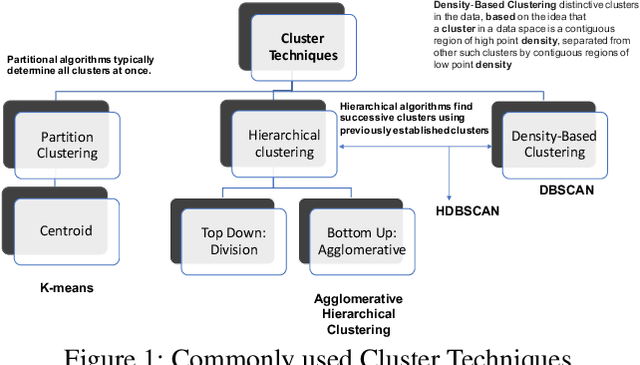
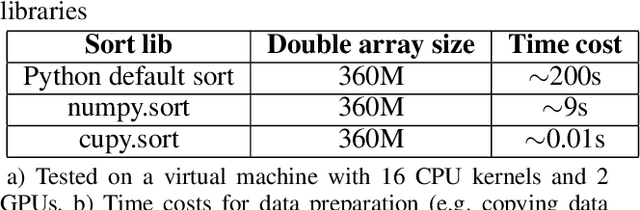
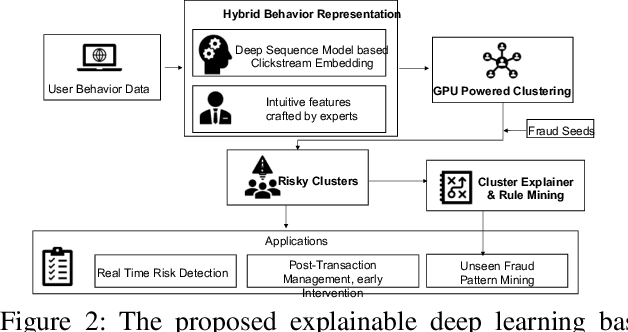
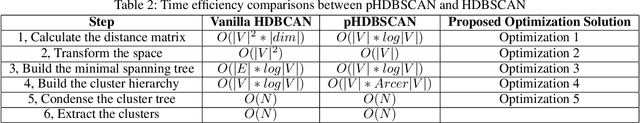
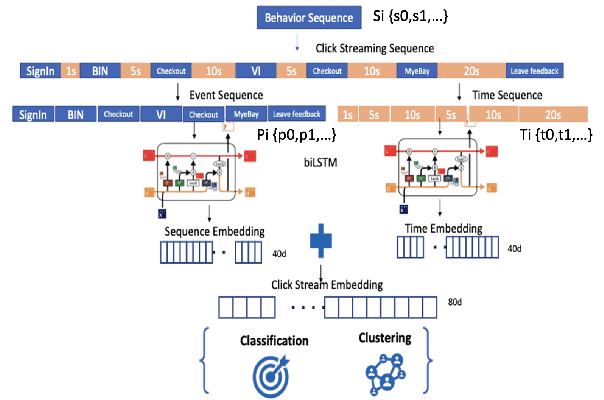
Abstract:In e-commerce industry, user behavior sequence data has been widely used in many business units such as search and merchandising to improve their products. However, it is rarely used in financial services not only due to its 3V characteristics - i.e. Volume, Velocity and Variety - but also due to its unstructured nature. In this paper, we propose a Financial Service scenario Deep learning based Behavior data representation method for Clustering (FinDeepBehaviorCluster) to detect fraudulent transactions. To utilize the behavior sequence data, we treat click stream data as event sequence, use time attention based Bi-LSTM to learn the sequence embedding in an unsupervised fashion, and combine them with intuitive features generated by risk experts to form a hybrid feature representation. We also propose a GPU powered HDBSCAN (pHDBSCAN) algorithm, which is an engineering optimization for the original HDBSCAN algorithm based on FAISS project, so that clustering can be carried out on hundreds of millions of transactions within a few minutes. The computation efficiency of the algorithm has increased 500 times compared with the original implementation, which makes flash fraud pattern detection feasible. Our experimental results show that the proposed FinDeepBehaviorCluster framework is able to catch missed fraudulent transactions with considerable business values. In addition, rule extraction method is applied to extract patterns from risky clusters using intuitive features, so that narrative descriptions can be attached to the risky clusters for case investigation, and unknown risk patterns can be mined for real-time fraud detection. In summary, FinDeepBehaviorCluster as a complementary risk management strategy to the existing real-time fraud detection engine, can further increase our fraud detection and proactive risk defense capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge