Tianchi Xie
InfoChartQA: A Benchmark for Multimodal Question Answering on Infographic Charts
May 25, 2025Abstract:Understanding infographic charts with design-driven visual elements (e.g., pictograms, icons) requires both visual recognition and reasoning, posing challenges for multimodal large language models (MLLMs). However, existing visual-question answering benchmarks fall short in evaluating these capabilities of MLLMs due to the lack of paired plain charts and visual-element-based questions. To bridge this gap, we introduce InfoChartQA, a benchmark for evaluating MLLMs on infographic chart understanding. It includes 5,642 pairs of infographic and plain charts, each sharing the same underlying data but differing in visual presentations. We further design visual-element-based questions to capture their unique visual designs and communicative intent. Evaluation of 20 MLLMs reveals a substantial performance decline on infographic charts, particularly for visual-element-based questions related to metaphors. The paired infographic and plain charts enable fine-grained error analysis and ablation studies, which highlight new opportunities for advancing MLLMs in infographic chart understanding. We release InfoChartQA at https://github.com/CoolDawnAnt/InfoChartQA.
Structural-Entropy-Based Sample Selection for Efficient and Effective Learning
Oct 03, 2024


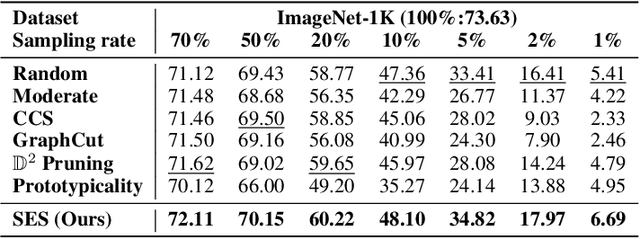
Abstract:Sample selection improves the efficiency and effectiveness of machine learning models by providing informative and representative samples. Typically, samples can be modeled as a sample graph, where nodes are samples and edges represent their similarities. Most existing methods are based on local information, such as the training difficulty of samples, thereby overlooking global information, such as connectivity patterns. This oversight can result in suboptimal selection because global information is crucial for ensuring that the selected samples well represent the structural properties of the graph. To address this issue, we employ structural entropy to quantify global information and losslessly decompose it from the whole graph to individual nodes using the Shapley value. Based on the decomposition, we present $\textbf{S}$tructural-$\textbf{E}$ntropy-based sample $\textbf{S}$election ($\textbf{SES}$), a method that integrates both global and local information to select informative and representative samples. SES begins by constructing a $k$NN-graph among samples based on their similarities. It then measures sample importance by combining structural entropy (global metric) with training difficulty (local metric). Finally, SES applies importance-biased blue noise sampling to select a set of diverse and representative samples. Comprehensive experiments on three learning scenarios -- supervised learning, active learning, and continual learning -- clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Semantic Equivariant Mixup
Aug 12, 2023Abstract:Mixup is a well-established data augmentation technique, which can extend the training distribution and regularize the neural networks by creating ''mixed'' samples based on the label-equivariance assumption, i.e., a proportional mixup of the input data results in the corresponding labels being mixed in the same proportion. However, previous mixup variants may fail to exploit the label-independent information in mixed samples during training, which usually contains richer semantic information. To further release the power of mixup, we first improve the previous label-equivariance assumption by the semantic-equivariance assumption, which states that the proportional mixup of the input data should lead to the corresponding representation being mixed in the same proportion. Then a generic mixup regularization at the representation level is proposed, which can further regularize the model with the semantic information in mixed samples. At a high level, the proposed semantic equivariant mixup (sem) encourages the structure of the input data to be preserved in the representation space, i.e., the change of input will result in the obtained representation information changing in the same way. Different from previous mixup variants, which tend to over-focus on the label-related information, the proposed method aims to preserve richer semantic information in the input with semantic-equivariance assumption, thereby improving the robustness of the model against distribution shifts. We conduct extensive empirical studies and qualitative analyzes to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The code of the manuscript is in the supplement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge