Tom Doel
Evaluation of automated airway morphological quantification for assessing fibrosing lung disease
Nov 19, 2021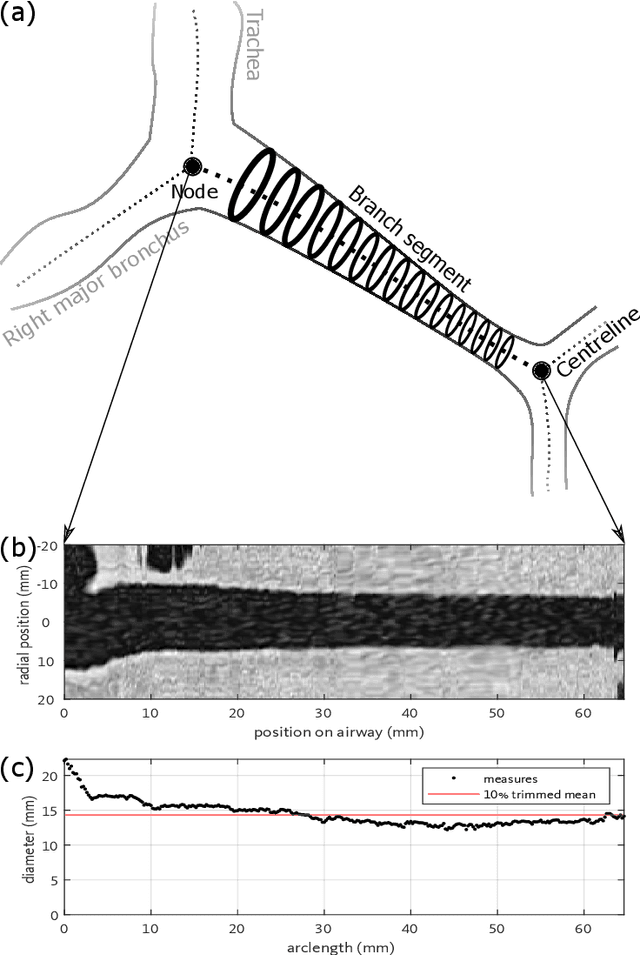
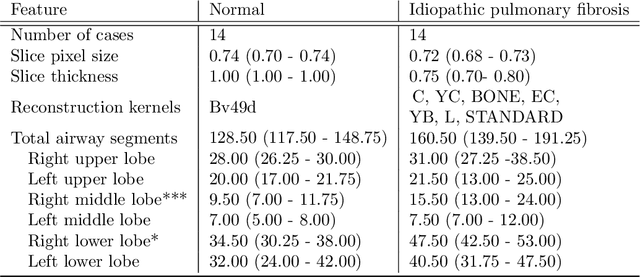
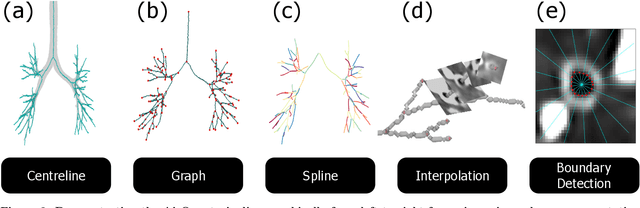
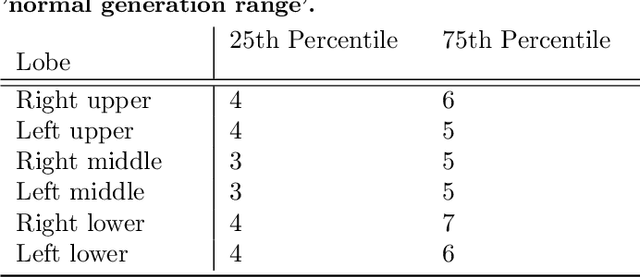
Abstract:Abnormal airway dilatation, termed traction bronchiectasis, is a typical feature of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Volumetric computed tomography (CT) imaging captures the loss of normal airway tapering in IPF. We postulated that automated quantification of airway abnormalities could provide estimates of IPF disease extent and severity. We propose AirQuant, an automated computational pipeline that systematically parcellates the airway tree into its lobes and generational branches from a deep learning based airway segmentation, deriving airway structural measures from chest CT. Importantly, AirQuant prevents the occurrence of spurious airway branches by thick wave propagation and removes loops in the airway-tree by graph search, overcoming limitations of existing airway skeletonisation algorithms. Tapering between airway segments (intertapering) and airway tortuosity computed by AirQuant were compared between 14 healthy participants and 14 IPF patients. Airway intertapering was significantly reduced in IPF patients, and airway tortuosity was significantly increased when compared to healthy controls. Differences were most marked in the lower lobes, conforming to the typical distribution of IPF-related damage. AirQuant is an open-source pipeline that avoids limitations of existing airway quantification algorithms and has clinical interpretability. Automated airway measurements may have potential as novel imaging biomarkers of IPF severity and disease extent.
NiftyNet: a deep-learning platform for medical imaging
Oct 16, 2017



Abstract:Medical image analysis and computer-assisted intervention problems are increasingly being addressed with deep-learning-based solutions. Established deep-learning platforms are flexible but do not provide specific functionality for medical image analysis and adapting them for this application requires substantial implementation effort. Thus, there has been substantial duplication of effort and incompatible infrastructure developed across many research groups. This work presents the open-source NiftyNet platform for deep learning in medical imaging. The ambition of NiftyNet is to accelerate and simplify the development of these solutions, and to provide a common mechanism for disseminating research outputs for the community to use, adapt and build upon. NiftyNet provides a modular deep-learning pipeline for a range of medical imaging applications including segmentation, regression, image generation and representation learning applications. Components of the NiftyNet pipeline including data loading, data augmentation, network architectures, loss functions and evaluation metrics are tailored to, and take advantage of, the idiosyncracies of medical image analysis and computer-assisted intervention. NiftyNet is built on TensorFlow and supports TensorBoard visualization of 2D and 3D images and computational graphs by default. We present 3 illustrative medical image analysis applications built using NiftyNet: (1) segmentation of multiple abdominal organs from computed tomography; (2) image regression to predict computed tomography attenuation maps from brain magnetic resonance images; and (3) generation of simulated ultrasound images for specified anatomical poses. NiftyNet enables researchers to rapidly develop and distribute deep learning solutions for segmentation, regression, image generation and representation learning applications, or extend the platform to new applications.
Interactive Medical Image Segmentation using Deep Learning with Image-specific Fine-tuning
Oct 11, 2017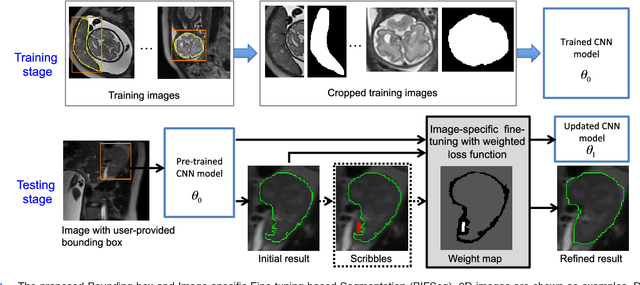
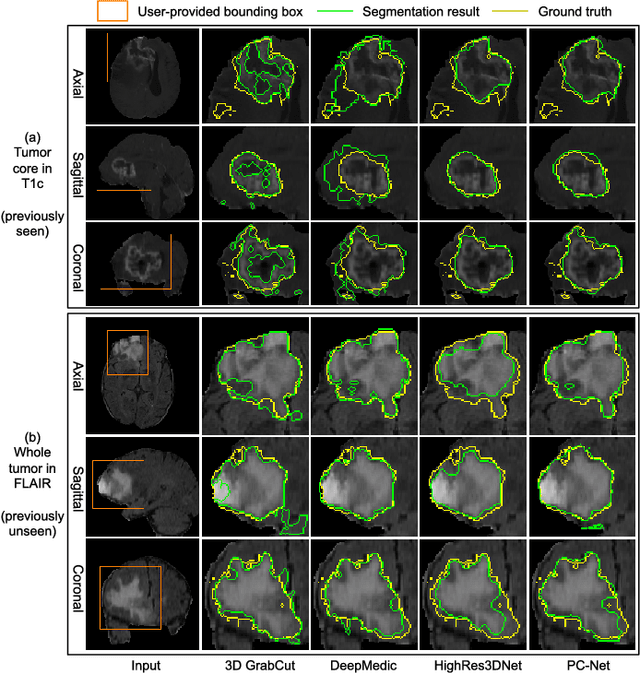
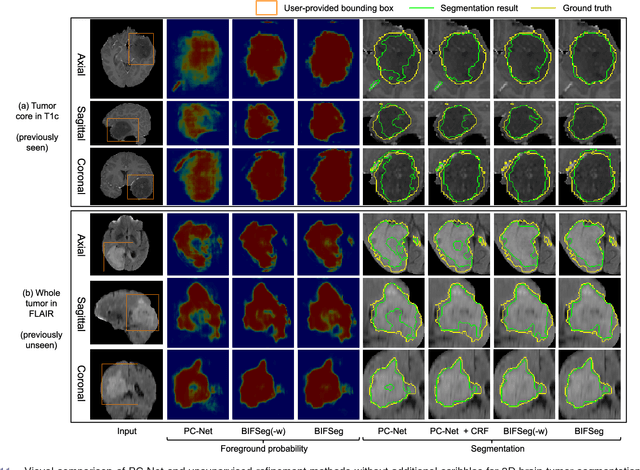
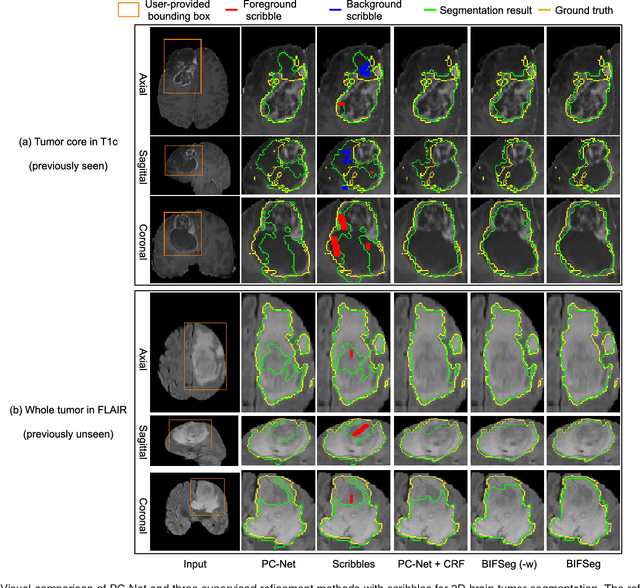
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance for automatic medical image segmentation. However, they have not demonstrated sufficiently accurate and robust results for clinical use. In addition, they are limited by the lack of image-specific adaptation and the lack of generalizability to previously unseen object classes. To address these problems, we propose a novel deep learning-based framework for interactive segmentation by incorporating CNNs into a bounding box and scribble-based segmentation pipeline. We propose image-specific fine-tuning to make a CNN model adaptive to a specific test image, which can be either unsupervised (without additional user interactions) or supervised (with additional scribbles). We also propose a weighted loss function considering network and interaction-based uncertainty for the fine-tuning. We applied this framework to two applications: 2D segmentation of multiple organs from fetal MR slices, where only two types of these organs were annotated for training; and 3D segmentation of brain tumor core (excluding edema) and whole brain tumor (including edema) from different MR sequences, where only tumor cores in one MR sequence were annotated for training. Experimental results show that 1) our model is more robust to segment previously unseen objects than state-of-the-art CNNs; 2) image-specific fine-tuning with the proposed weighted loss function significantly improves segmentation accuracy; and 3) our method leads to accurate results with fewer user interactions and less user time than traditional interactive segmentation methods.
DeepIGeoS: A Deep Interactive Geodesic Framework for Medical Image Segmentation
Sep 19, 2017



Abstract:Accurate medical image segmentation is essential for diagnosis, surgical planning and many other applications. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have become the state-of-the-art automatic segmentation methods. However, fully automatic results may still need to be refined to become accurate and robust enough for clinical use. We propose a deep learning-based interactive segmentation method to improve the results obtained by an automatic CNN and to reduce user interactions during refinement for higher accuracy. We use one CNN to obtain an initial automatic segmentation, on which user interactions are added to indicate mis-segmentations. Another CNN takes as input the user interactions with the initial segmentation and gives a refined result. We propose to combine user interactions with CNNs through geodesic distance transforms, and propose a resolution-preserving network that gives a better dense prediction. In addition, we integrate user interactions as hard constraints into a back-propagatable Conditional Random Field. We validated the proposed framework in the context of 2D placenta segmentation from fetal MRI and 3D brain tumor segmentation from FLAIR images. Experimental results show our method achieves a large improvement from automatic CNNs, and obtains comparable and even higher accuracy with fewer user interventions and less time compared with traditional interactive methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge