Tom Sander
Learning to Watermark in the Latent Space of Generative Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Existing approaches for watermarking AI-generated images often rely on post-hoc methods applied in pixel space, introducing computational overhead and potential visual artifacts. In this work, we explore latent space watermarking and introduce DistSeal, a unified approach for latent watermarking that works across both diffusion and autoregressive models. Our approach works by training post-hoc watermarking models in the latent space of generative models. We demonstrate that these latent watermarkers can be effectively distilled either into the generative model itself or into the latent decoder, enabling in-model watermarking. The resulting latent watermarks achieve competitive robustness while offering similar imperceptibility and up to 20x speedup compared to pixel-space baselines. Our experiments further reveal that distilling latent watermarkers outperforms distilling pixel-space ones, providing a solution that is both more efficient and more robust.
Pixel Seal: Adversarial-only training for invisible image and video watermarking
Dec 18, 2025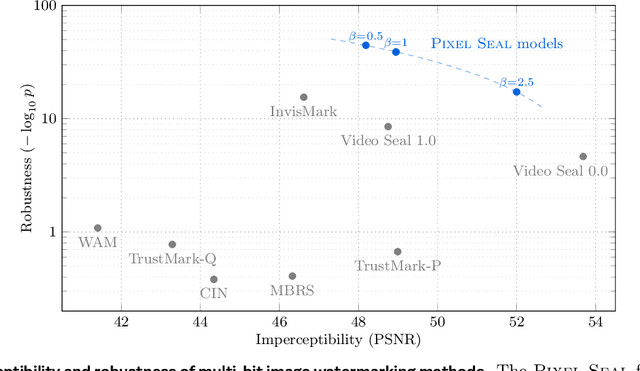
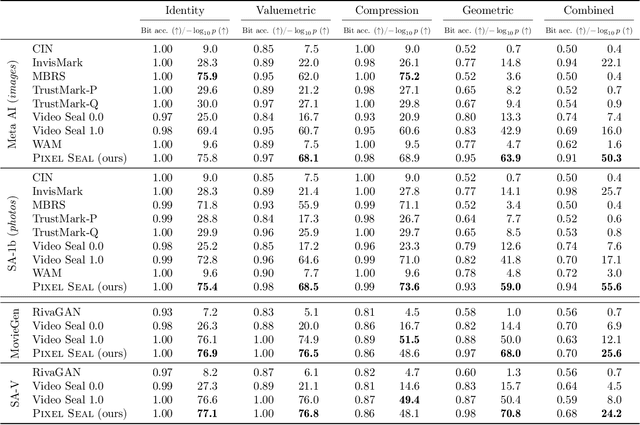
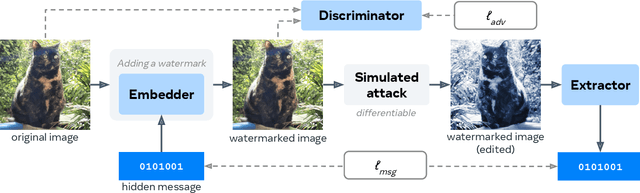
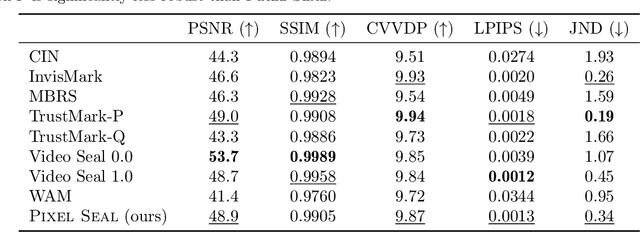
Abstract:Invisible watermarking is essential for tracing the provenance of digital content. However, training state-of-the-art models remains notoriously difficult, with current approaches often struggling to balance robustness against true imperceptibility. This work introduces Pixel Seal, which sets a new state-of-the-art for image and video watermarking. We first identify three fundamental issues of existing methods: (i) the reliance on proxy perceptual losses such as MSE and LPIPS that fail to mimic human perception and result in visible watermark artifacts; (ii) the optimization instability caused by conflicting objectives, which necessitates exhaustive hyperparameter tuning; and (iii) reduced robustness and imperceptibility of watermarks when scaling models to high-resolution images and videos. To overcome these issues, we first propose an adversarial-only training paradigm that eliminates unreliable pixel-wise imperceptibility losses. Second, we introduce a three-stage training schedule that stabilizes convergence by decoupling robustness and imperceptibility. Third, we address the resolution gap via high-resolution adaptation, employing JND-based attenuation and training-time inference simulation to eliminate upscaling artifacts. We thoroughly evaluate the robustness and imperceptibility of Pixel Seal on different image types and across a wide range of transformations, and show clear improvements over the state-of-the-art. We finally demonstrate that the model efficiently adapts to video via temporal watermark pooling, positioning Pixel Seal as a practical and scalable solution for reliable provenance in real-world image and video settings.
How Good is Post-Hoc Watermarking With Language Model Rephrasing?
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Generation-time text watermarking embeds statistical signals into text for traceability of AI-generated content. We explore *post-hoc watermarking* where an LLM rewrites existing text while applying generation-time watermarking, to protect copyrighted documents, or detect their use in training or RAG via watermark radioactivity. Unlike generation-time approaches, which is constrained by how LLMs are served, this setting offers additional degrees of freedom for both generation and detection. We investigate how allocating compute (through larger rephrasing models, beam search, multi-candidate generation, or entropy filtering at detection) affects the quality-detectability trade-off. Our strategies achieve strong detectability and semantic fidelity on open-ended text such as books. Among our findings, the simple Gumbel-max scheme surprisingly outperforms more recent alternatives under nucleus sampling, and most methods benefit significantly from beam search. However, most approaches struggle when watermarking verifiable text such as code, where we counterintuitively find that smaller models outperform larger ones. This study reveals both the potential and limitations of post-hoc watermarking, laying groundwork for practical applications and future research.
The Moon's Many Faces: A Single Unified Transformer for Multimodal Lunar Reconstruction
May 08, 2025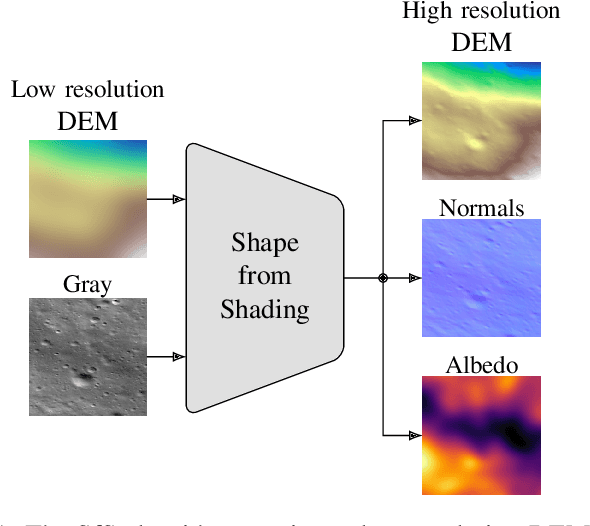
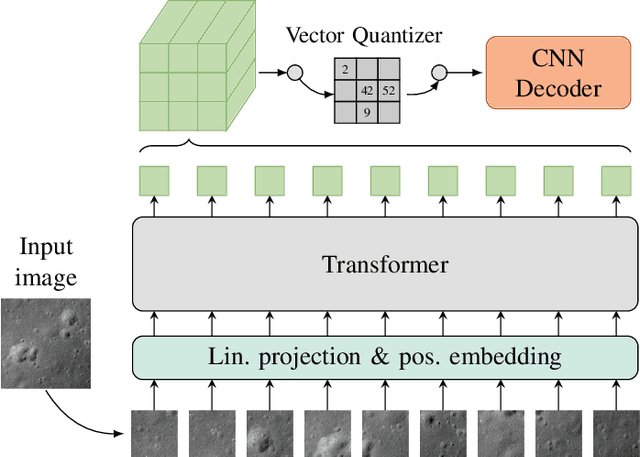
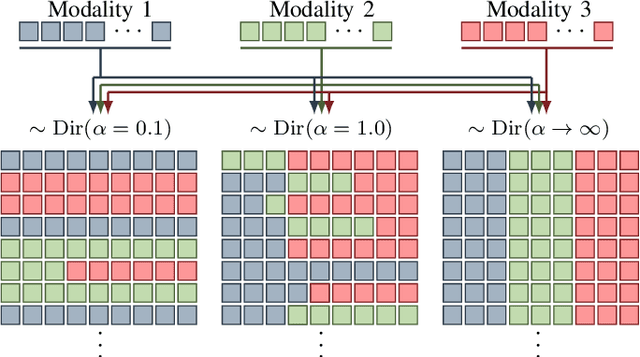
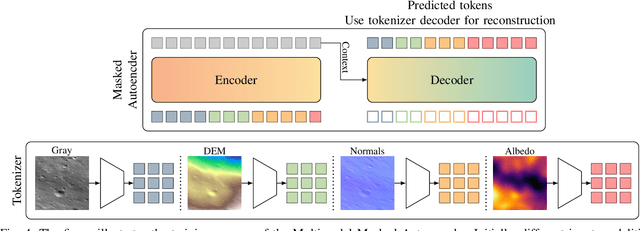
Abstract:Multimodal learning is an emerging research topic across multiple disciplines but has rarely been applied to planetary science. In this contribution, we identify that reflectance parameter estimation and image-based 3D reconstruction of lunar images can be formulated as a multimodal learning problem. We propose a single, unified transformer architecture trained to learn shared representations between multiple sources like grayscale images, digital elevation models, surface normals, and albedo maps. The architecture supports flexible translation from any input modality to any target modality. Predicting DEMs and albedo maps from grayscale images simultaneously solves the task of 3D reconstruction of planetary surfaces and disentangles photometric parameters and height information. Our results demonstrate that our foundation model learns physically plausible relations across these four modalities. Adding more input modalities in the future will enable tasks such as photometric normalization and co-registration.
Detecting Benchmark Contamination Through Watermarking
Feb 24, 2025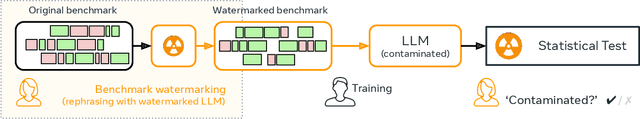
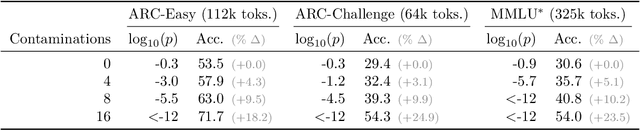
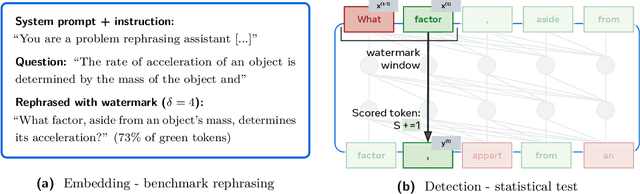
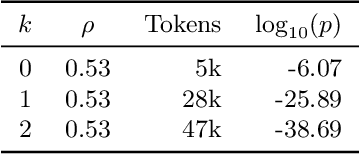
Abstract:Benchmark contamination poses a significant challenge to the reliability of Large Language Models (LLMs) evaluations, as it is difficult to assert whether a model has been trained on a test set. We introduce a solution to this problem by watermarking benchmarks before their release. The embedding involves reformulating the original questions with a watermarked LLM, in a way that does not alter the benchmark utility. During evaluation, we can detect ``radioactivity'', \ie traces that the text watermarks leave in the model during training, using a theoretically grounded statistical test. We test our method by pre-training 1B models from scratch on 10B tokens with controlled benchmark contamination, and validate its effectiveness in detecting contamination on ARC-Easy, ARC-Challenge, and MMLU. Results show similar benchmark utility post-watermarking and successful contamination detection when models are contaminated enough to enhance performance, e.g. $p$-val $=10^{-3}$ for +5$\%$ on ARC-Easy.
Watermark Anything with Localized Messages
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Image watermarking methods are not tailored to handle small watermarked areas. This restricts applications in real-world scenarios where parts of the image may come from different sources or have been edited. We introduce a deep-learning model for localized image watermarking, dubbed the Watermark Anything Model (WAM). The WAM embedder imperceptibly modifies the input image, while the extractor segments the received image into watermarked and non-watermarked areas and recovers one or several hidden messages from the areas found to be watermarked. The models are jointly trained at low resolution and without perceptual constraints, then post-trained for imperceptibility and multiple watermarks. Experiments show that WAM is competitive with state-of-the art methods in terms of imperceptibility and robustness, especially against inpainting and splicing, even on high-resolution images. Moreover, it offers new capabilities: WAM can locate watermarked areas in spliced images and extract distinct 32-bit messages with less than 1 bit error from multiple small regions - no larger than 10% of the image surface - even for small $256\times 256$ images.
Differentially Private Representation Learning via Image Captioning
Mar 04, 2024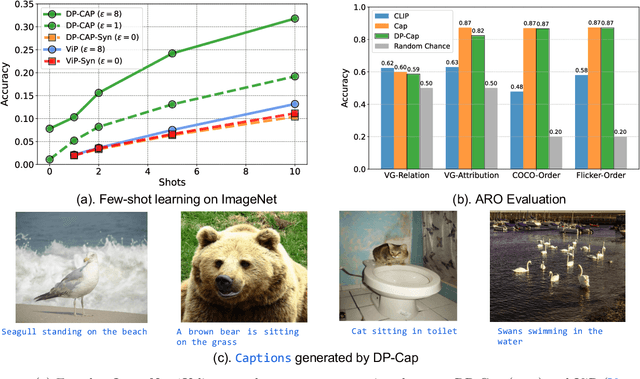
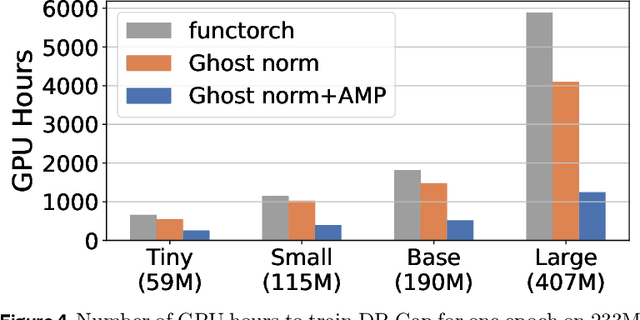
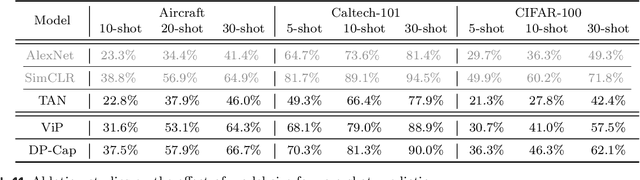
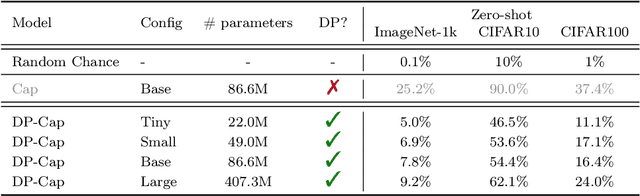
Abstract:Differentially private (DP) machine learning is considered the gold-standard solution for training a model from sensitive data while still preserving privacy. However, a major barrier to achieving this ideal is its sub-optimal privacy-accuracy trade-off, which is particularly visible in DP representation learning. Specifically, it has been shown that under modest privacy budgets, most models learn representations that are not significantly better than hand-crafted features. In this work, we show that effective DP representation learning can be done via image captioning and scaling up to internet-scale multimodal datasets. Through a series of engineering tricks, we successfully train a DP image captioner (DP-Cap) on a 233M subset of LAION-2B from scratch using a reasonable amount of computation, and obtaining unprecedented high-quality image features that can be used in a variety of downstream vision and vision-language tasks. For example, under a privacy budget of $\varepsilon=8$, a linear classifier trained on top of learned DP-Cap features attains 65.8% accuracy on ImageNet-1K, considerably improving the previous SOTA of 56.5%. Our work challenges the prevailing sentiment that high-utility DP representation learning cannot be achieved by training from scratch.
Watermarking Makes Language Models Radioactive
Feb 22, 2024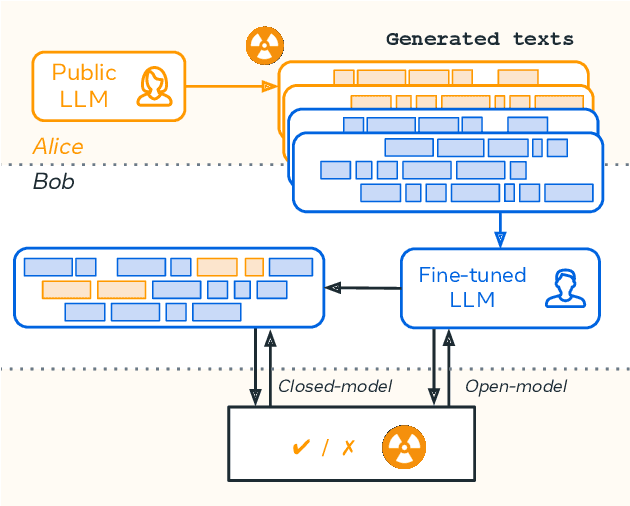
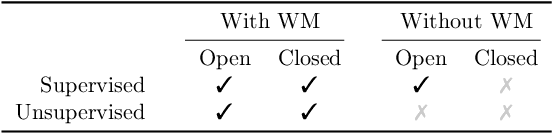
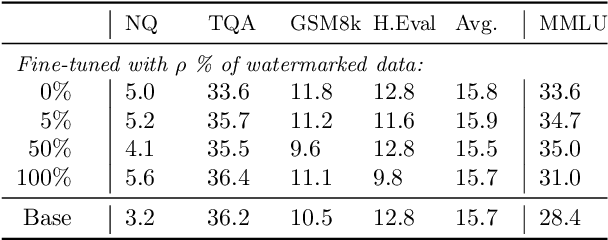
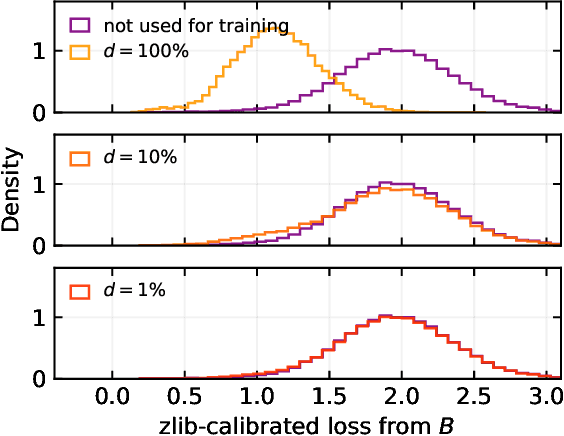
Abstract:This paper investigates the radioactivity of LLM-generated texts, i.e. whether it is possible to detect that such input was used as training data. Conventional methods like membership inference can carry out this detection with some level of accuracy. We show that watermarked training data leaves traces easier to detect and much more reliable than membership inference. We link the contamination level to the watermark robustness, its proportion in the training set, and the fine-tuning process. We notably demonstrate that training on watermarked synthetic instructions can be detected with high confidence (p-value < 1e-5) even when as little as 5% of training text is watermarked. Thus, LLM watermarking, originally designed for detecting machine-generated text, gives the ability to easily identify if the outputs of a watermarked LLM were used to fine-tune another LLM.
Implicit Bias in Noisy-SGD: With Applications to Differentially Private Training
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:Training Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) with small batches using Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) yields superior test performance compared to larger batches. The specific noise structure inherent to SGD is known to be responsible for this implicit bias. DP-SGD, used to ensure differential privacy (DP) in DNNs' training, adds Gaussian noise to the clipped gradients. Surprisingly, large-batch training still results in a significant decrease in performance, which poses an important challenge because strong DP guarantees necessitate the use of massive batches. We first show that the phenomenon extends to Noisy-SGD (DP-SGD without clipping), suggesting that the stochasticity (and not the clipping) is the cause of this implicit bias, even with additional isotropic Gaussian noise. We theoretically analyse the solutions obtained with continuous versions of Noisy-SGD for the Linear Least Square and Diagonal Linear Network settings, and reveal that the implicit bias is indeed amplified by the additional noise. Thus, the performance issues of large-batch DP-SGD training are rooted in the same underlying principles as SGD, offering hope for potential improvements in large batch training strategies.
TAN without a burn: Scaling Laws of DP-SGD
Oct 07, 2022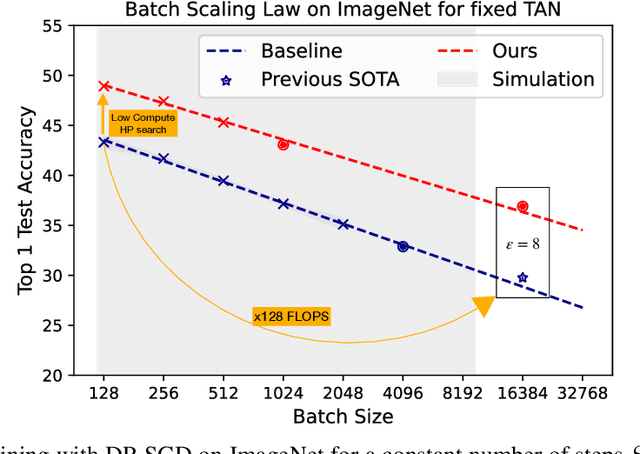

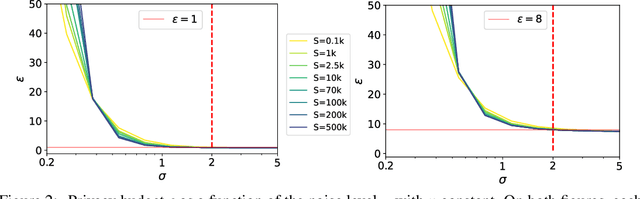
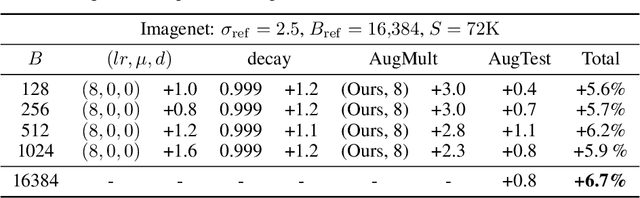
Abstract:Differentially Private methods for training Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have progressed recently, in particular with the use of massive batches and aggregated data augmentations for a large number of steps. These techniques require much more compute than their non-private counterparts, shifting the traditional privacy-accuracy trade-off to a privacy-accuracy-compute trade-off and making hyper-parameter search virtually impossible for realistic scenarios. In this work, we decouple privacy analysis and experimental behavior of noisy training to explore the trade-off with minimal computational requirements. We first use the tools of R\'enyi Differential Privacy (RDP) to show that the privacy budget, when not overcharged, only depends on the total amount of noise (TAN) injected throughout training. We then derive scaling laws for training models with DP-SGD to optimize hyper-parameters with more than a 100 reduction in computational budget. We apply the proposed method on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet and, in particular, strongly improve the state-of-the-art on ImageNet with a +9 points gain in accuracy for a privacy budget epsilon=8.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge