Tsung-Shan Yang
Efficient Human-Object-Interaction (EHOI) Detection via Interaction Label Coding and Conditional Decision
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection is a fundamental task in image understanding. While deep-learning-based HOI methods provide high performance in terms of mean Average Precision (mAP), they are computationally expensive and opaque in training and inference processes. An Efficient HOI (EHOI) detector is proposed in this work to strike a good balance between detection performance, inference complexity, and mathematical transparency. EHOI is a two-stage method. In the first stage, it leverages a frozen object detector to localize the objects and extract various features as intermediate outputs. In the second stage, the first-stage outputs predict the interaction type using the XGBoost classifier. Our contributions include the application of error correction codes (ECCs) to encode rare interaction cases, which reduces the model size and the complexity of the XGBoost classifier in the second stage. Additionally, we provide a mathematical formulation of the relabeling and decision-making process. Apart from the architecture, we present qualitative results to explain the functionalities of the feedforward modules. Experimental results demonstrate the advantages of ECC-coded interaction labels and the excellent balance of detection performance and complexity of the proposed EHOI method.
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on NonHomogeneous Dehazing
May 07, 2020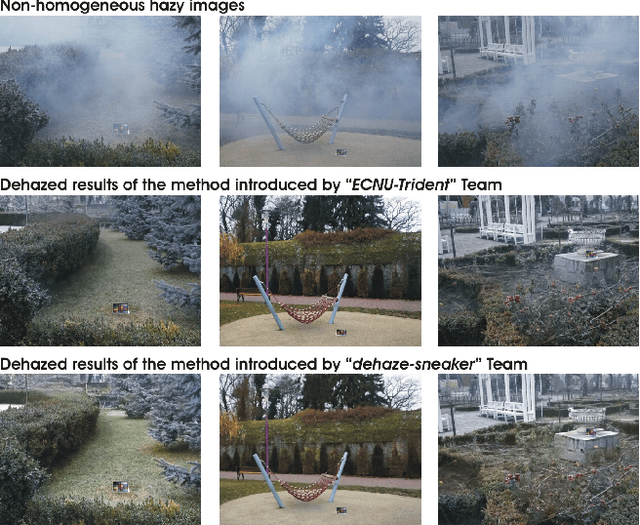
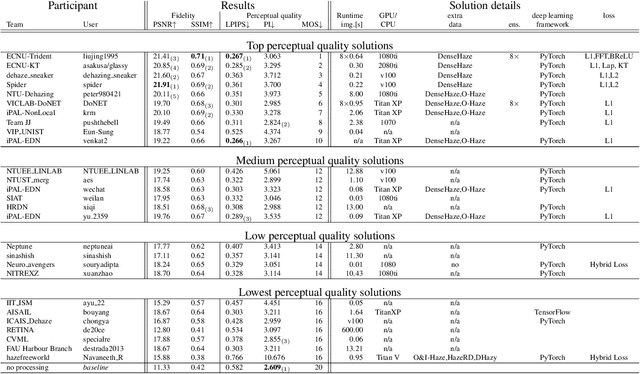
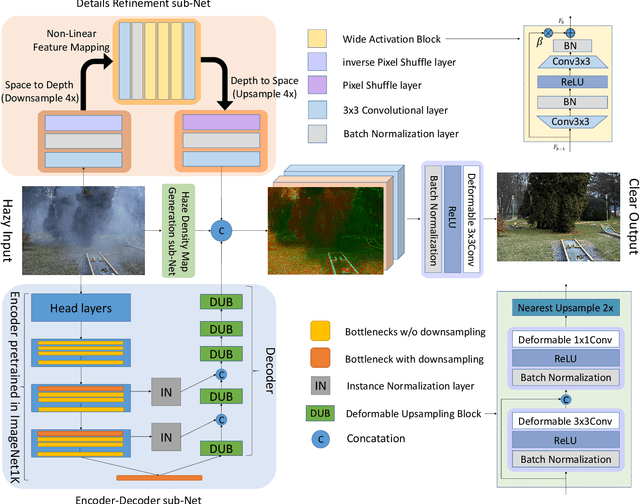
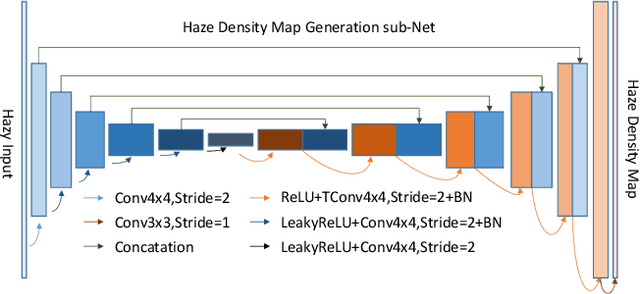
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2020 Challenge on NonHomogeneous Dehazing of images (restoration of rich details in hazy image). We focus on the proposed solutions and their results evaluated on NH-Haze, a novel dataset consisting of 55 pairs of real haze free and nonhomogeneous hazy images recorded outdoor. NH-Haze is the first realistic nonhomogeneous haze dataset that provides ground truth images. The nonhomogeneous haze has been produced using a professional haze generator that imitates the real conditions of haze scenes. 168 participants registered in the challenge and 27 teams competed in the final testing phase. The proposed solutions gauge the state-of-the-art in image dehazing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge