Théophile Gervet
Mixtral of Experts
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Mixtral 8x7B, a Sparse Mixture of Experts (SMoE) language model. Mixtral has the same architecture as Mistral 7B, with the difference that each layer is composed of 8 feedforward blocks (i.e. experts). For every token, at each layer, a router network selects two experts to process the current state and combine their outputs. Even though each token only sees two experts, the selected experts can be different at each timestep. As a result, each token has access to 47B parameters, but only uses 13B active parameters during inference. Mixtral was trained with a context size of 32k tokens and it outperforms or matches Llama 2 70B and GPT-3.5 across all evaluated benchmarks. In particular, Mixtral vastly outperforms Llama 2 70B on mathematics, code generation, and multilingual benchmarks. We also provide a model fine-tuned to follow instructions, Mixtral 8x7B - Instruct, that surpasses GPT-3.5 Turbo, Claude-2.1, Gemini Pro, and Llama 2 70B - chat model on human benchmarks. Both the base and instruct models are released under the Apache 2.0 license.
Autonomous Graph Mining Algorithm Search with Best Speed/Accuracy Trade-off
Nov 26, 2020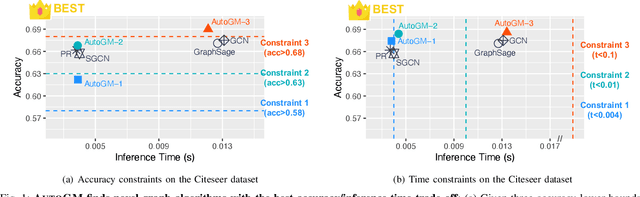
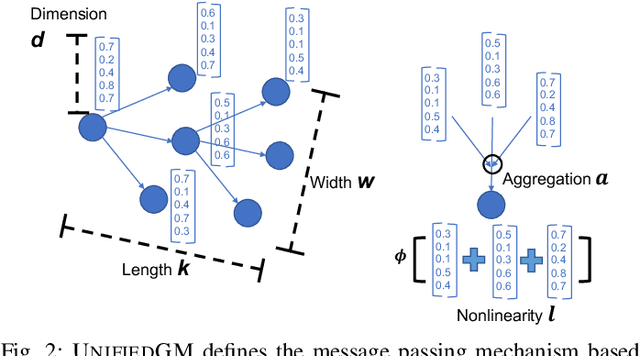
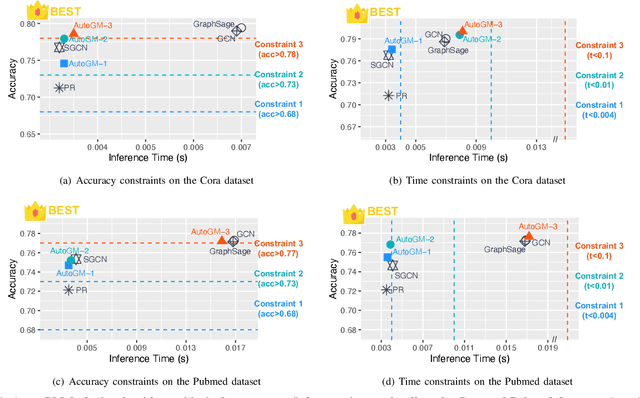
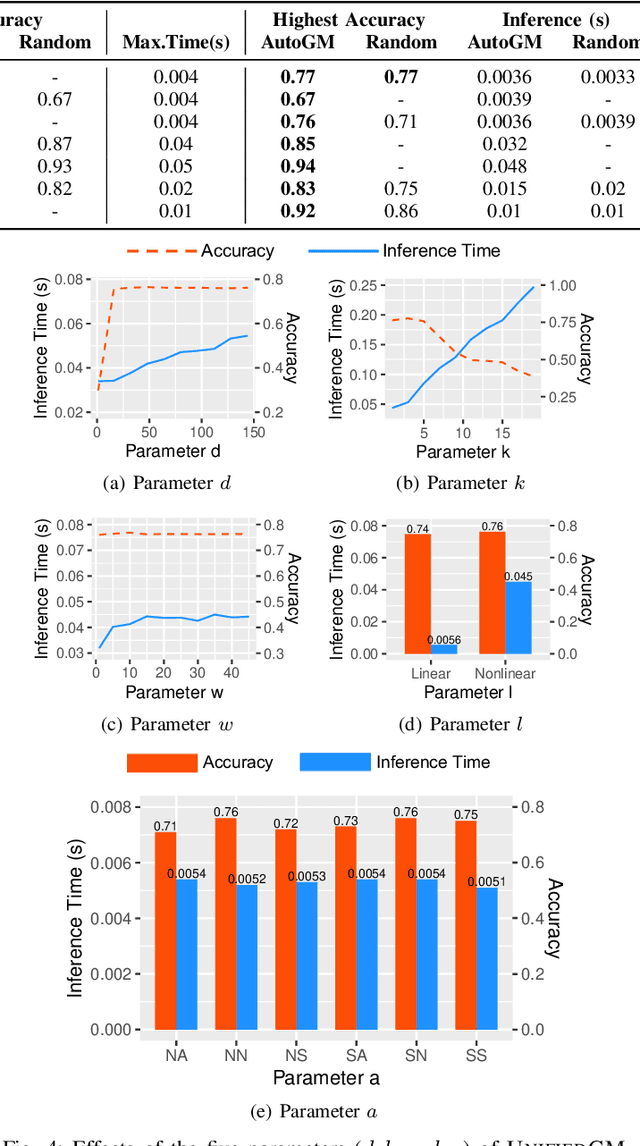
Abstract:Graph data is ubiquitous in academia and industry, from social networks to bioinformatics. The pervasiveness of graphs today has raised the demand for algorithms that can answer various questions: Which products would a user like to purchase given her order list? Which users are buying fake followers to increase their public reputation? Myriads of new graph mining algorithms are proposed every year to answer such questions - each with a distinct problem formulation, computational time, and memory footprint. This lack of unity makes it difficult for a practitioner to compare different algorithms and pick the most suitable one for a specific application. These challenges - even more severe for non-experts - create a gap in which state-of-the-art techniques developed in academic settings fail to be optimally deployed in real-world applications. To bridge this gap, we propose AUTOGM, an automated system for graph mining algorithm development. We first define a unified framework UNIFIEDGM that integrates various message-passing based graph algorithms, ranging from conventional algorithms like PageRank to graph neural networks. Then UNIFIEDGM defines a search space in which five parameters are required to determine a graph algorithm. Under this search space, AUTOGM explicitly optimizes for the optimal parameter set of UNIFIEDGM using Bayesian Optimization. AUTOGM defines a novel budget-aware objective function for the optimization to incorporate a practical issue - finding the best speed-accuracy trade-off under a computation budget - into the graph algorithm generation problem. Experiments on real-world benchmark datasets demonstrate that AUTOGM generates novel graph mining algorithms with the best speed/accuracy trade-off compared to existing models with heuristic parameters.
TarMAC: Targeted Multi-Agent Communication
Oct 26, 2018



Abstract:We explore a collaborative multi-agent reinforcement learning setting where a team of agents attempts to solve cooperative tasks in partially-observable environments. In this scenario, learning an effective communication protocol is key. We propose a communication architecture that allows for targeted communication, where agents learn both what messages to send and who to send them to, solely from downstream task-specific reward without any communication supervision. Additionally, we introduce a multi-stage communication approach where the agents co-ordinate via multiple rounds of communication before taking actions in the environment. We evaluate our approach on a diverse set of cooperative multi-agent tasks, of varying difficulties, with varying number of agents, in a variety of environments ranging from 2D grid layouts of shapes and simulated traffic junctions to complex 3D indoor environments. We demonstrate the benefits of targeted as well as multi-stage communication. Moreover, we show that the targeted communication strategies learned by agents are both interpretable and intuitive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge