Tong Shao
Plug-and-Play Fidelity Optimization for Diffusion Transformer Acceleration via Cumulative Error Minimization
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Although Diffusion Transformer (DiT) has emerged as a predominant architecture for image and video generation, its iterative denoising process results in slow inference, which hinders broader applicability and development. Caching-based methods achieve training-free acceleration, while suffering from considerable computational error. Existing methods typically incorporate error correction strategies such as pruning or prediction to mitigate it. However, their fixed caching strategy fails to adapt to the complex error variations during denoising, which limits the full potential of error correction. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel fidelity-optimization plugin for existing error correction methods via cumulative error minimization, named CEM. CEM predefines the error to characterize the sensitivity of model to acceleration jointly influenced by timesteps and cache intervals. Guided by this prior, we formulate a dynamic programming algorithm with cumulative error approximation for strategy optimization, which achieves the caching error minimization, resulting in a substantial improvement in generation fidelity. CEM is model-agnostic and exhibits strong generalization, which is adaptable to arbitrary acceleration budgets. It can be seamlessly integrated into existing error correction frameworks and quantized models without introducing any additional computational overhead. Extensive experiments conducted on nine generation models and quantized methods across three tasks demonstrate that CEM significantly improves generation fidelity of existing acceleration models, and outperforms the original generation performance on FLUX.1-dev, PixArt-$α$, StableDiffusion1.5 and Hunyuan. The code will be made publicly available.
Binarized Mamba-Transformer for Lightweight Quad Bayer HybridEVS Demosaicing
Mar 20, 2025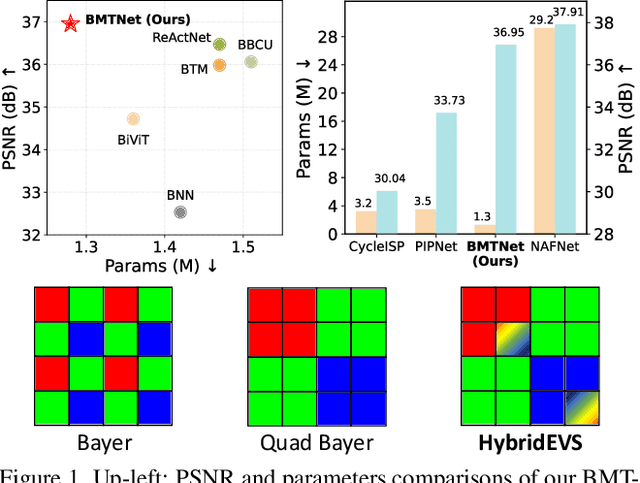
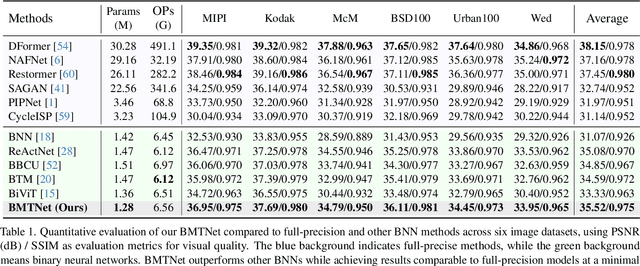
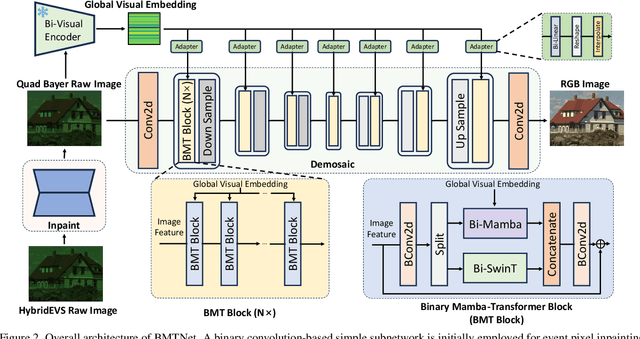
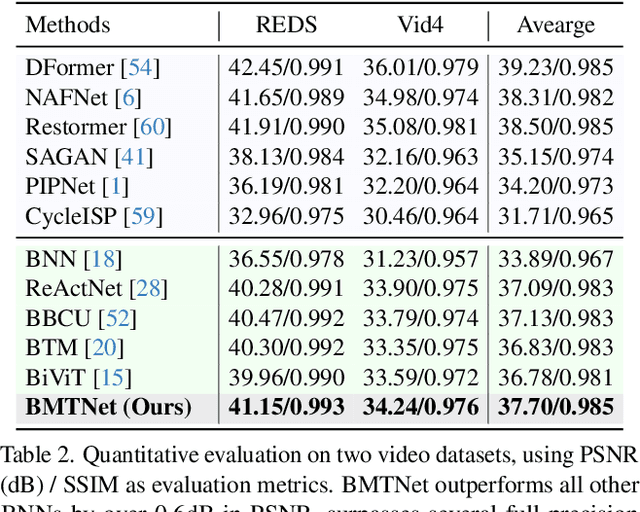
Abstract:Quad Bayer demosaicing is the central challenge for enabling the widespread application of Hybrid Event-based Vision Sensors (HybridEVS). Although existing learning-based methods that leverage long-range dependency modeling have achieved promising results, their complexity severely limits deployment on mobile devices for real-world applications. To address these limitations, we propose a lightweight Mamba-based binary neural network designed for efficient and high-performing demosaicing of HybridEVS RAW images. First, to effectively capture both global and local dependencies, we introduce a hybrid Binarized Mamba-Transformer architecture that combines the strengths of the Mamba and Swin Transformer architectures. Next, to significantly reduce computational complexity, we propose a binarized Mamba (Bi-Mamba), which binarizes all projections while retaining the core Selective Scan in full precision. Bi-Mamba also incorporates additional global visual information to enhance global context and mitigate precision loss. We conduct quantitative and qualitative experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of BMTNet in both performance and computational efficiency, providing a lightweight demosaicing solution suited for real-world edge devices. Our codes and models are available at https://github.com/Clausy9/BMTNet.
A Survey of fMRI to Image Reconstruction
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) based image reconstruction plays a pivotal role in decoding human perception, with applications in neuroscience and brain-computer interfaces. While recent advancements in deep learning and large-scale datasets have driven progress, challenges such as data scarcity, cross-subject variability, and low semantic consistency persist. To address these issues, we introduce the concept of fMRI-to-Image Learning (fMRI2Image) and present the first systematic review in this field. This review highlights key challenges, categorizes methodologies such as fMRI signal encoding, feature mapping, and image generator. Finally, promising research directions are proposed to advance this emerging frontier, providing a reference for future studies.
Explore the Potential of CLIP for Training-Free Open Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Jul 11, 2024Abstract:CLIP, as a vision-language model, has significantly advanced Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) with its zero-shot capabilities. Despite its success, its application to OVSS faces challenges due to its initial image-level alignment training, which affects its performance in tasks requiring detailed local context. Our study delves into the impact of CLIP's [CLS] token on patch feature correlations, revealing a dominance of "global" patches that hinders local feature discrimination. To overcome this, we propose CLIPtrase, a novel training-free semantic segmentation strategy that enhances local feature awareness through recalibrated self-correlation among patches. This approach demonstrates notable improvements in segmentation accuracy and the ability to maintain semantic coherence across objects.Experiments show that we are 22.3% ahead of CLIP on average on 9 segmentation benchmarks, outperforming existing state-of-the-art training-free methods.The code are made publicly available at: https://github.com/leaves162/CLIPtrase.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge