Pruning-then-Expanding Model for Domain Adaptation of Neural Machine Translation
Paper and Code
Apr 14, 2021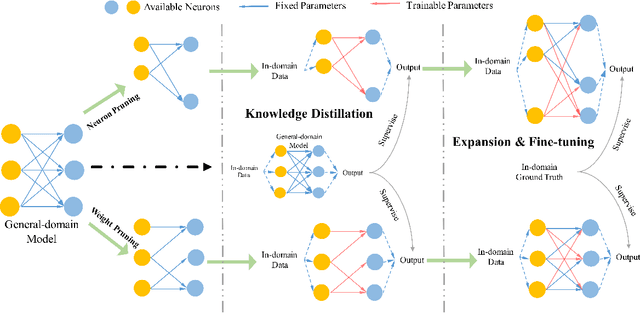
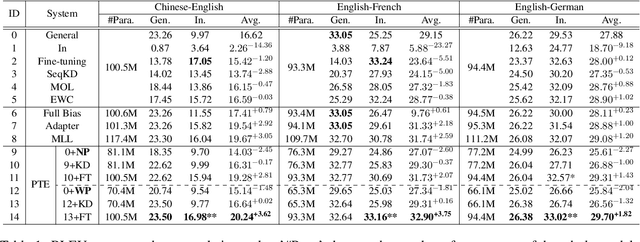
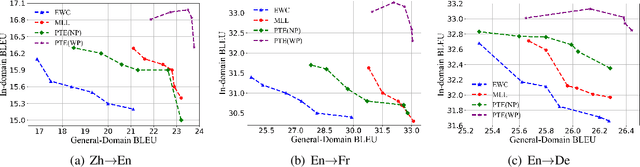
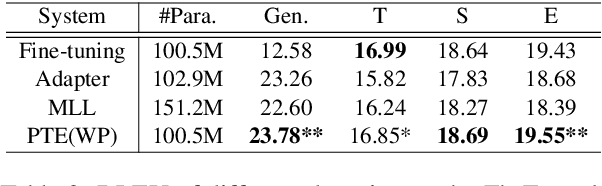
Domain Adaptation is widely used in practical applications of neural machine translation, which aims to achieve good performance on both the general-domain and in-domain. However, the existing methods for domain adaptation usually suffer from catastrophic forgetting, domain divergence, and model explosion. To address these three problems, we propose a method of "divide and conquer" which is based on the importance of neurons or parameters in the translation model. In our method, we first prune the model and only keep the important neurons or parameters, making them responsible for both general-domain and in-domain translation. Then we further train the pruned model supervised by the original unpruned model with the knowledge distillation method. Last we expand the model to the original size and fine-tune the added parameters for the in-domain translation. We conduct experiments on different languages and domains and the results show that our method can achieve significant improvements compared with several strong baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge