Wanting Zhou
VM-DDPM: Vision Mamba Diffusion for Medical Image Synthesis
May 09, 2024Abstract:In the realm of smart healthcare, researchers enhance the scale and diversity of medical datasets through medical image synthesis. However, existing methods are limited by CNN local perception and Transformer quadratic complexity, making it difficult to balance structural texture consistency. To this end, we propose the Vision Mamba DDPM (VM-DDPM) based on State Space Model (SSM), fully combining CNN local perception and SSM global modeling capabilities, while maintaining linear computational complexity. Specifically, we designed a multi-level feature extraction module called Multi-level State Space Block (MSSBlock), and a basic unit of encoder-decoder structure called State Space Layer (SSLayer) for medical pathological images. Besides, we designed a simple, Plug-and-Play, zero-parameter Sequence Regeneration strategy for the Cross-Scan Module (CSM), which enabled the S6 module to fully perceive the spatial features of the 2D image and stimulate the generalization potential of the model. To our best knowledge, this is the first medical image synthesis model based on the SSM-CNN hybrid architecture. Our experimental evaluation on three datasets of different scales, i.e., ACDC, BraTS2018, and ChestXRay, as well as qualitative evaluation by radiologists, demonstrate that VM-DDPM achieves state-of-the-art performance.
HAGAN: Hybrid Augmented Generative Adversarial Network for Medical Image Synthesis
May 08, 2024



Abstract:Medical Image Synthesis (MIS) plays an important role in the intelligent medical field, which greatly saves the economic and time costs of medical diagnosis. However, due to the complexity of medical images and similar characteristics of different tissue cells, existing methods face great challenges in meeting their biological consistency. To this end, we propose the Hybrid Augmented Generative Adversarial Network (HAGAN) to maintain the authenticity of structural texture and tissue cells. HAGAN contains Attention Mixed (AttnMix) Generator, Hierarchical Discriminator and Reverse Skip Connection between Discriminator and Generator. The AttnMix consistency differentiable regularization encourages the perception in structural and textural variations between real and fake images, which improves the pathological integrity of synthetic images and the accuracy of features in local areas. The Hierarchical Discriminator introduces pixel-by-pixel discriminant feedback to generator for enhancing the saliency and discriminance of global and local details simultaneously. The Reverse Skip Connection further improves the accuracy for fine details by fusing real and synthetic distribution features. Our experimental evaluations on three datasets of different scales, i.e., COVID-CT, ACDC and BraTS2018, demonstrate that HAGAN outperforms the existing methods and achieves state-of-the-art performance in both high-resolution and low-resolution.
LightVessel: Exploring Lightweight Coronary Artery Vessel Segmentation via Similarity Knowledge Distillation
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:In recent years, deep convolution neural networks (DCNNs) have achieved great prospects in coronary artery vessel segmentation. However, it is difficult to deploy complicated models in clinical scenarios since high-performance approaches have excessive parameters and high computation costs. To tackle this problem, we propose \textbf{LightVessel}, a Similarity Knowledge Distillation Framework, for lightweight coronary artery vessel segmentation. Primarily, we propose a Feature-wise Similarity Distillation (FSD) module for semantic-shift modeling. Specifically, we calculate the feature similarity between the symmetric layers from the encoder and decoder. Then the similarity is transferred as knowledge from a cumbersome teacher network to a non-trained lightweight student network. Meanwhile, for encouraging the student model to learn more pixel-wise semantic information, we introduce the Adversarial Similarity Distillation (ASD) module. Concretely, the ASD module aims to construct the spatial adversarial correlation between the annotation and prediction from the teacher and student models, respectively. Through the ASD module, the student model obtains fined-grained subtle edge segmented results of the coronary artery vessel. Extensive experiments conducted on Clinical Coronary Artery Vessel Dataset demonstrate that LightVessel outperforms various knowledge distillation counterparts.
ShowFace: Coordinated Face Inpainting with Memory-Disentangled Refinement Networks
Apr 16, 2022


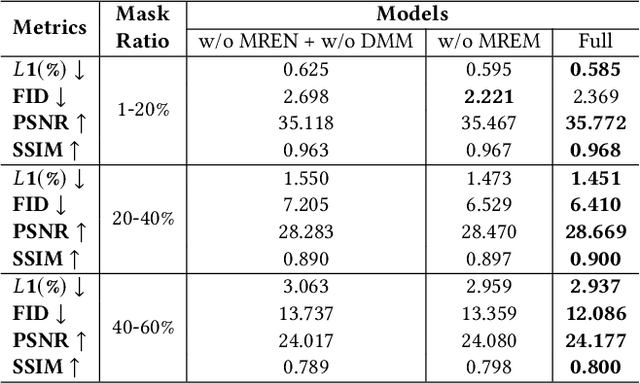
Abstract:Face inpainting aims to complete the corrupted regions of the face images, which requires coordination between the completed areas and the non-corrupted areas. Recently, memory-oriented methods illustrate great prospects in the generation related tasks by introducing an external memory module to improve image coordination. However, such methods still have limitations in restoring the consistency and continuity for specificfacial semantic parts. In this paper, we propose the coarse-to-fine Memory-Disentangled Refinement Networks (MDRNets) for coordinated face inpainting, in which two collaborative modules are integrated, Disentangled Memory Module (DMM) and Mask-Region Enhanced Module (MREM). Specifically, the DMM establishes a group of disentangled memory blocks to store the semantic-decoupled face representations, which could provide the most relevant information to refine the semantic-level coordination. The MREM involves a masked correlation mining mechanism to enhance the feature relationships into the corrupted regions, which could also make up for the correlation loss caused by memory disentanglement. Furthermore, to better improve the inter-coordination between the corrupted and non-corrupted regions and enhance the intra-coordination in corrupted regions, we design InCo2 Loss, a pair of similarity based losses to constrain the feature consistency. Eventually, extensive experiments conducted on CelebA-HQ and FFHQ datasets demonstrate the superiority of our MDRNets compared with previous State-Of-The-Art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge