Wanying Xie
Importance-based Neuron Allocation for Multilingual Neural Machine Translation
Jul 14, 2021
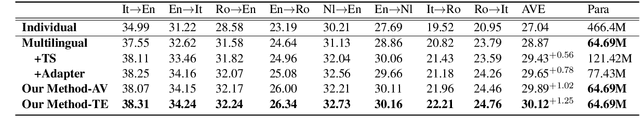
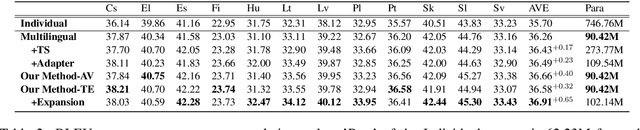
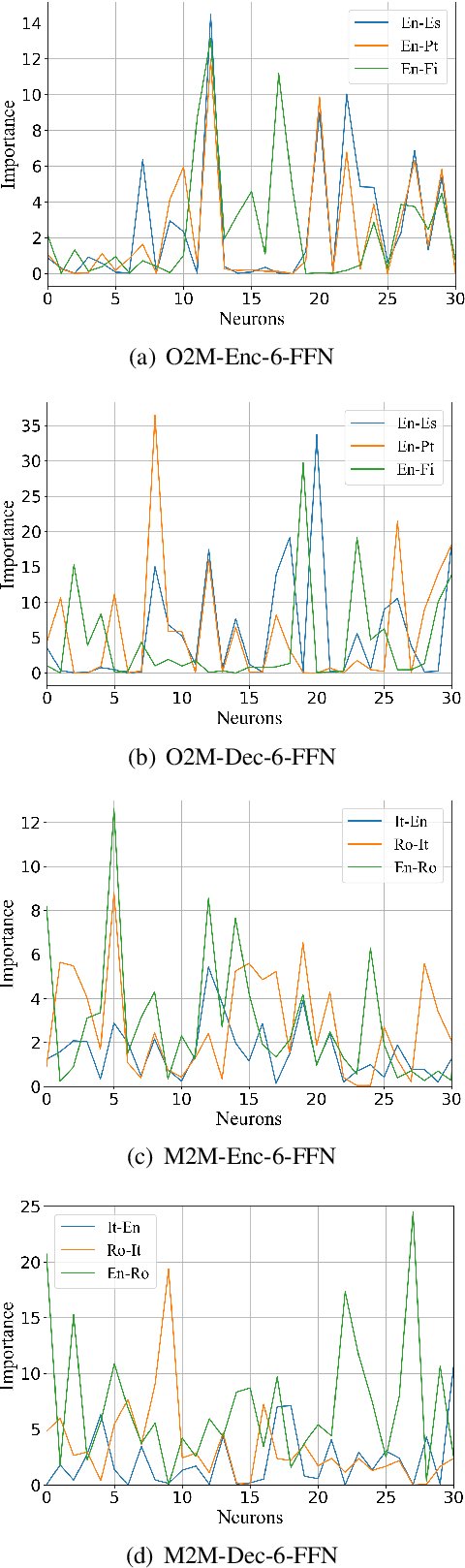
Abstract:Multilingual neural machine translation with a single model has drawn much attention due to its capability to deal with multiple languages. However, the current multilingual translation paradigm often makes the model tend to preserve the general knowledge, but ignore the language-specific knowledge. Some previous works try to solve this problem by adding various kinds of language-specific modules to the model, but they suffer from the parameter explosion problem and require specialized manual design. To solve these problems, we propose to divide the model neurons into general and language-specific parts based on their importance across languages. The general part is responsible for preserving the general knowledge and participating in the translation of all the languages, while the language-specific part is responsible for preserving the language-specific knowledge and participating in the translation of some specific languages. Experimental results on several language pairs, covering IWSLT and Europarl corpus datasets, demonstrate the effectiveness and universality of the proposed method.
Pruning-then-Expanding Model for Domain Adaptation of Neural Machine Translation
Apr 14, 2021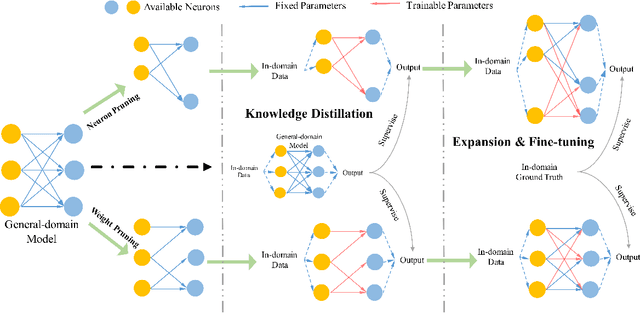
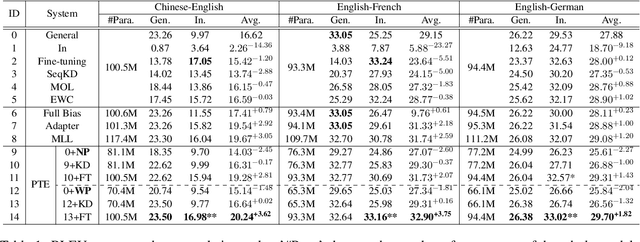
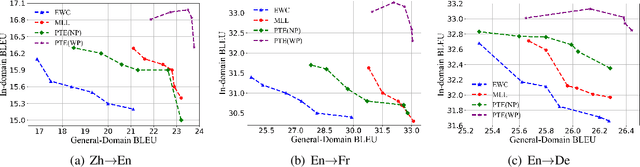
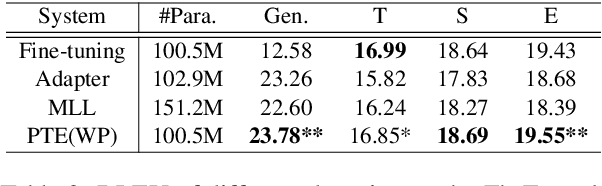
Abstract:Domain Adaptation is widely used in practical applications of neural machine translation, which aims to achieve good performance on both the general-domain and in-domain. However, the existing methods for domain adaptation usually suffer from catastrophic forgetting, domain divergence, and model explosion. To address these three problems, we propose a method of "divide and conquer" which is based on the importance of neurons or parameters in the translation model. In our method, we first prune the model and only keep the important neurons or parameters, making them responsible for both general-domain and in-domain translation. Then we further train the pruned model supervised by the original unpruned model with the knowledge distillation method. Last we expand the model to the original size and fine-tune the added parameters for the in-domain translation. We conduct experiments on different languages and domains and the results show that our method can achieve significant improvements compared with several strong baselines.
Token-level Adaptive Training for Neural Machine Translation
Oct 09, 2020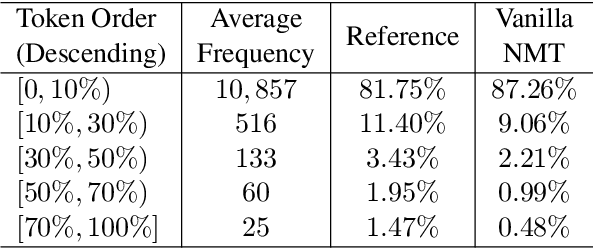
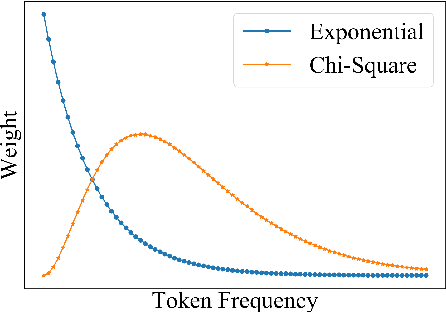
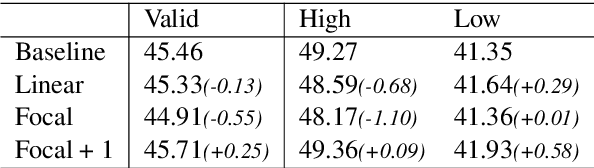
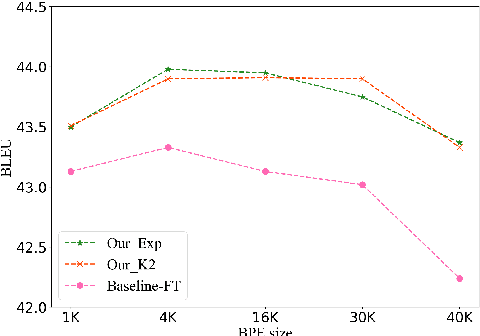
Abstract:There exists a token imbalance phenomenon in natural language as different tokens appear with different frequencies, which leads to different learning difficulties for tokens in Neural Machine Translation (NMT). The vanilla NMT model usually adopts trivial equal-weighted objectives for target tokens with different frequencies and tends to generate more high-frequency tokens and less low-frequency tokens compared with the golden token distribution. However, low-frequency tokens may carry critical semantic information that will affect the translation quality once they are neglected. In this paper, we explored target token-level adaptive objectives based on token frequencies to assign appropriate weights for each target token during training. We aimed that those meaningful but relatively low-frequency words could be assigned with larger weights in objectives to encourage the model to pay more attention to these tokens. Our method yields consistent improvements in translation quality on ZH-EN, EN-RO, and EN-DE translation tasks, especially on sentences that contain more low-frequency tokens where we can get 1.68, 1.02, and 0.52 BLEU increases compared with baseline, respectively. Further analyses show that our method can also improve the lexical diversity of translation.
Modeling Fluency and Faithfulness for Diverse Neural Machine Translation
Nov 30, 2019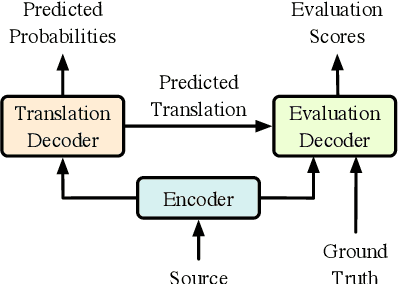
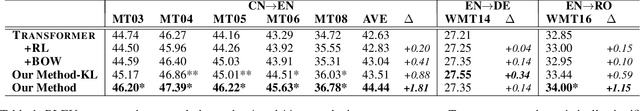
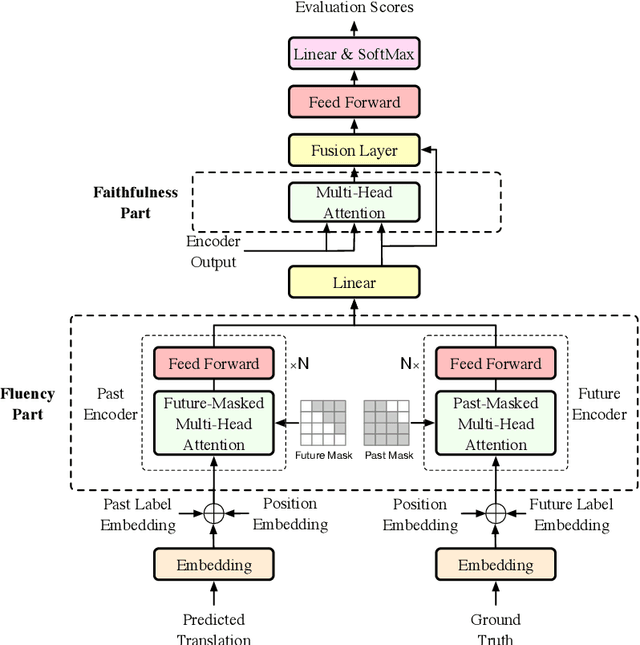
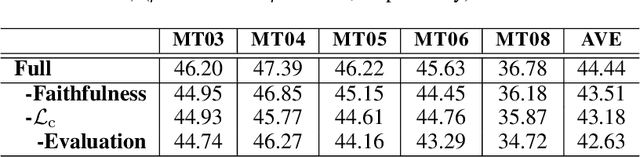
Abstract:Neural machine translation models usually adopt the teacher forcing strategy for training which requires the predicted sequence matches ground truth word by word and forces the probability of each prediction to approach a 0-1 distribution. However, the strategy casts all the portion of the distribution to the ground truth word and ignores other words in the target vocabulary even when the ground truth word cannot dominate the distribution. To address the problem of teacher forcing, we propose a method to introduce an evaluation module to guide the distribution of the prediction. The evaluation module accesses each prediction from the perspectives of fluency and faithfulness to encourage the model to generate the word which has a fluent connection with its past and future translation and meanwhile tends to form a translation equivalent in meaning to the source. The experiments on multiple translation tasks show that our method can achieve significant improvements over strong baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge