Tim Kwang-Ting Cheng
DS-CIM: Digital Stochastic Computing-In-Memory Featuring Accurate OR-Accumulation via Sample Region Remapping for Edge AI Models
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Stochastic computing (SC) offers hardware simplicity but suffers from low throughput, while high-throughput Digital Computing-in-Memory (DCIM) is bottlenecked by costly adder logic for matrix-vector multiplication (MVM). To address this trade-off, this paper introduces a digital stochastic CIM (DS-CIM) architecture that achieves both high accuracy and efficiency. We implement signed multiply-accumulation (MAC) in a compact, unsigned OR-based circuit by modifying the data representation. Throughput is enhanced by replicating this low-cost circuit 64 times with only a 1x area increase. Our core strategy, a shared Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG) with 2D partitioning, enables single-cycle mutually exclusive activation to eliminate OR-gate collisions. We also resolve the 1s saturation issue via stochastic process analysis and data remapping, significantly improving accuracy and resilience to input sparsity. Our high-accuracy DS-CIM1 variant achieves 94.45% accuracy for INT8 ResNet18 on CIFAR-10 with a root-mean-squared error (RMSE) of just 0.74%. Meanwhile, our high-efficiency DS-CIM2 variant attains an energy efficiency of 3566.1 TOPS/W and an area efficiency of 363.7 TOPS/mm^2, while maintaining a low RMSE of 3.81%. The DS-CIM capability with larger models is further demonstrated through experiments with INT8 ResNet50 on ImageNet and the FP8 LLaMA-7B model.
MetaPruning: Meta Learning for Automatic Neural Network Channel Pruning
Apr 03, 2019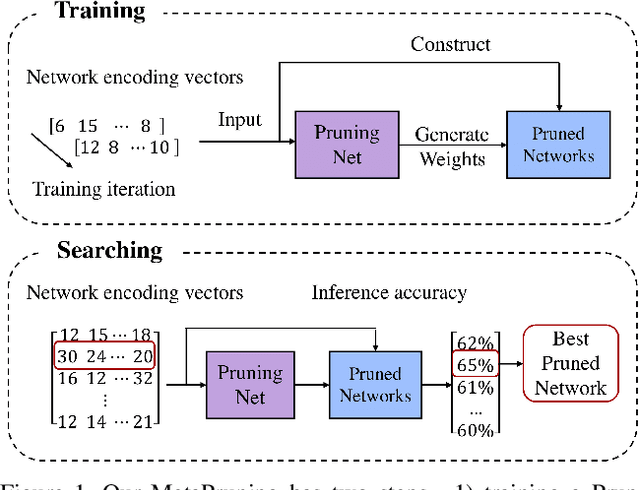
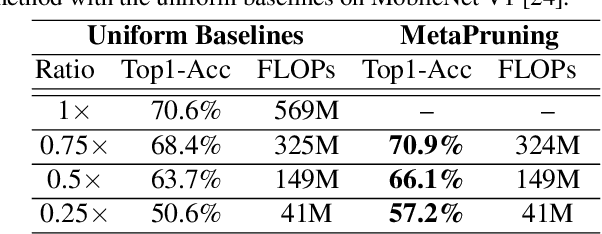
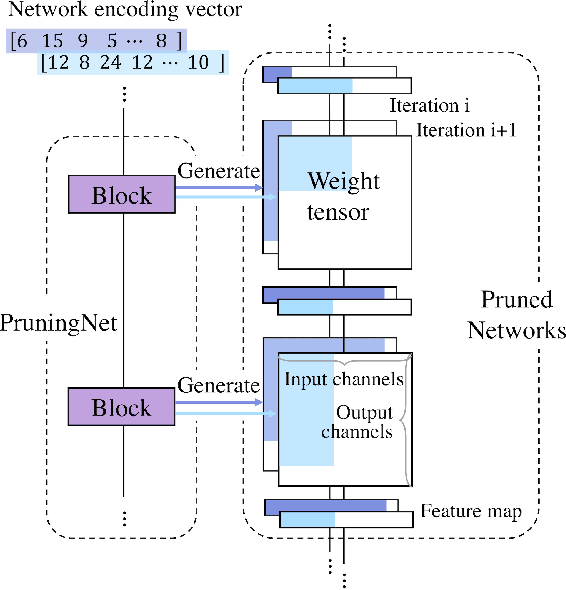
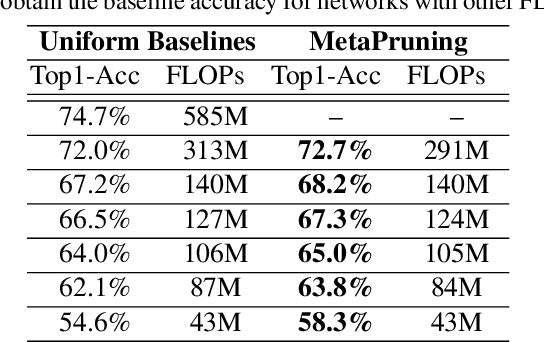
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel meta learning approach for automatic channel pruning of very deep neural networks. We first train a PruningNet, a kind of meta network, which is able to generate weight parameters for any pruned structure given the target network. We use a simple stochastic structure sampling method for training the PruningNet. Then, we apply an evolutionary procedure to search for good-performing pruned networks. The search is highly efficient because the weights are directly generated by the trained PruningNet and we do not need any finetuning. With a single PruningNet trained for the target network, we can search for various Pruned Networks under different constraints with little human participation. We have demonstrated competitive performances on MobileNet V1/V2 networks, up to 9.0/9.9 higher ImageNet accuracy than V1/V2. Compared to the previous state-of-the-art AutoML-based pruning methods, like AMC and NetAdapt, we achieve higher or comparable accuracy under various conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge